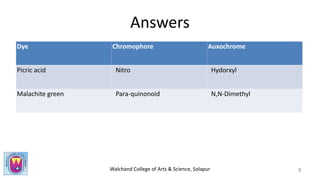
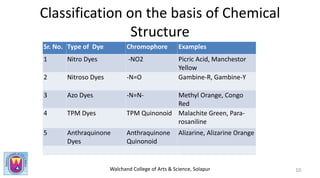
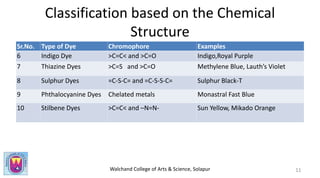
The document provides a comprehensive overview of dyes, including their definition, qualities, and classification. It details the chromophore-auxochrome theory and classifies dyes based on chemical structure and application methods. Additionally, it highlights various types of dyes with examples and characteristics.