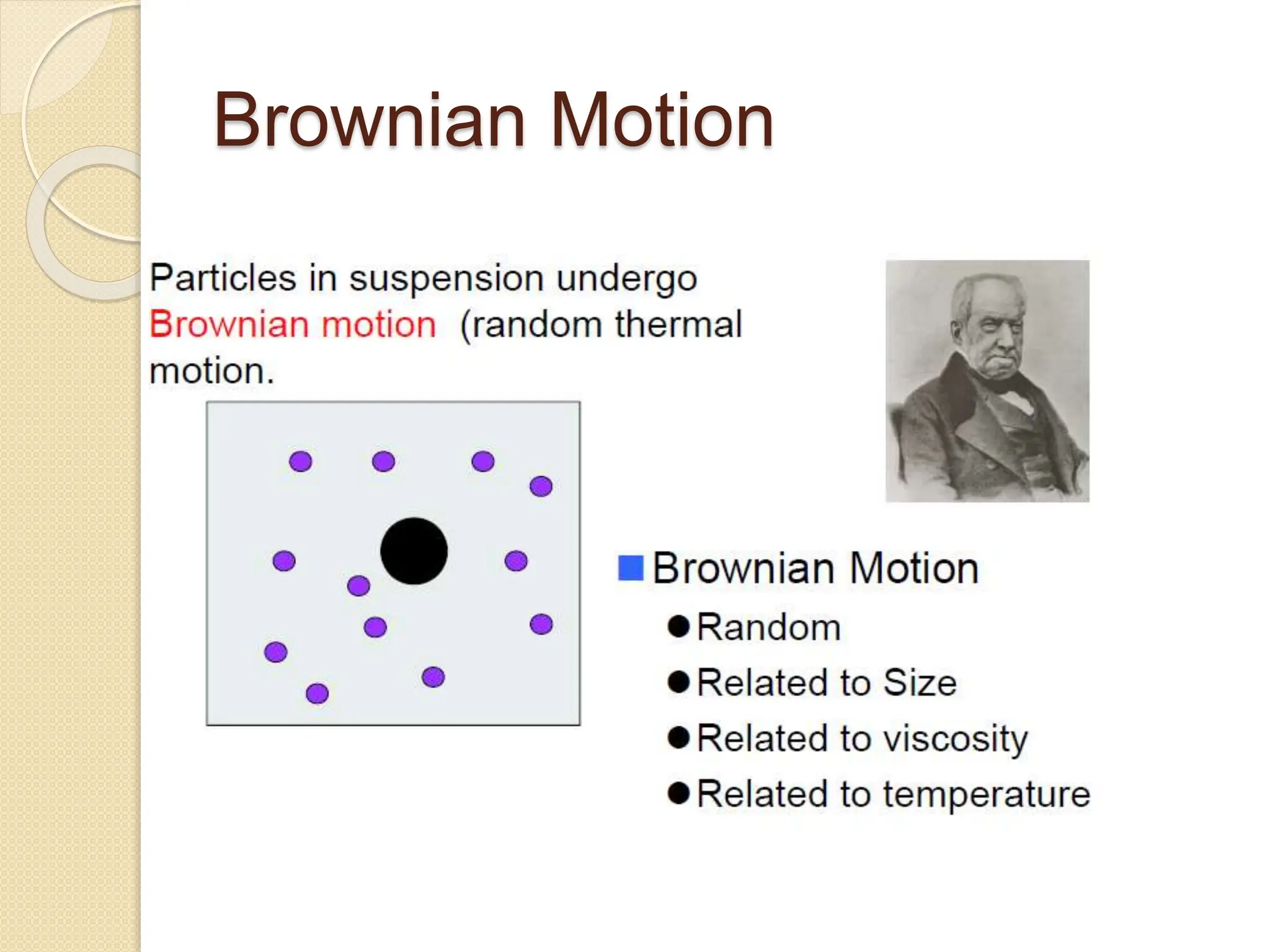
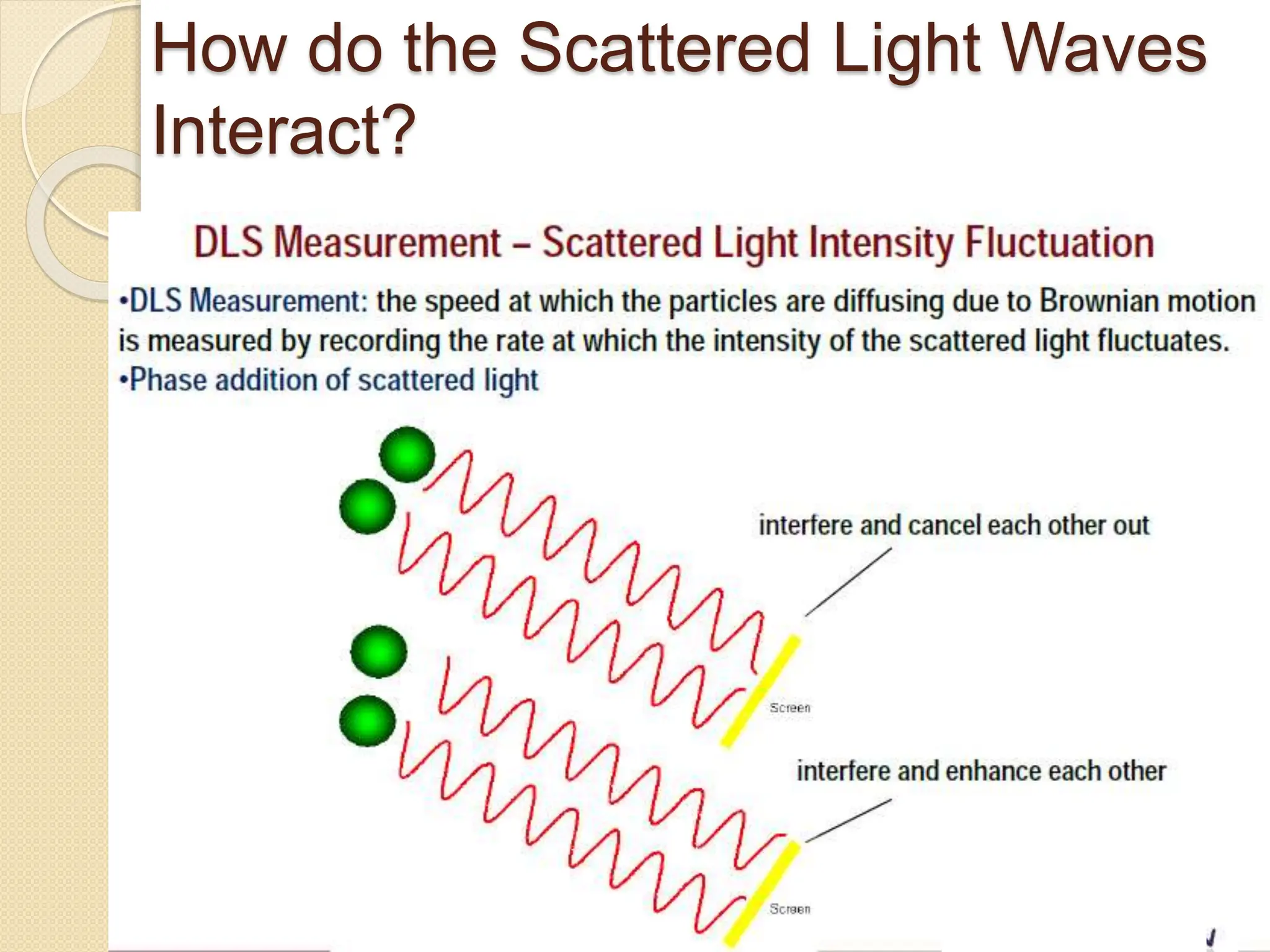
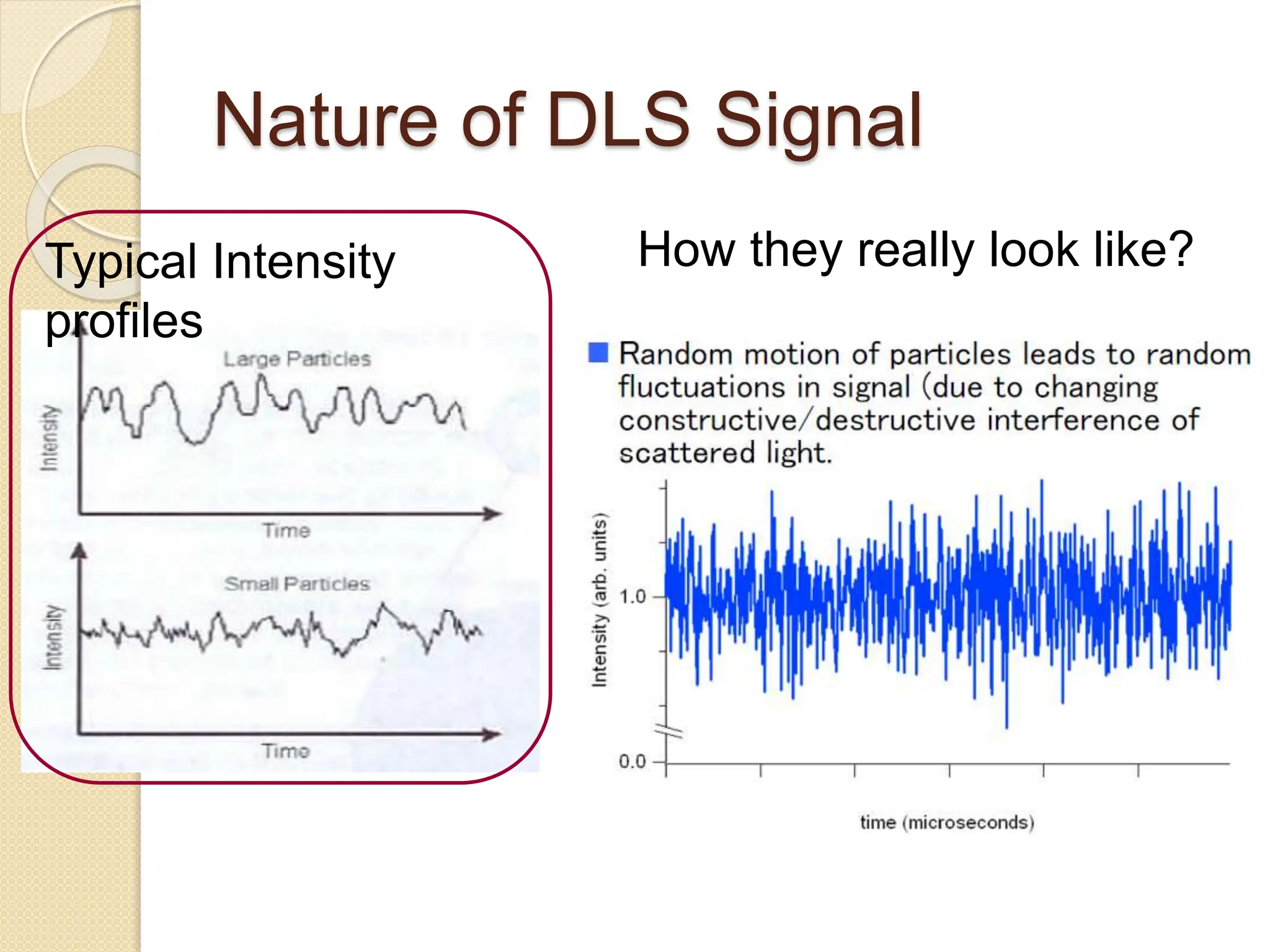
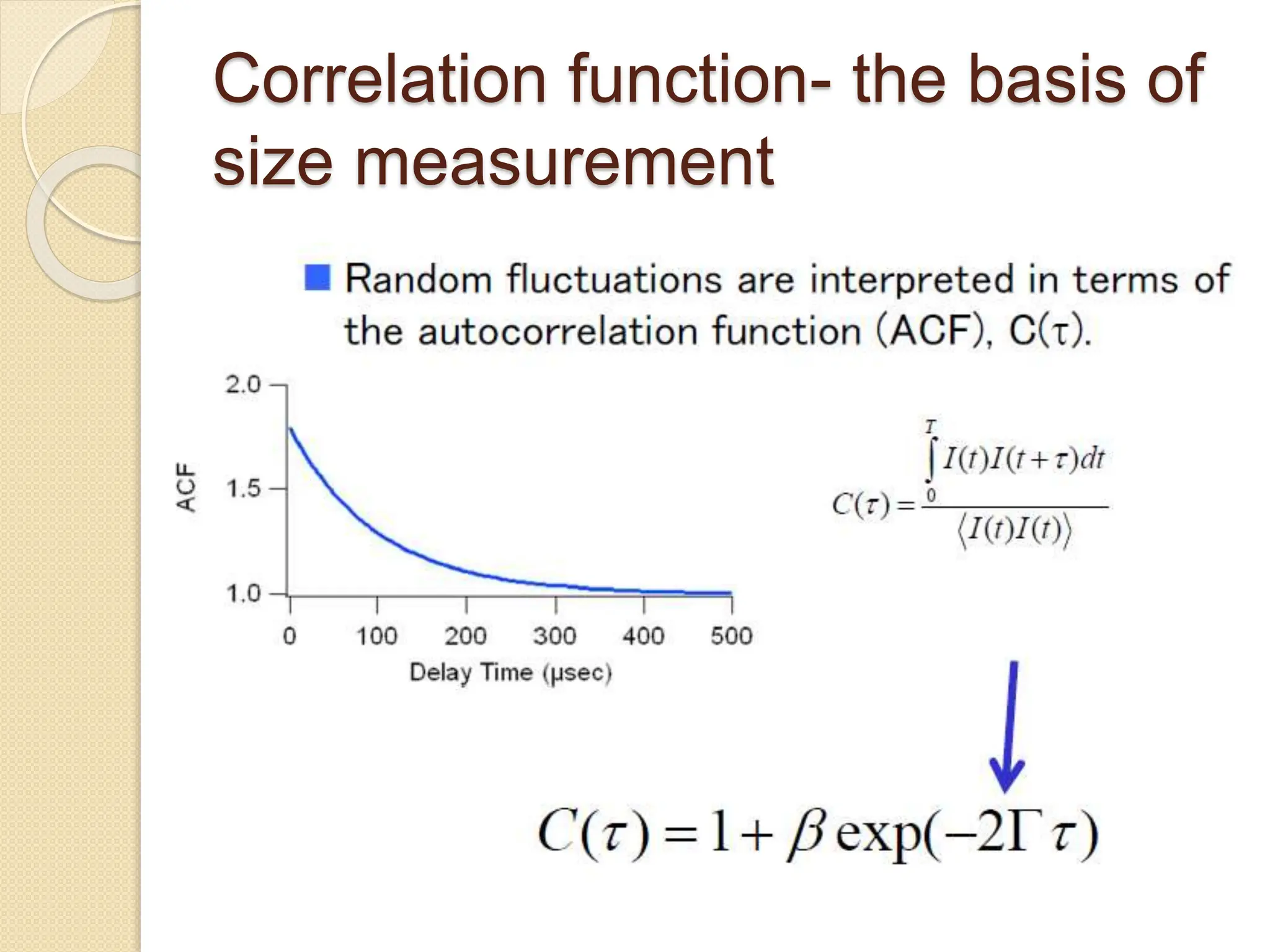
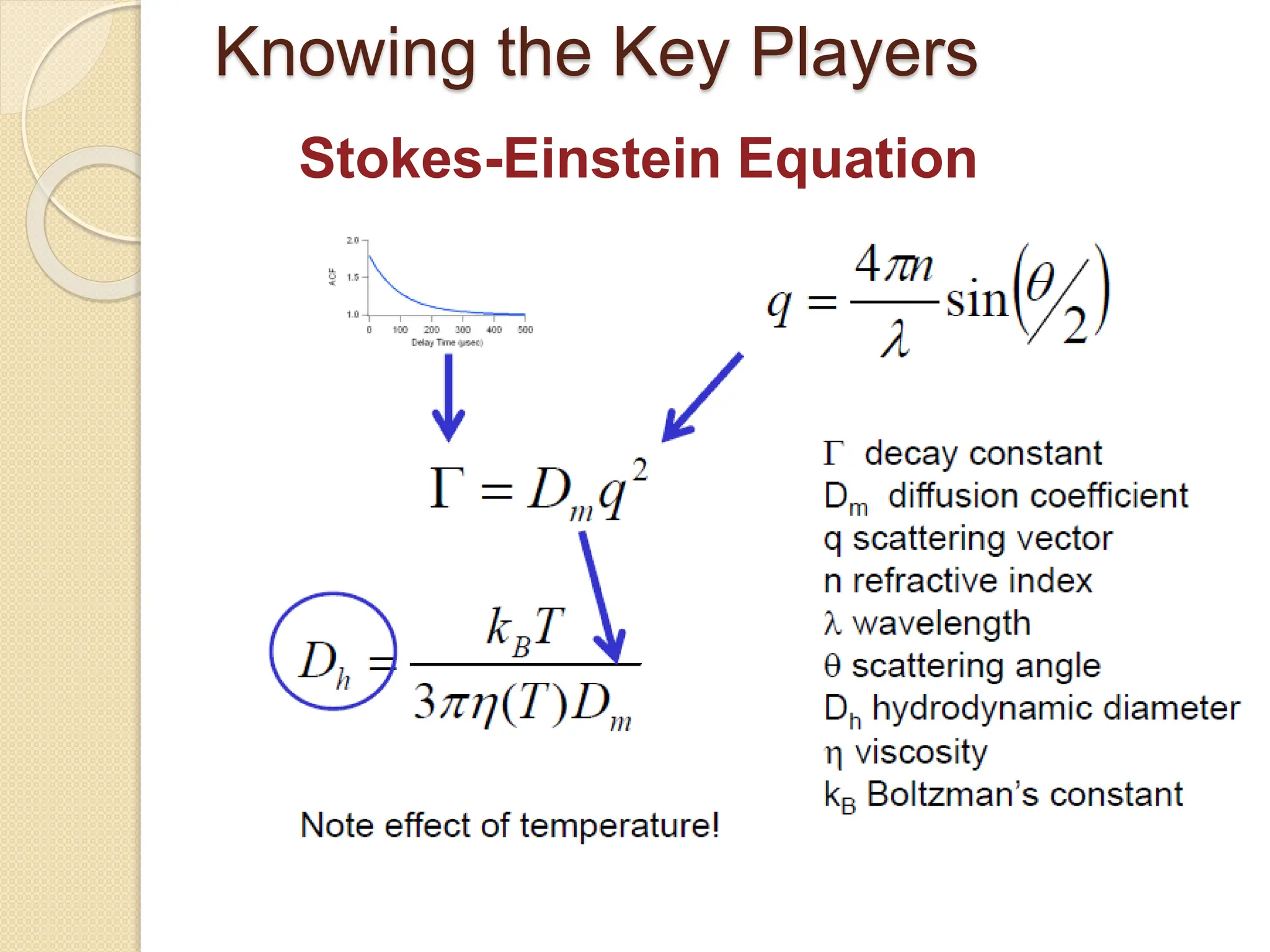
