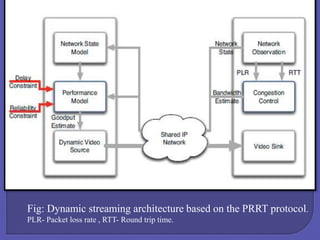
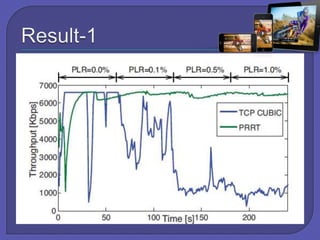
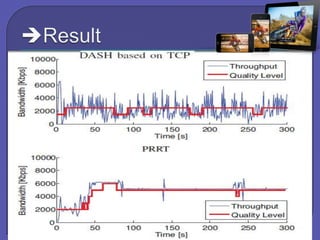
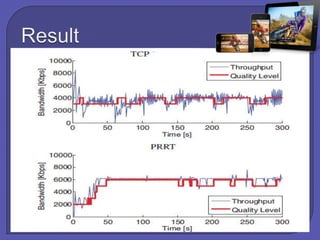
The document discusses internet and wireless technologies such as IEEE 802.11, HTTP, and Mobile IP. It describes experiments on dynamic media streaming over wireless networks using different transport protocols like TCP and PRRT. The experiments showed that TCP suffers from throughput variations on wireless networks leading to underutilization of bandwidth. In contrast, PRRT, which implements predictably reliable transport, was able to optimize bandwidth utilization for media streaming over wireless and mobile internet paths.







![
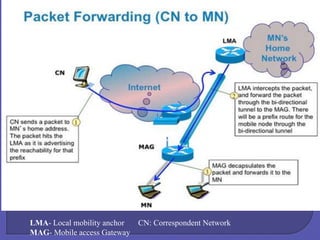
A protocol enhancements that allow transparent routing of IP
datagram's to mobile nodes in the Internet.
Each mobile node is always identified by its home
address, regardless of its current point of attachment to the
Internet. While situated away from its home.
[RFC-
2002]
A mobile node is associated with a care-of address, which
provides information about its current point of attachment to
the Internet.
The home agent sends datagram's destined for the mobile node
through a tunnel to the care- of address. After arriving at the
end of the tunnel, each datagram is then delivered to the mobile](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/naveen-wmc-140210033757-phpapp01/85/dynamic-media-streaming-over-wireless-and-ip-networks-13-320.jpg)