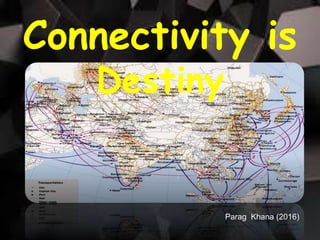
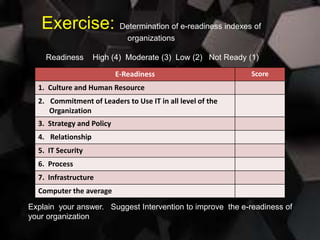
The document discusses several topics related to digital governance and the future of technology:
1. Global connectivity through digital infrastructure is transforming governments and the world system. Vast new infrastructure networks are being built for roads, railways, internet cables, and more.
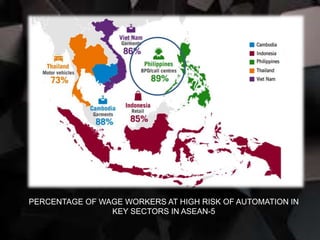
2. Technologies are disrupting jobs and businesses across Southeast Asia, with over half of salaried workers at high risk of losing jobs to automation. This is pushing a shift from manufacturing to service industries like tourism and healthcare.
3. Countries like the Philippines face challenges in developing digital governance and readiness for future technologies. While e-government initiatives have improved rankings, businesses still lag in fully implementing digital transformation strategies. Urgent efforts are needed to



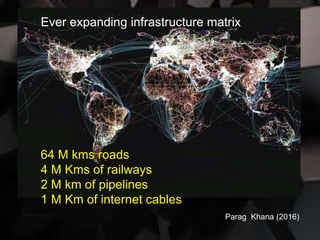

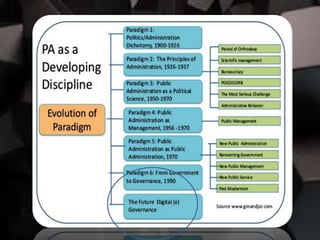














![[WEF (Sep. 2018)
Shaping ASEAN’s
Future Readiness]
Global value chains are continuing to
shift, especially from East Asia, but also
increasing reshoring. New technologies
are disrupting and fostering a technology-
based model of production, challenging
especially the region’s SMEs.”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitalgovernancepl1bfp-200926091817/85/Digital-Governance-PL-1-23-320.jpg)
![“Can ASEAN Turn
Geostrategic
and Technological Disruption
into Opportunity?”
[Project Syndicate, Sep. 4, 2018]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitalgovernancepl1bfp-200926091817/85/Digital-Governance-PL-1-24-320.jpg)
![“Trade war and costs speeding shifts
of production to ASEAN and USA”
[Next Big Future, Sep. 21, 2018]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitalgovernancepl1bfp-200926091817/85/Digital-Governance-PL-1-25-320.jpg)






![[ASEC Aldaba, DTI, quoted by the Philippine
Information Agency on May 17, 2018]
“The recent assessment
report of WEF
showed that Philippines has
a low level of
readiness for future
production ”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitalgovernancepl1bfp-200926091817/85/Digital-Governance-PL-1-32-320.jpg)