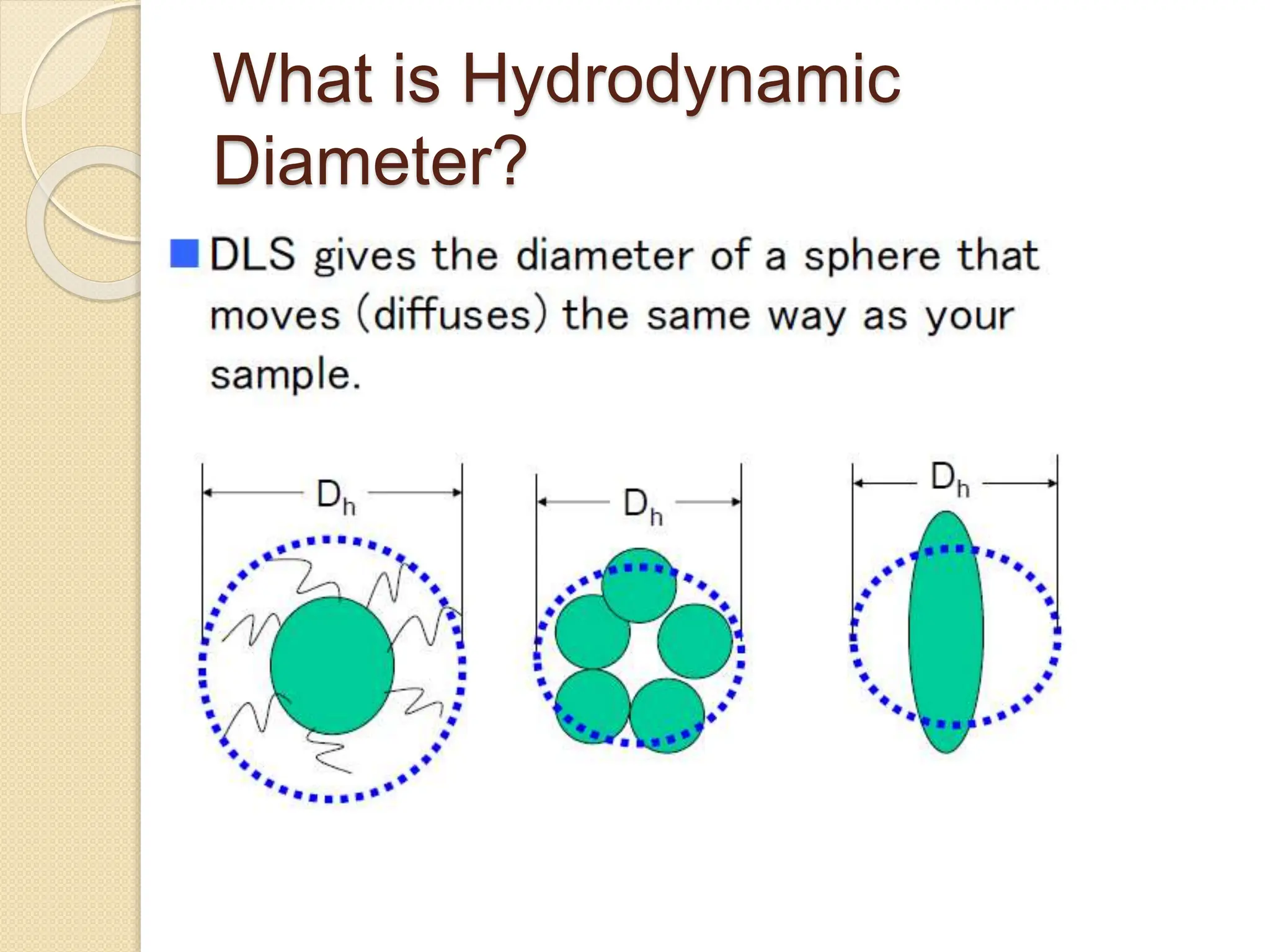
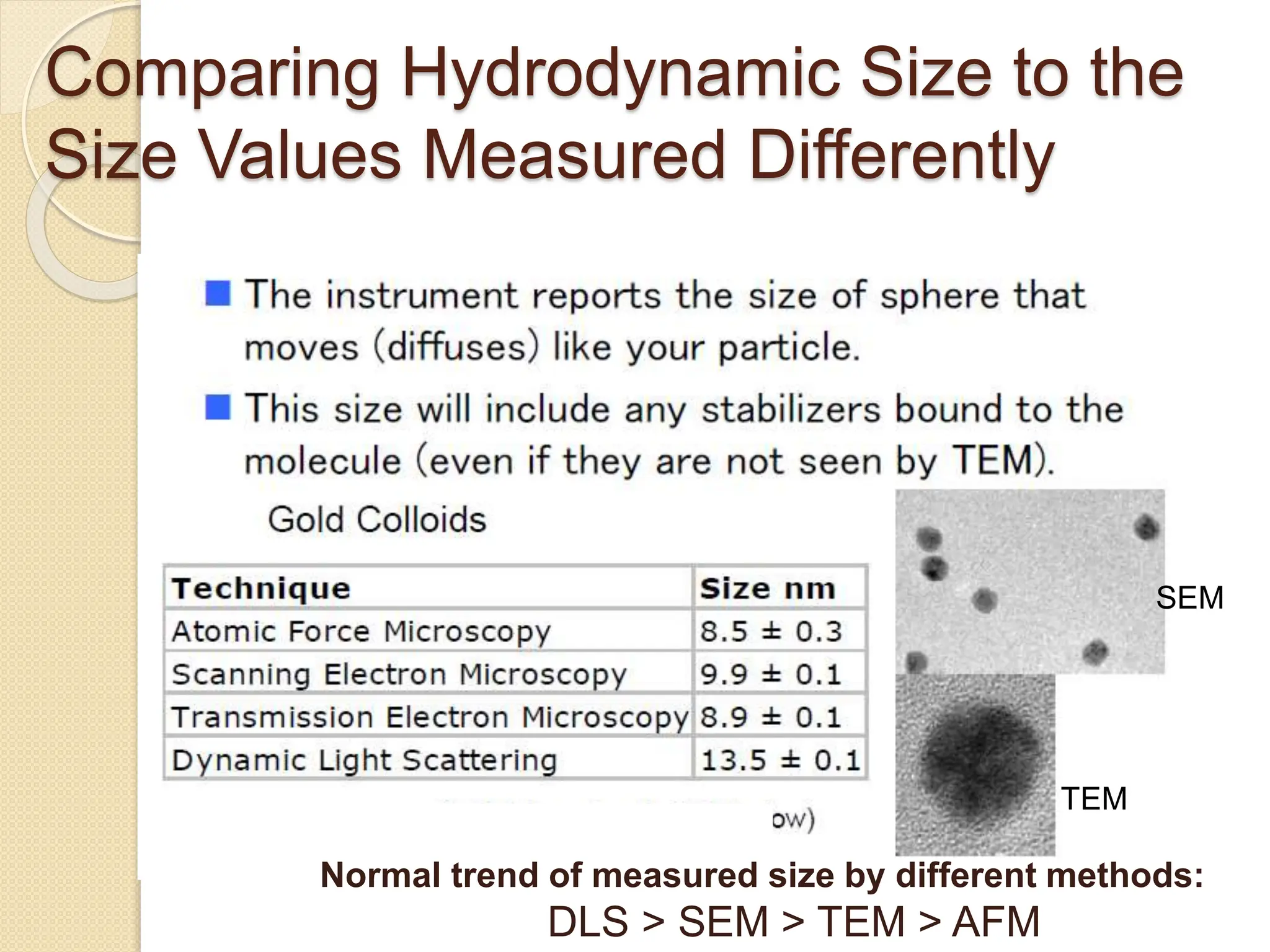
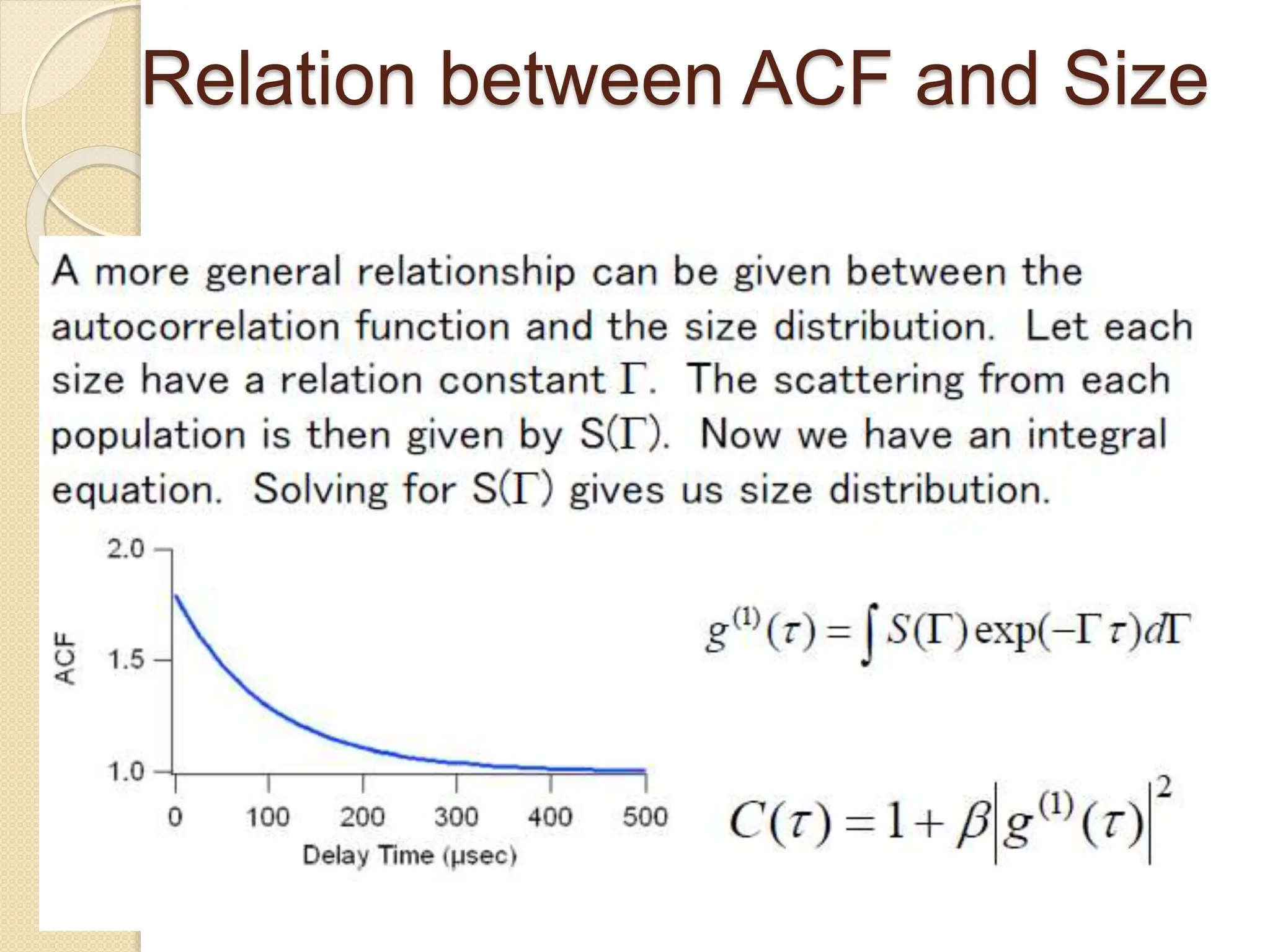
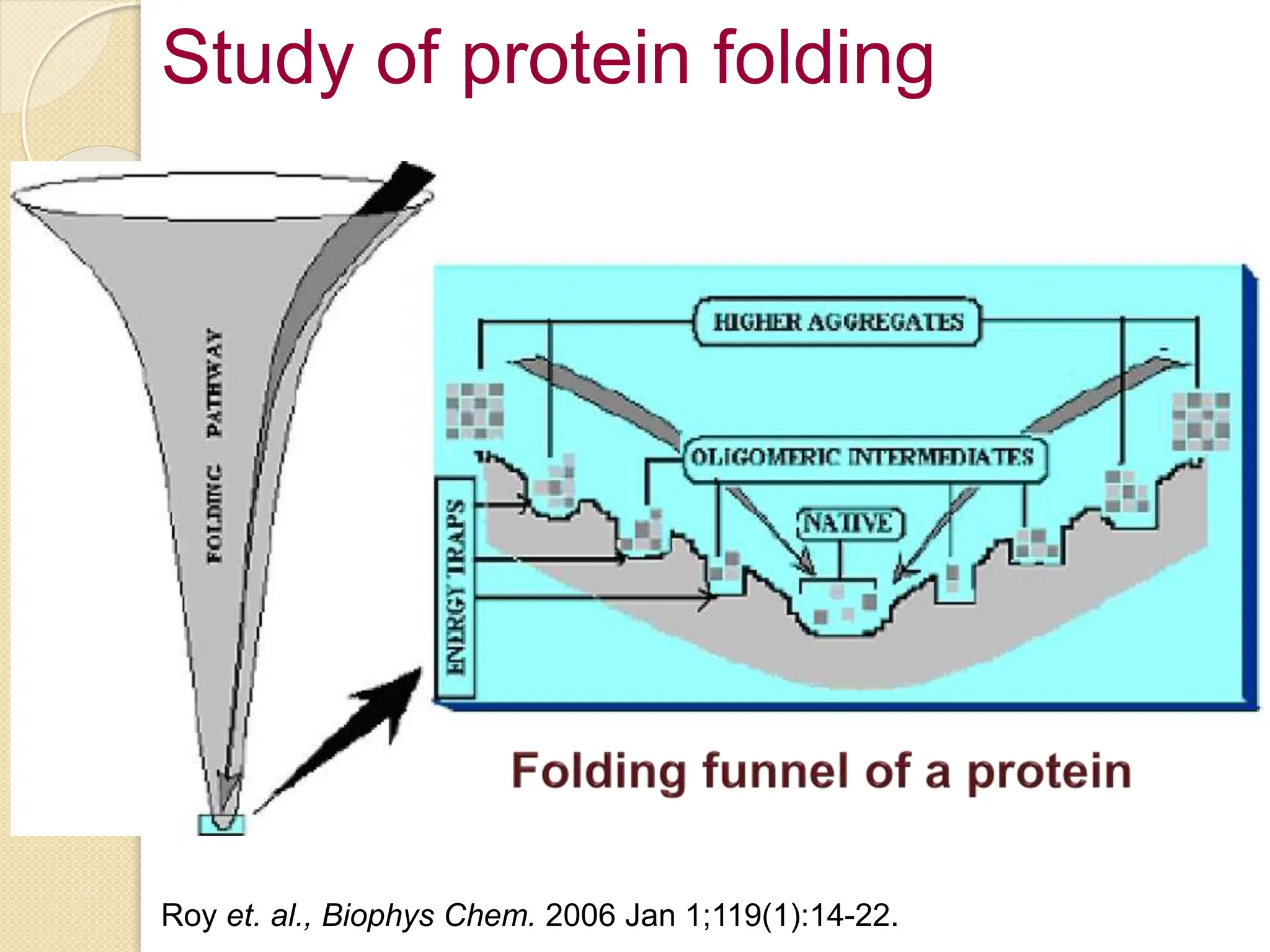
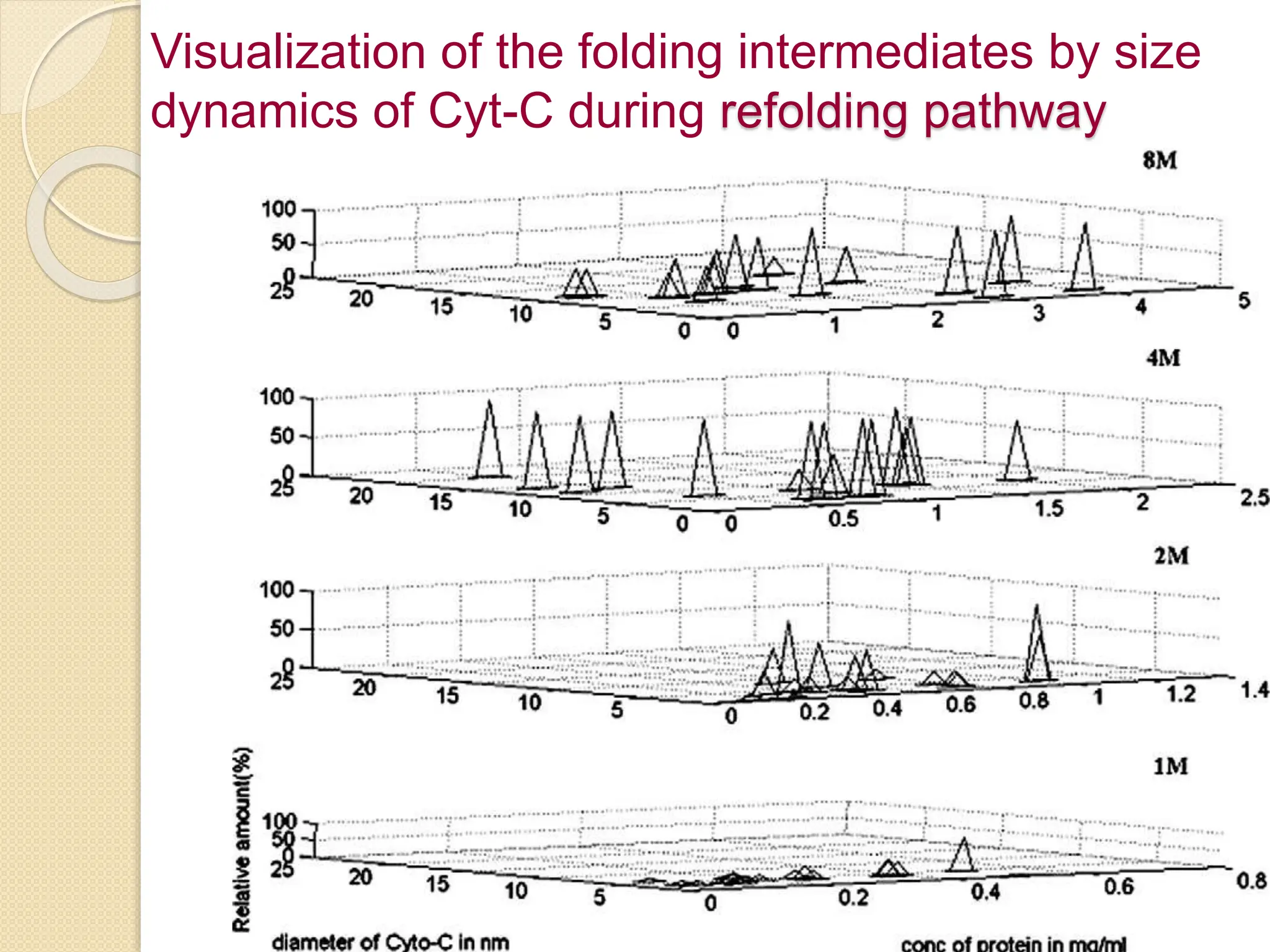
