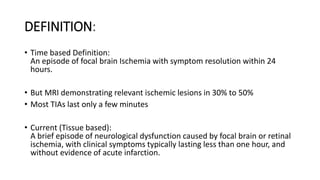
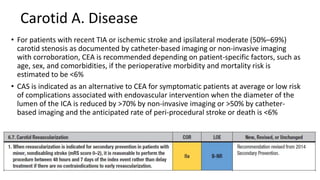
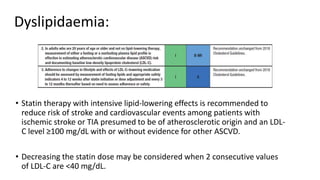
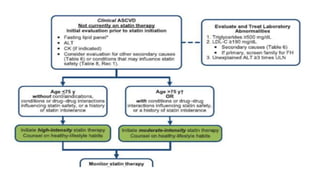
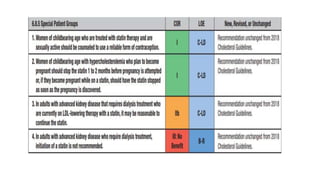
1. A transient ischemic attack (TIA) is a brief episode of neurological dysfunction caused by focal brain or retinal ischemia, with symptoms typically lasting less than one hour without evidence of acute infarction.
2. The risk of stroke is highest in the first few days after a TIA, with about a 10% risk of stroke in the first week and 15% risk within the first 90 days.
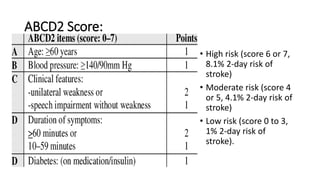
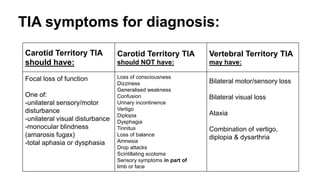
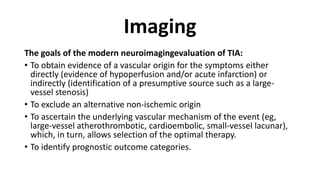
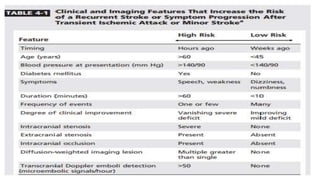
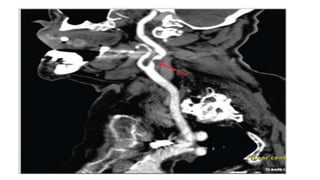
3. Evaluation of patients with suspected TIA involves detailed history, neurological exam, prognostic testing like the ABCD2 score, and investigations including blood tests, brain and vascular imaging to identify the cause and risk of future stroke.