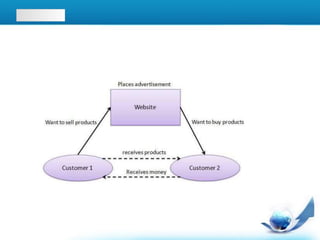
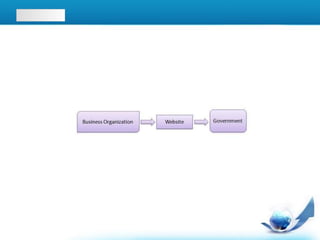
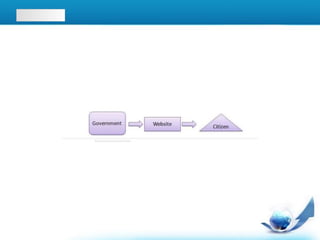
E-commerce has evolved from early electronic data exchange between businesses in the 1970s to the widespread use of online shopping and retail sales to consumers via the internet today. Key developments include the commercialization of the internet in the early 1990s allowing businesses to sell products online, the growth of e-commerce giants like Amazon and eBay in the late 1990s and 2000s, and the rise of business-to-business electronic transactions reaching $700 billion by 2001. While the dot-com crash set back some companies, e-commerce has continued to grow and now accounts for over 3% of total retail sales globally.