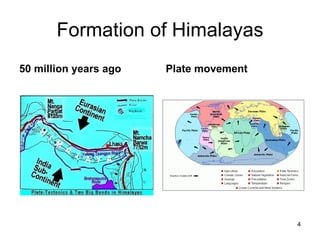
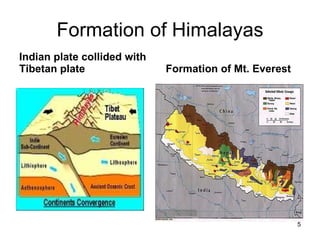
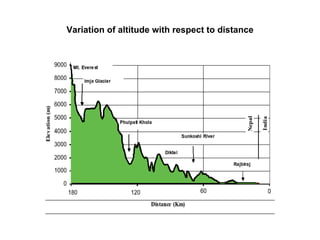
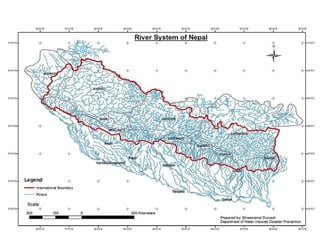
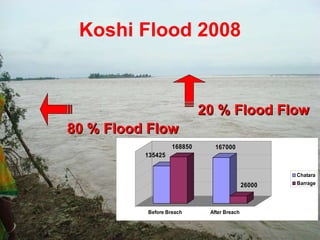
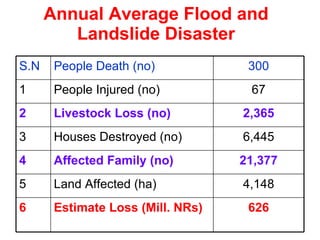
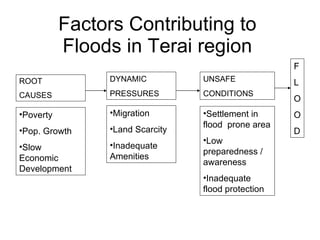
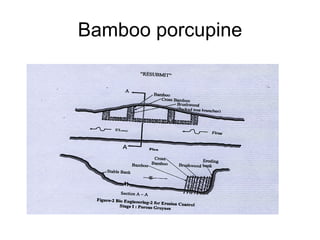
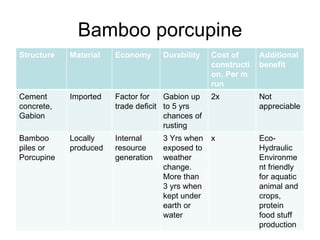
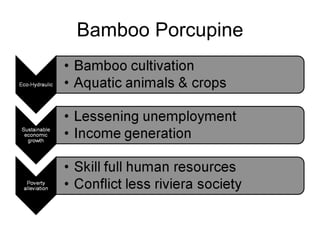
The document discusses water-induced disasters in Nepal such as glacial lake outburst floods, monsoon floods, and landslides. It notes that Nepal experiences high temporal and spatial variation in runoff and rainfall due to its geological formation in the Himalayas. On average, disasters in Nepal cause 300 deaths, 67 injuries, and over $600 million in losses annually. The document then highlights non-structural mitigation measures used in Nepal, including disaster preparedness maps and a bamboo porcupine riverbank protection innovation. It concludes by emphasizing the importance of networking to reduce disaster risks.