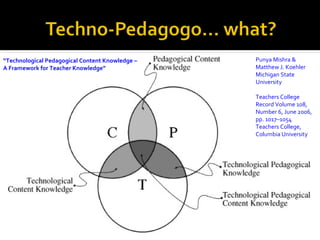
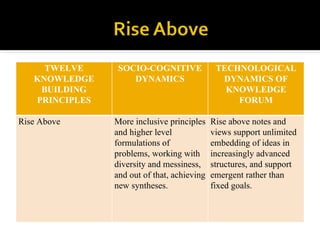
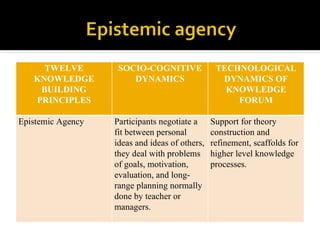
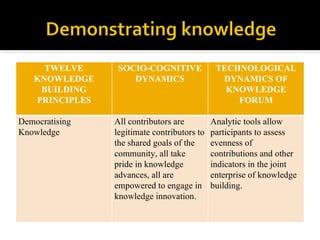
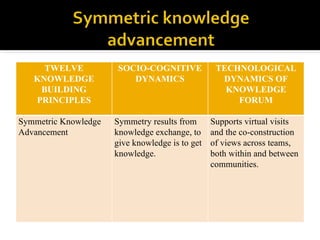
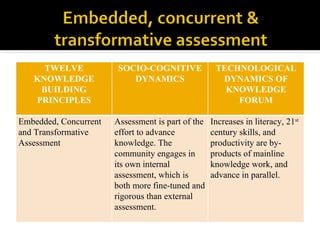
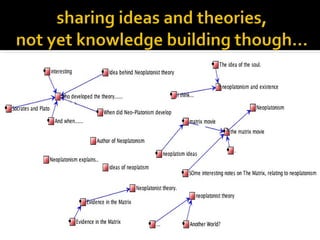
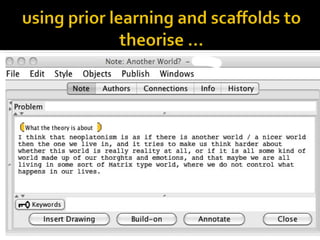
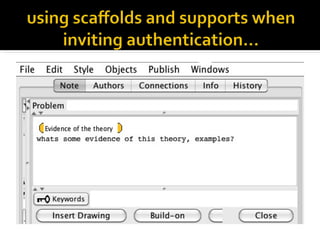
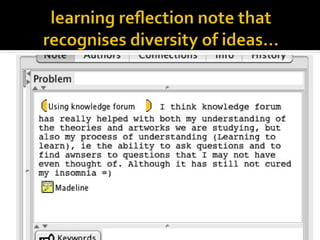
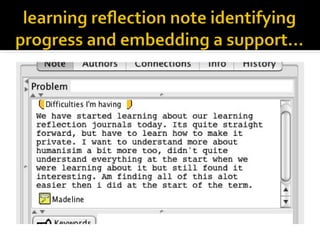
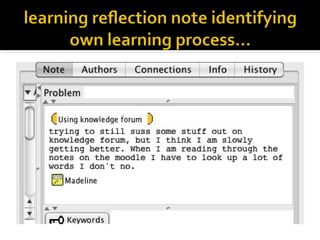
This document discusses Knowledge Building, a pedagogical approach developed by Marlene Scardamalia and Carl Bereiter that aims to create classroom cultures focused on collaboratively improving ideas and building knowledge. Key aspects of Knowledge Building include developing real-world problems, treating all ideas as improvable, promoting idea diversity, and facilitating the emergence of new ideas through synthesis. Knowledge Building is supported by the digital environment Knowledge Forum, which provides scaffolds and mechanisms to help students organize, link, and build upon one another's ideas. The document outlines twelve principles of Knowledge Building and how they are realized through socio-cognitive dynamics and the technological features of Knowledge Forum.