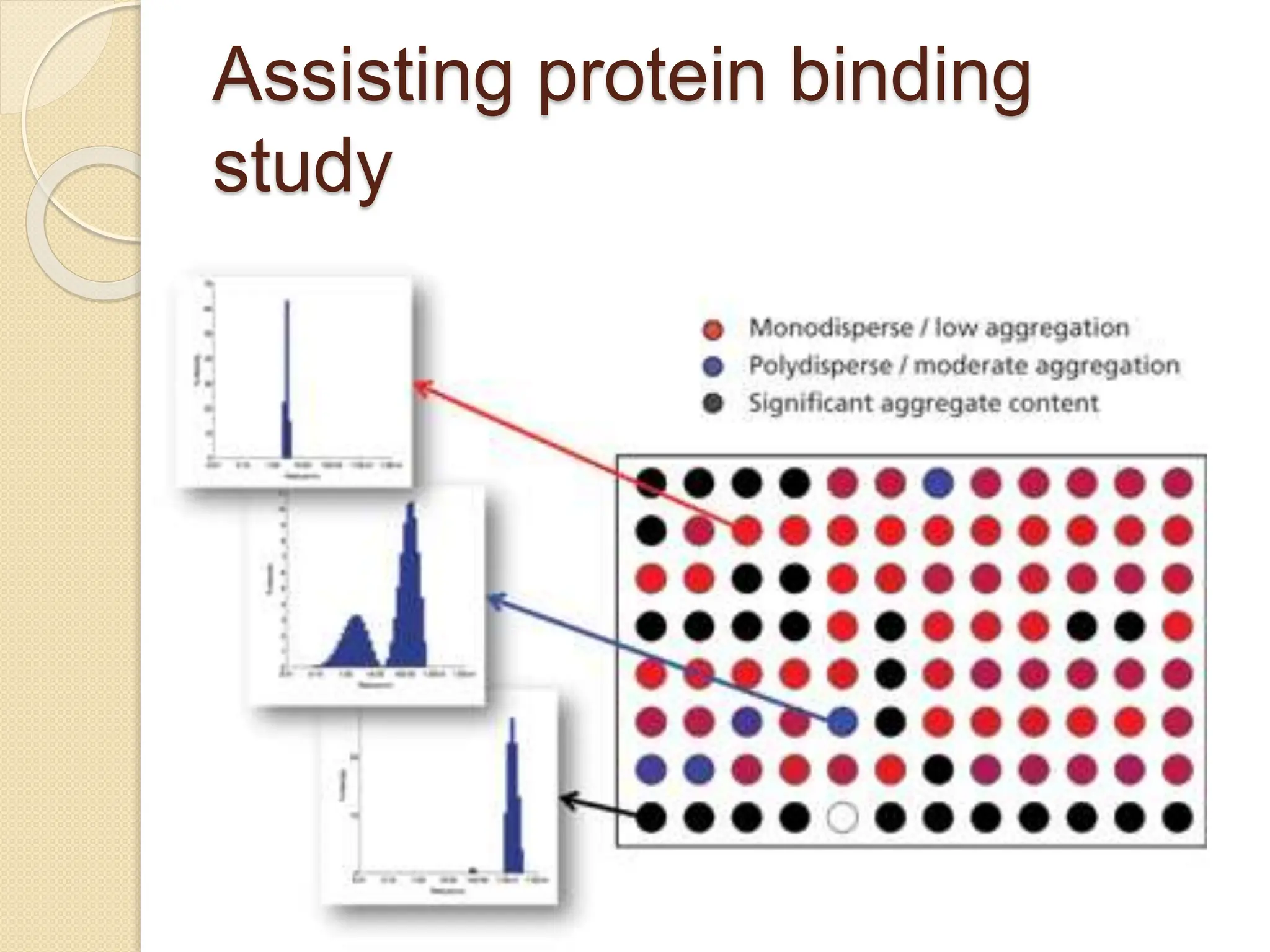
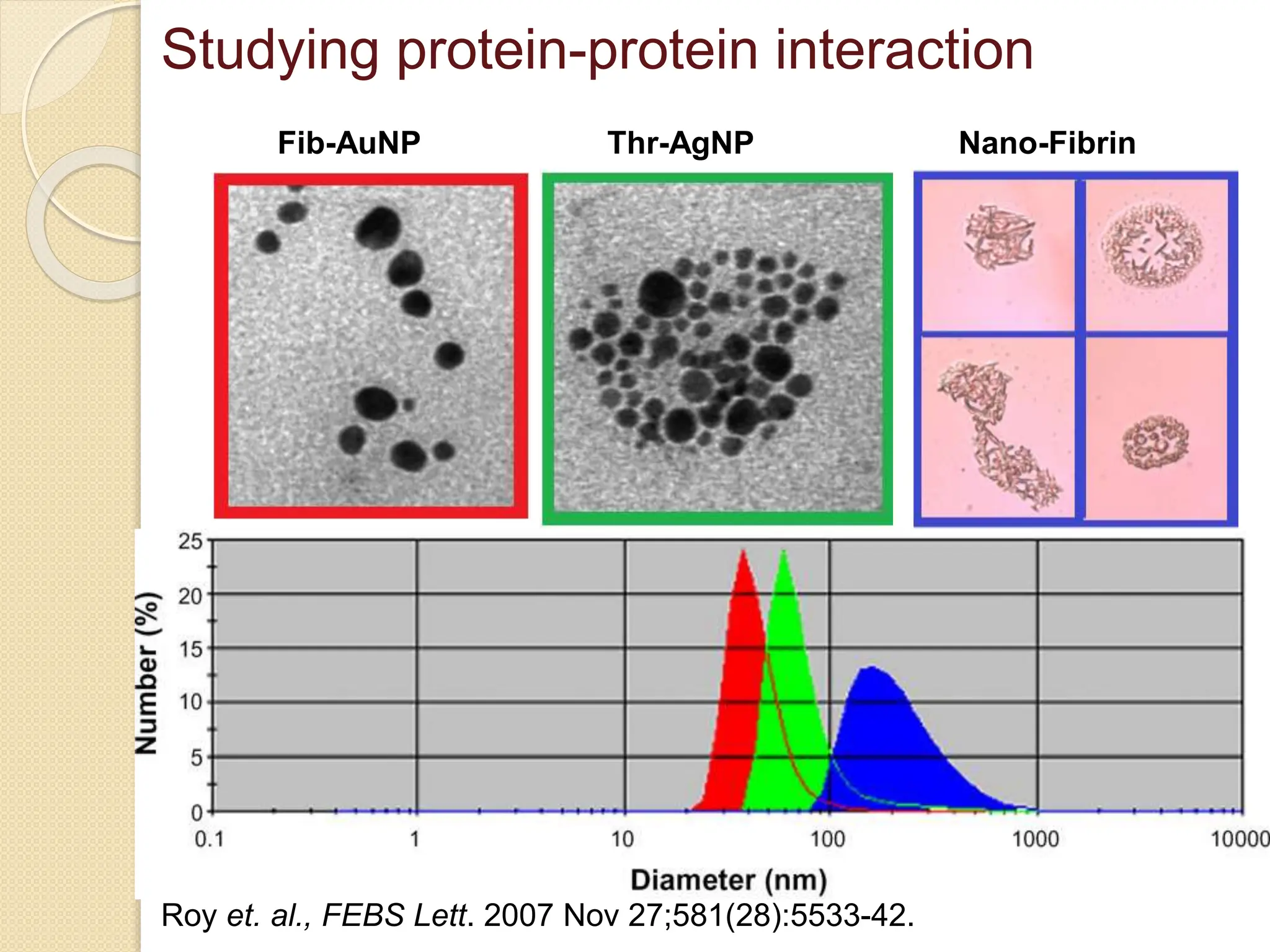
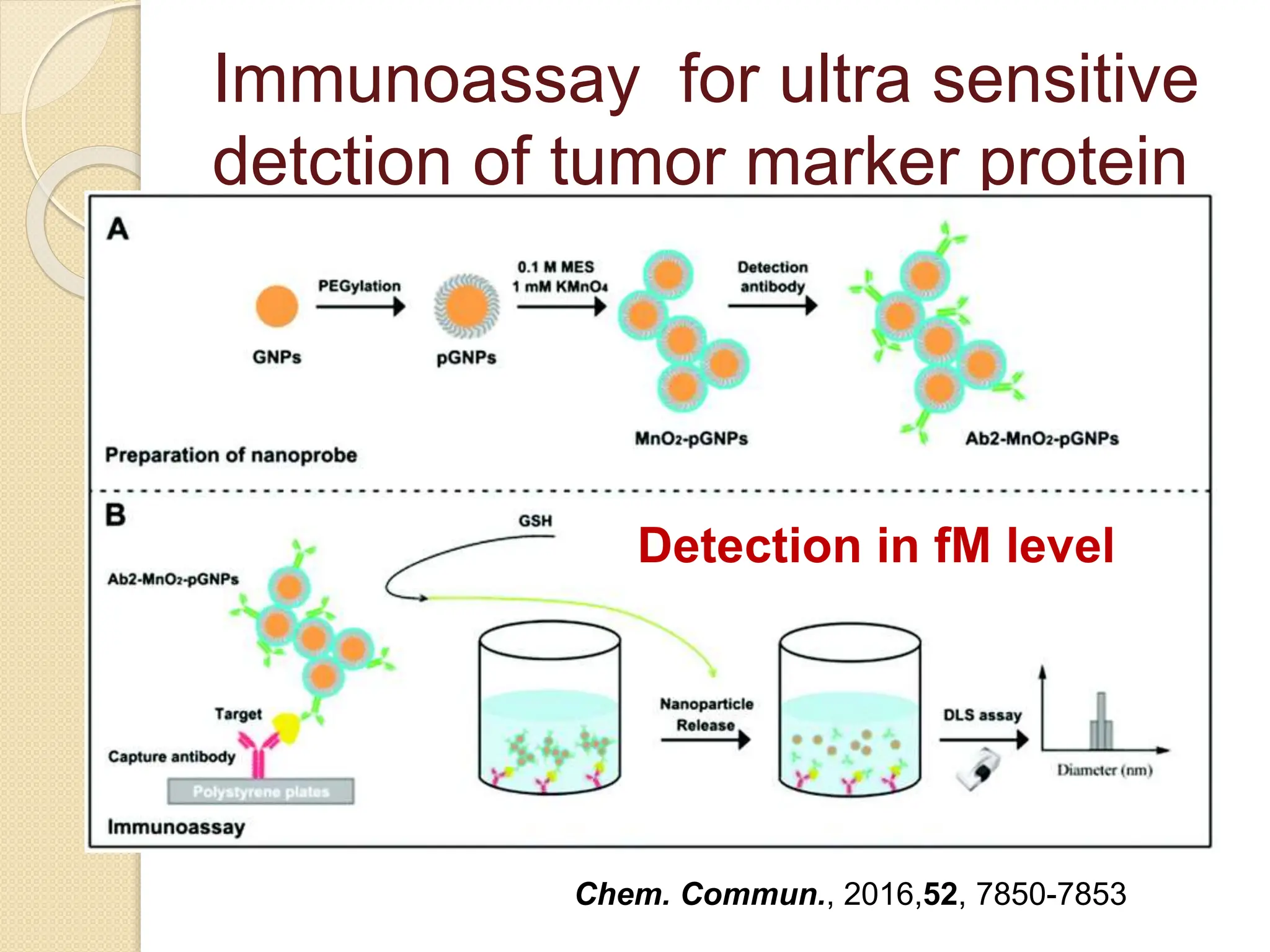
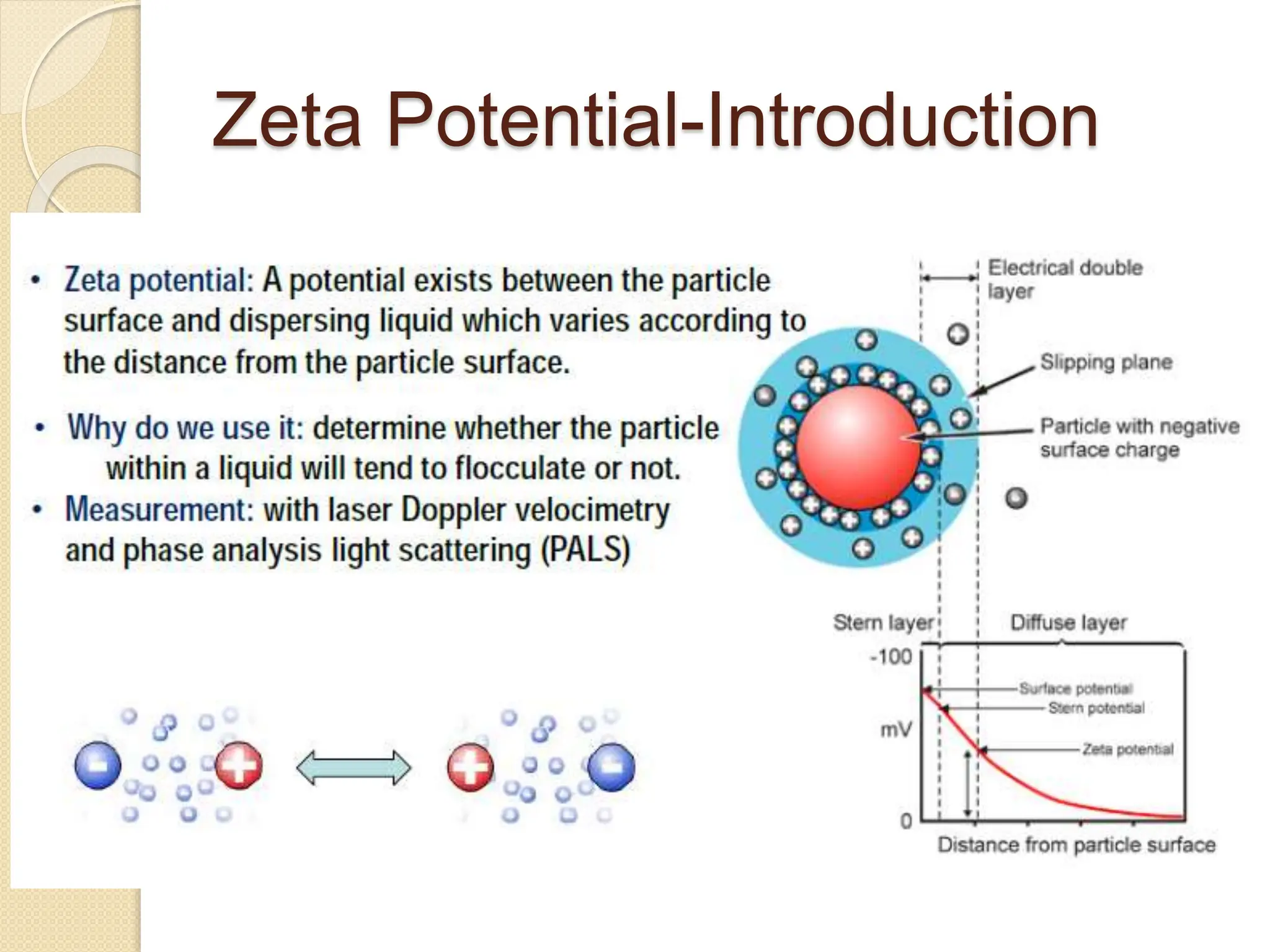
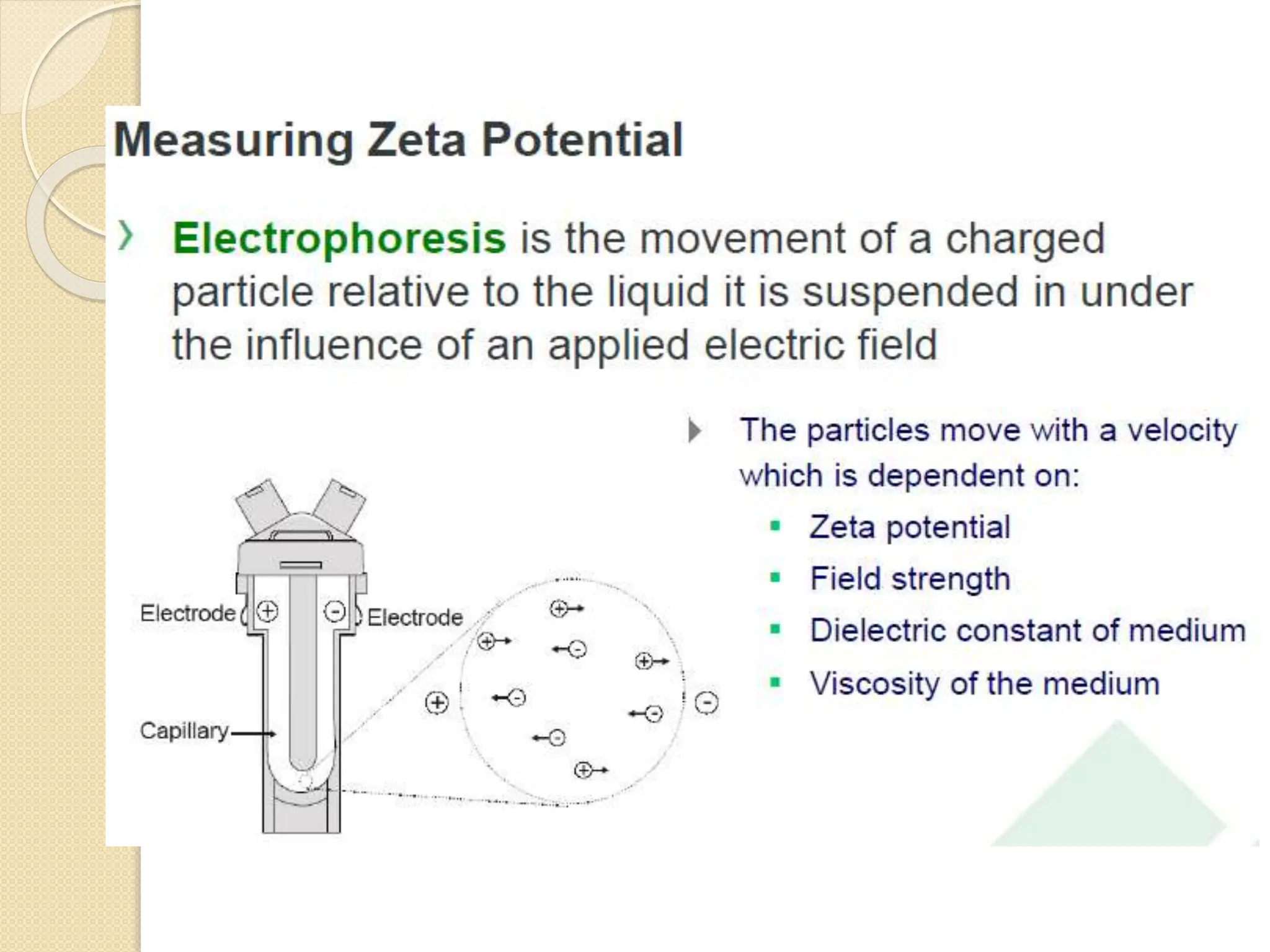
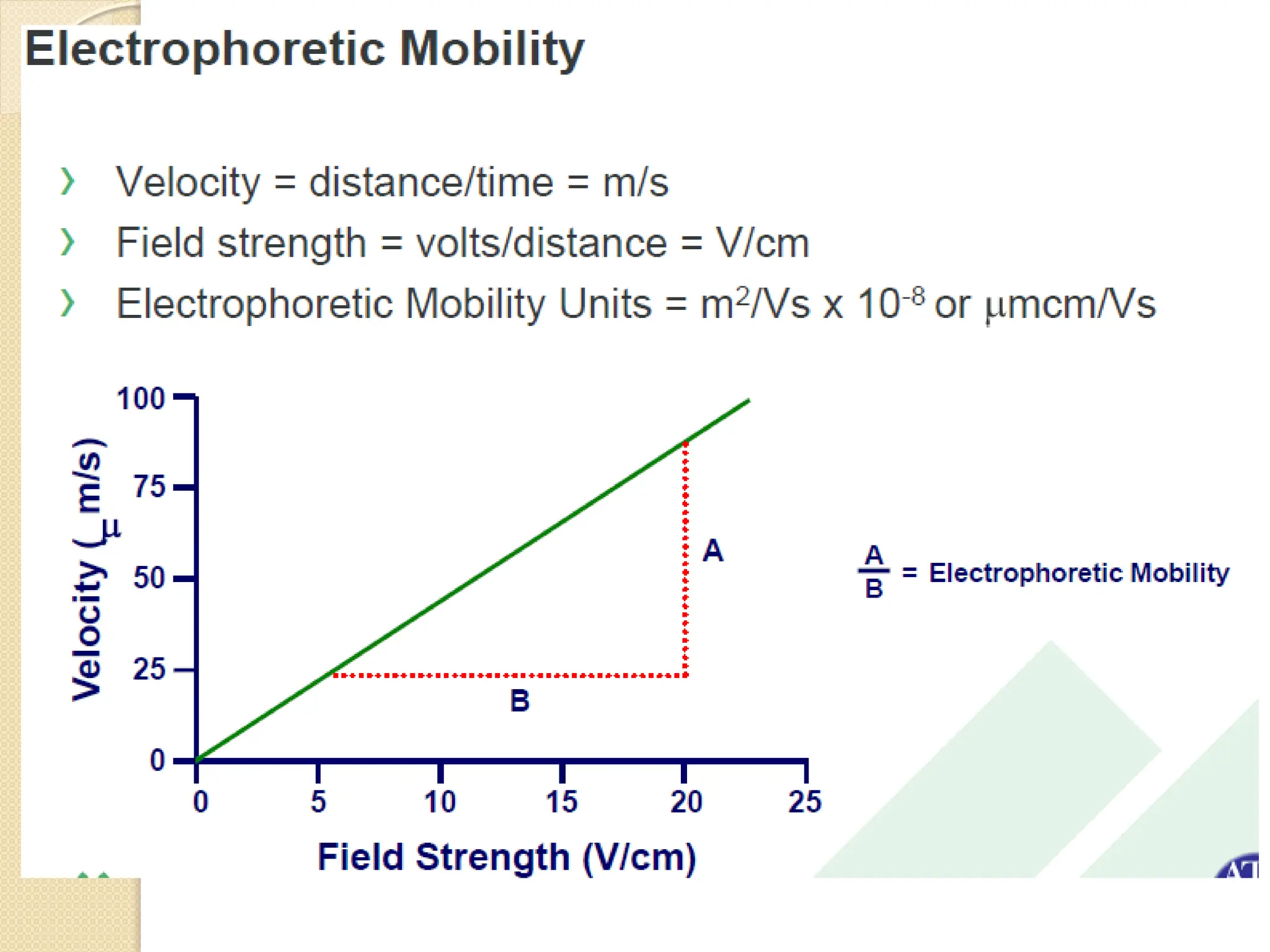
