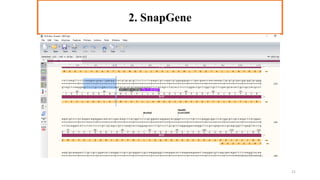
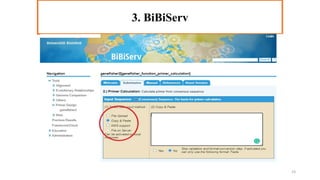
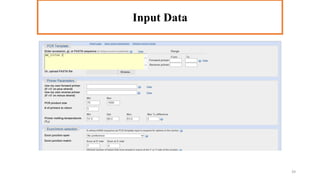
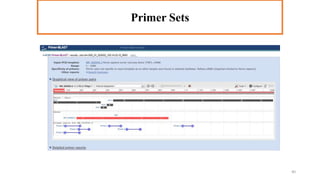
In silico PCR is a computational technique used to simulate and evaluate PCR reactions, allowing researchers to predict outcomes such as amplicon size and primer specificity without laboratory experiments. The process involves collecting DNA sequence information, selecting appropriate software tools, and analyzing primer sequences for effective experimental design. Key criteria for primer selection include length, GC content, specificity, and avoiding self-complementarity to ensure successful PCR results.