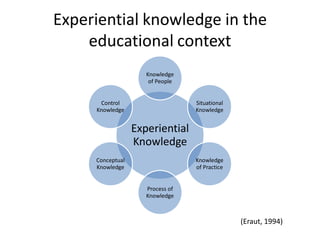
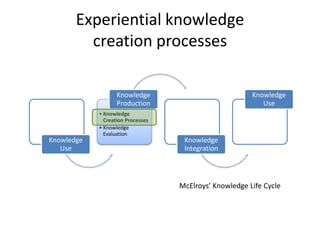
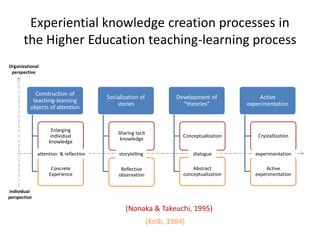
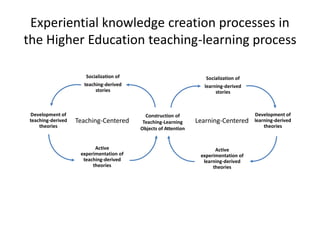
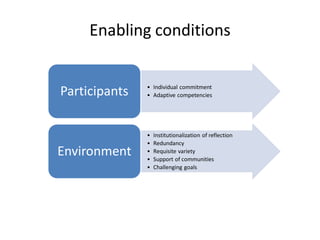
The document discusses the significance of experiential knowledge in enhancing innovation within higher education teaching-learning processes. It outlines critical concepts, processes of knowledge creation, and enabling conditions that facilitate this type of knowledge for teaching and learning. The authors emphasize the need for approaches that develop adaptive competencies and reflect on informal community support to foster innovation.