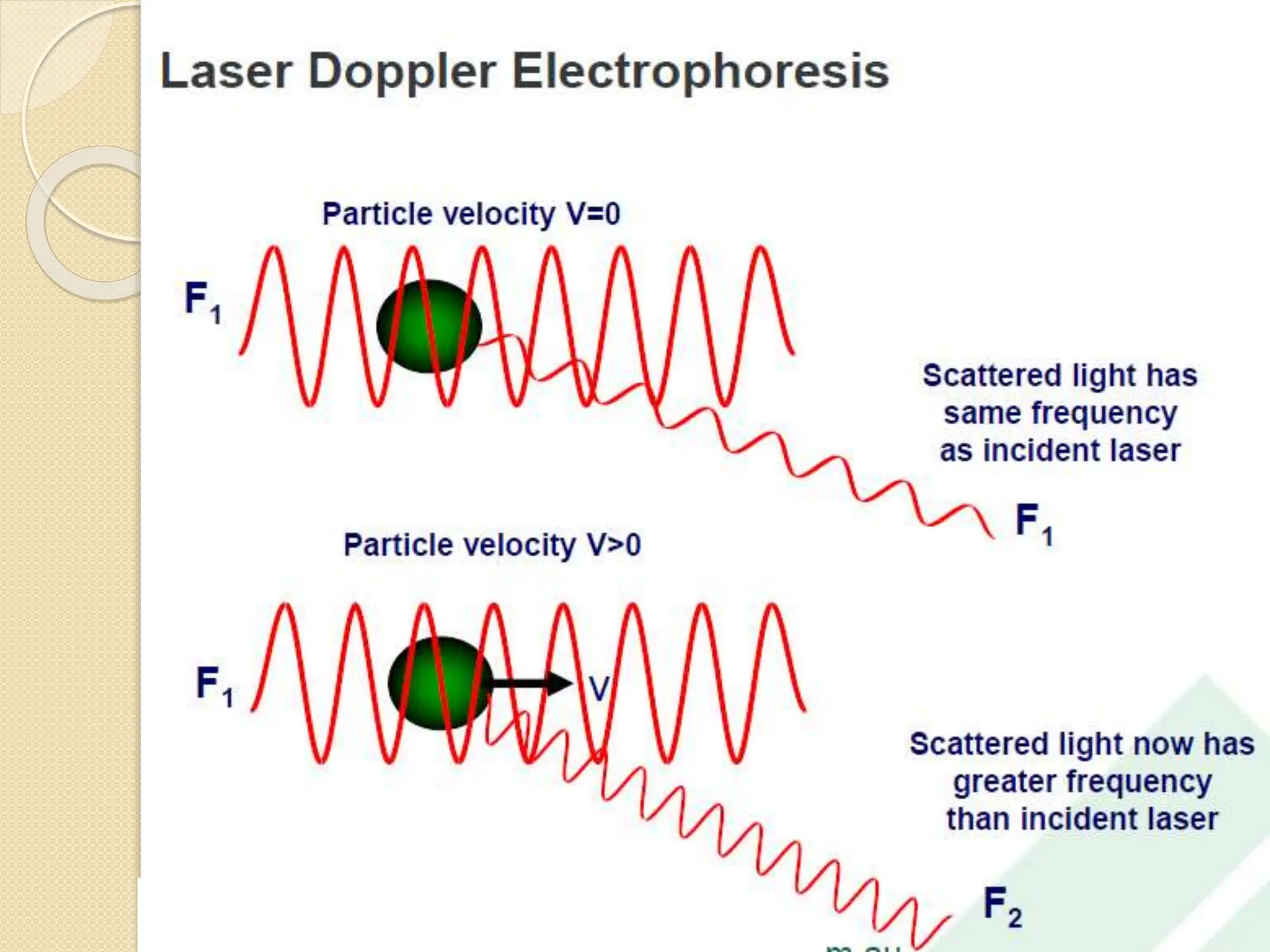
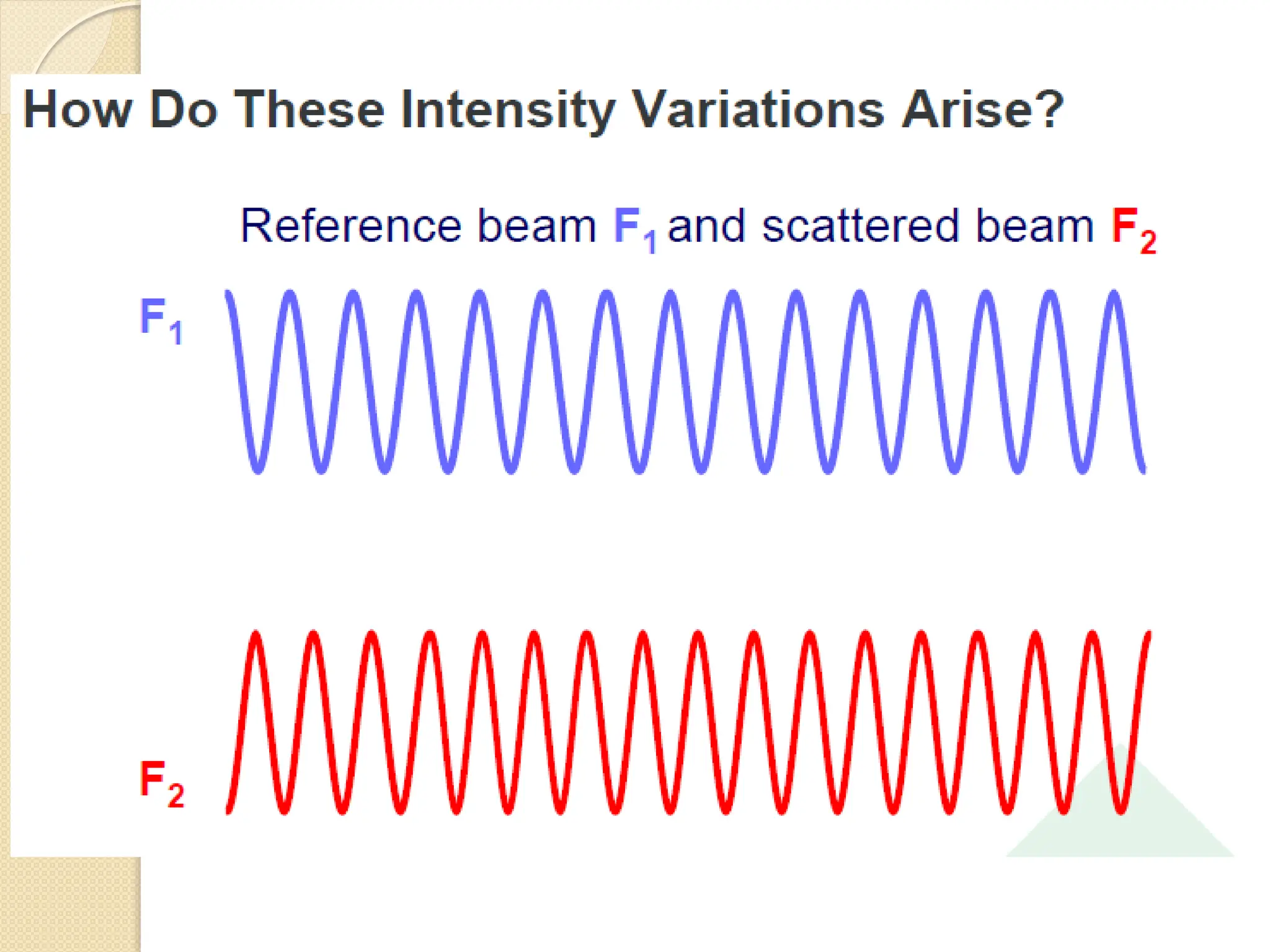
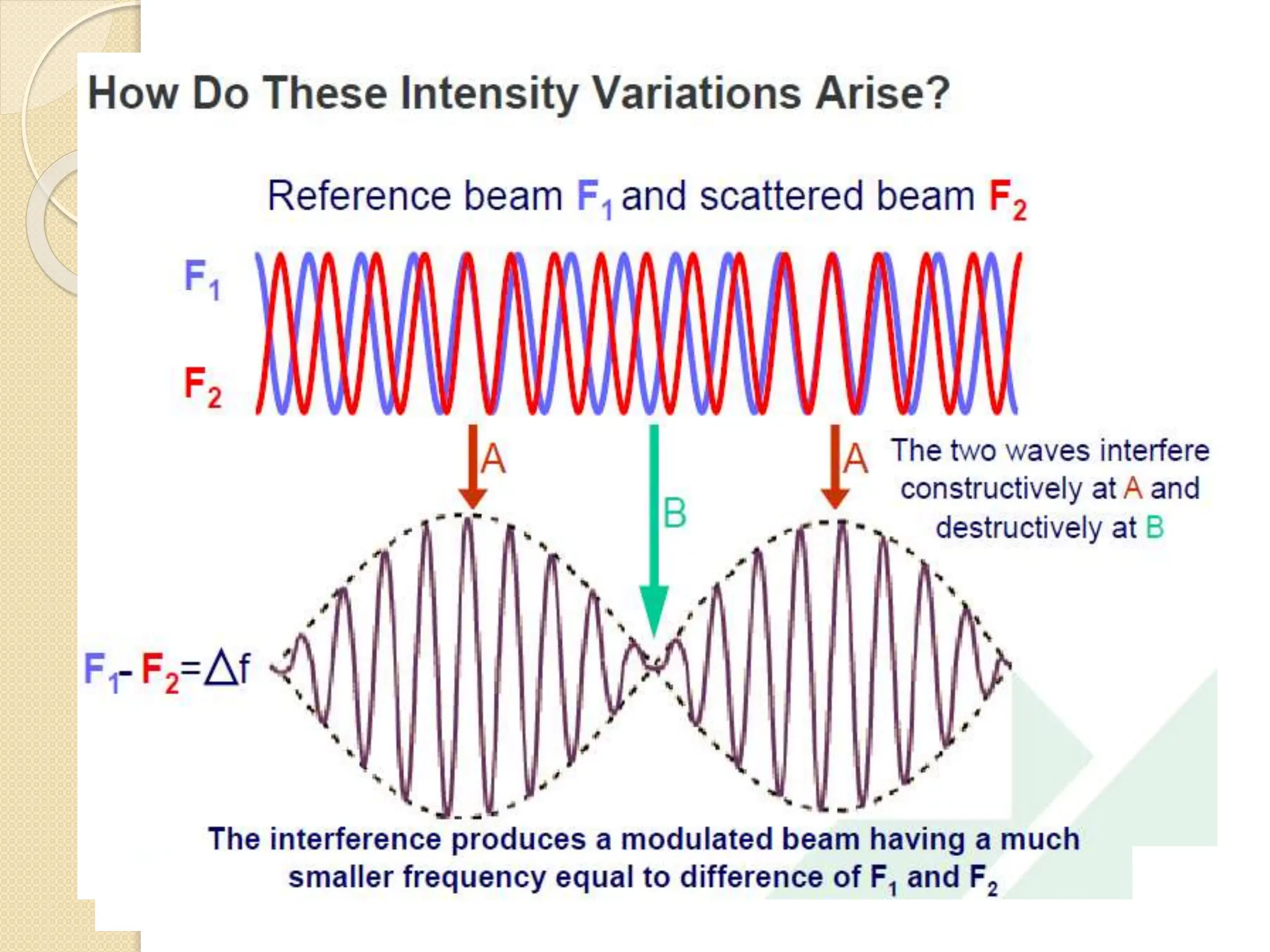
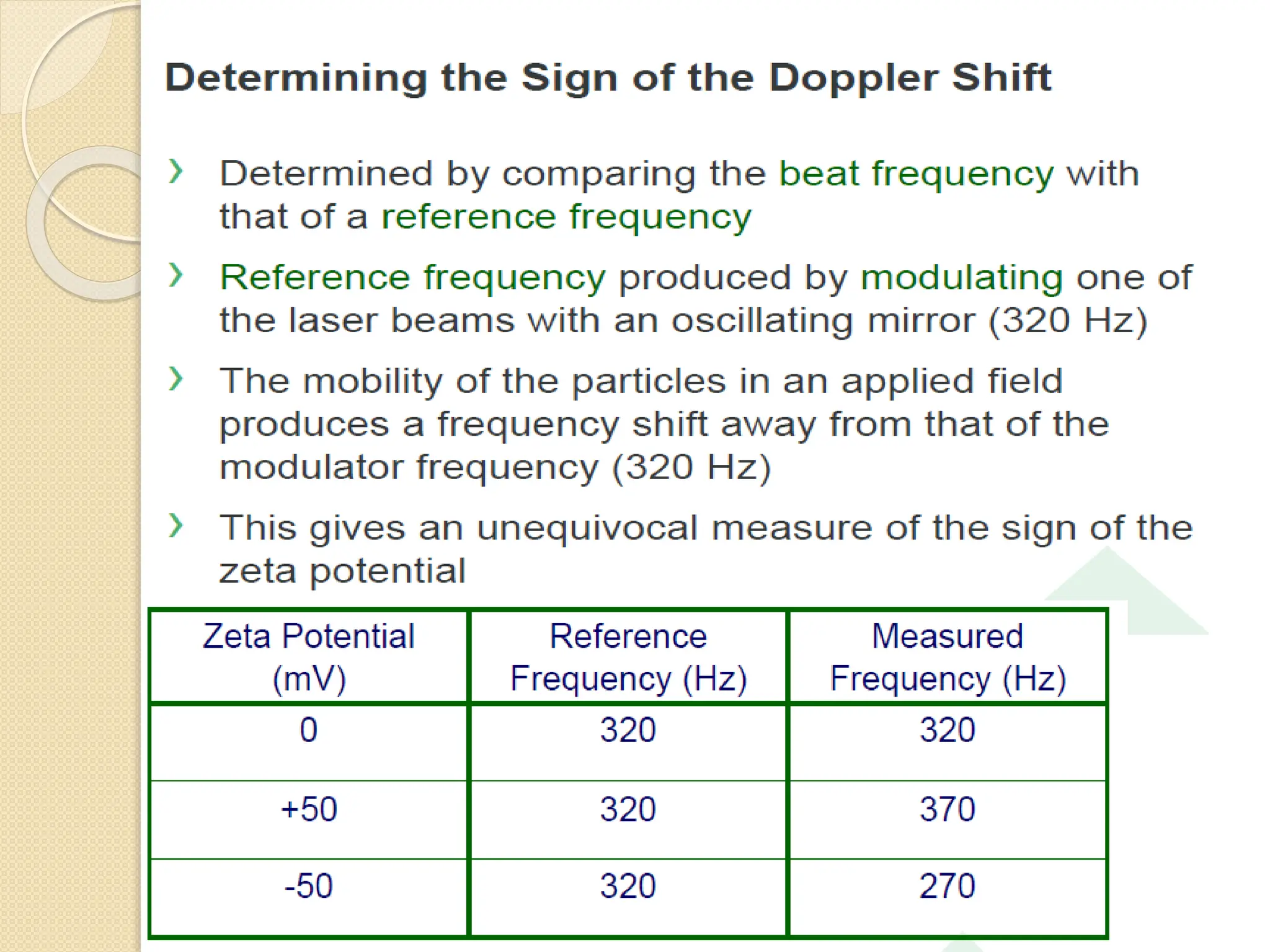
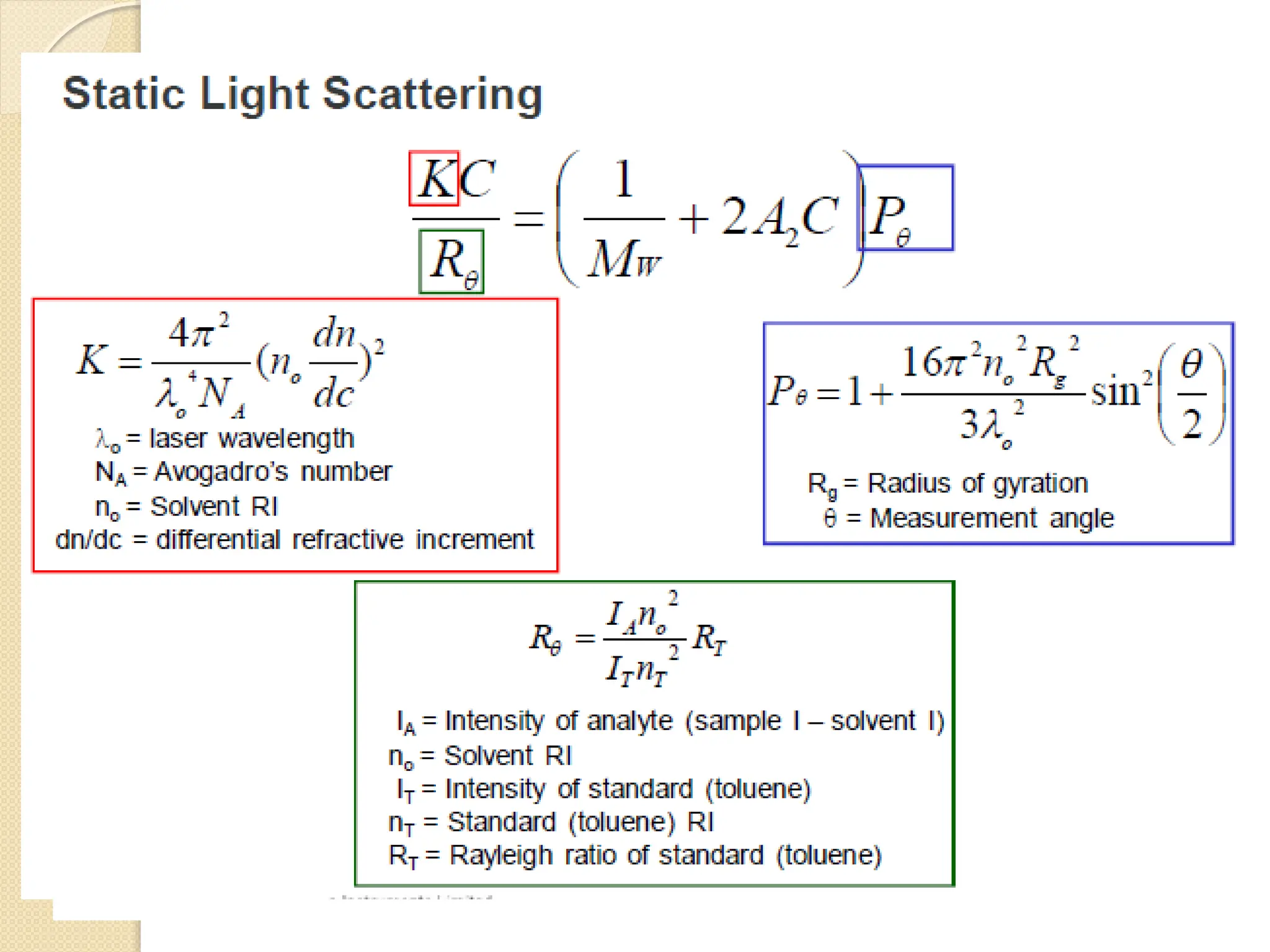
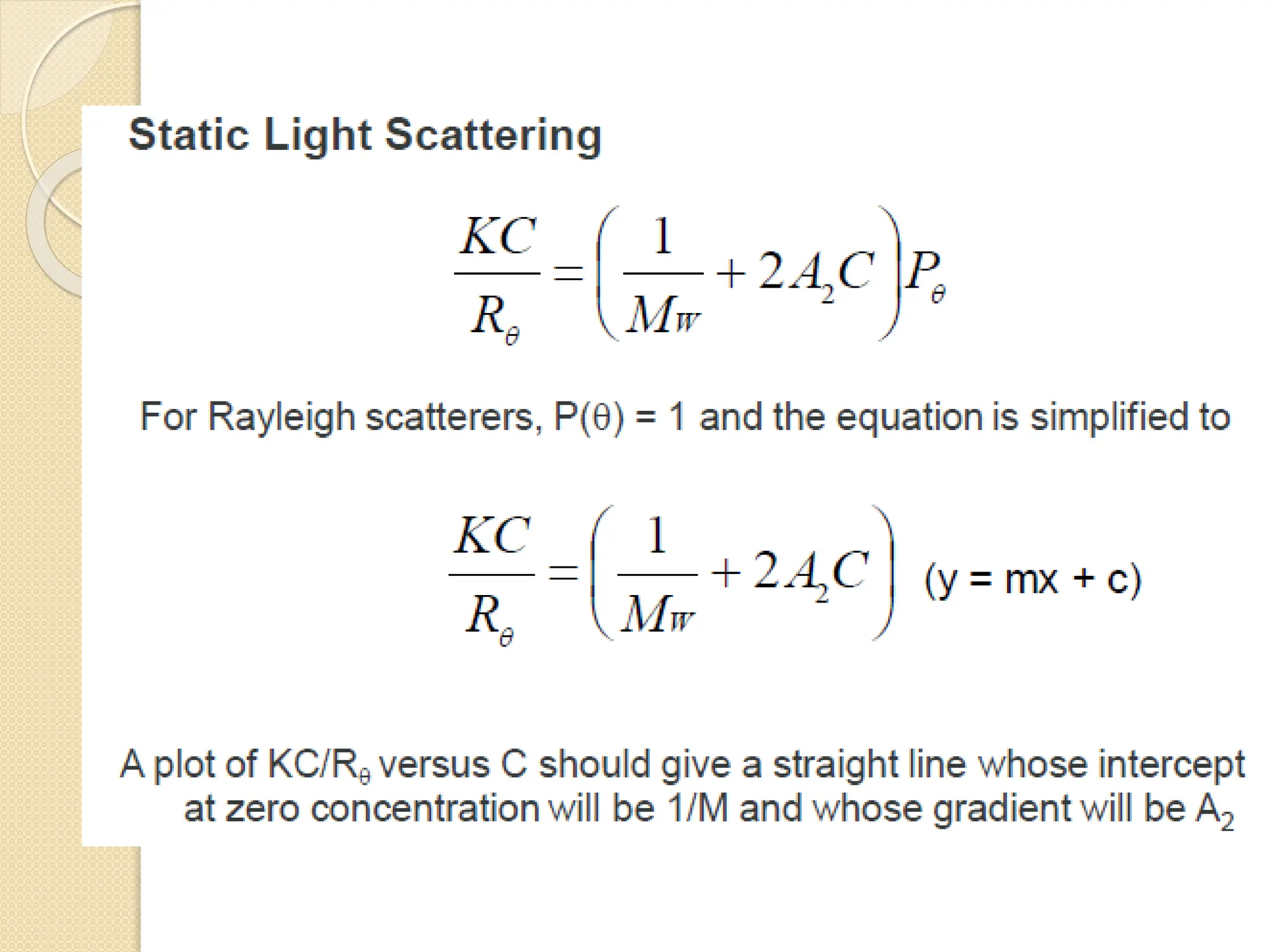
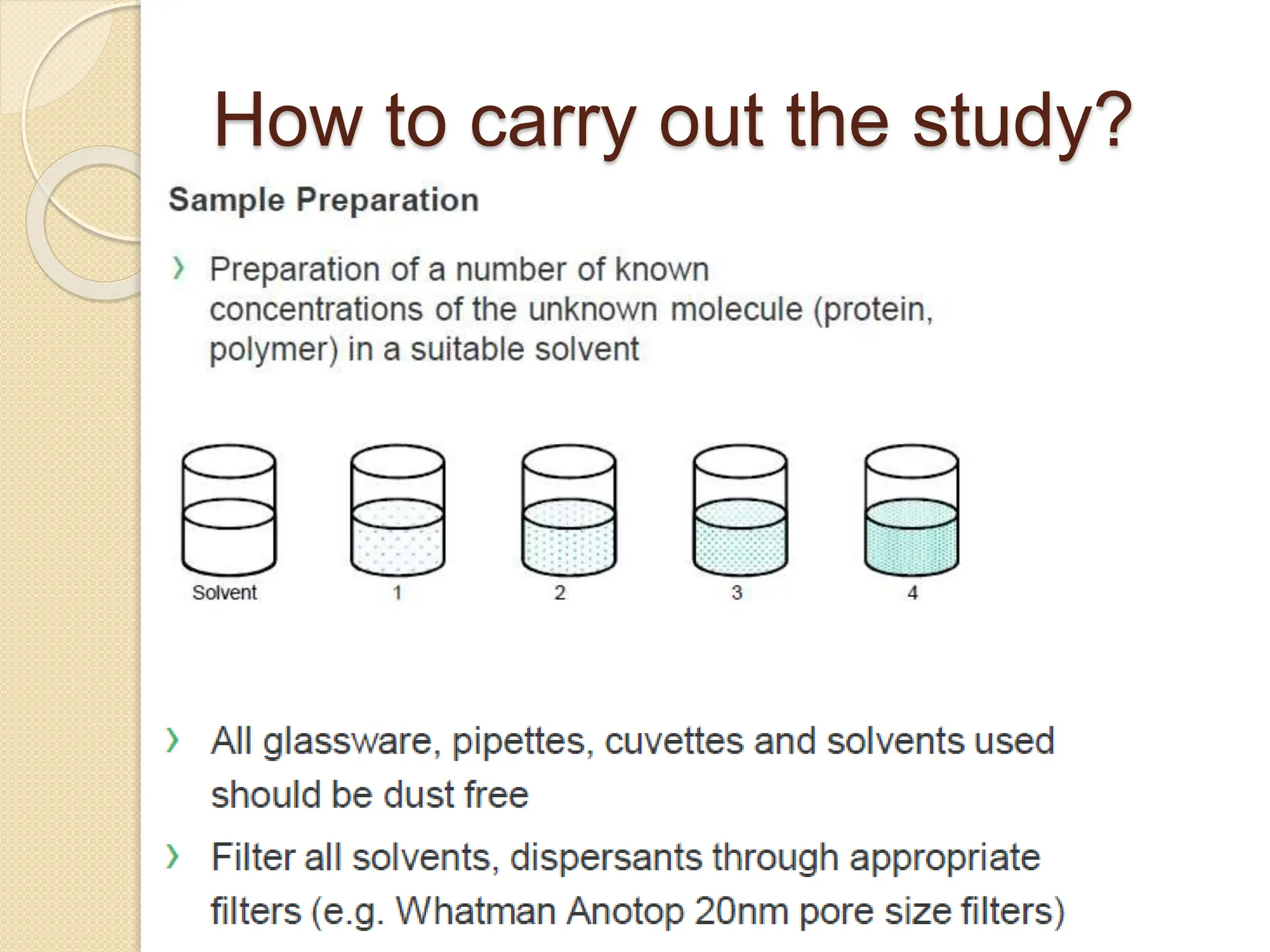
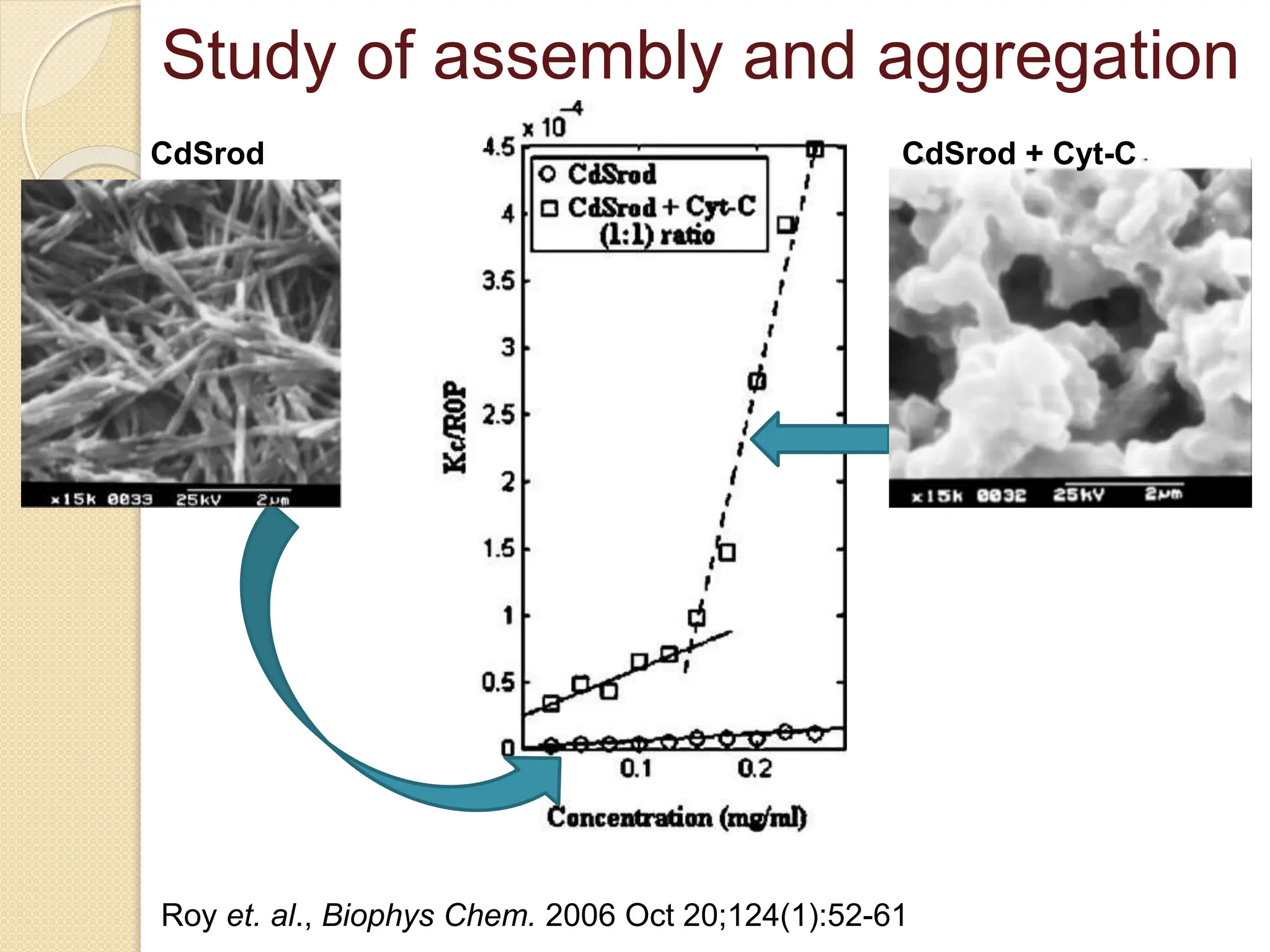
The document discusses the limitations of conventional techniques for biomolecular investigation, emphasizing the need for dynamic light scattering (DLS) and related methods for accurate size measurements in the nanometer scale. It details the importance of hydrodynamic properties, the principles of DLS, and its advantages over traditional methods such as TEM and SEM. Additionally, it highlights applications in protein analysis and the significance of maintaining sample integrity during measurement.





![Basic DLS Optics
[Alternatively 632nm,
558nm WLs are there
also]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dlssrou-240605060515-32e05f56/75/Dynamic_Light_Scattering_principle_and_application-pptx-10-2048.jpg)