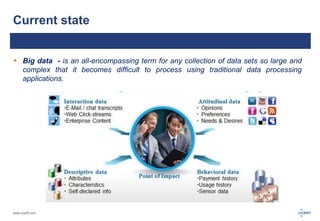
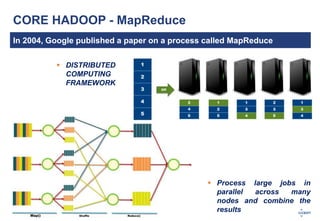
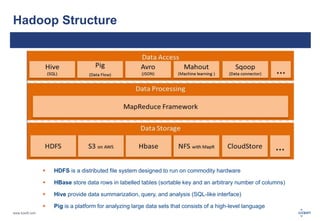
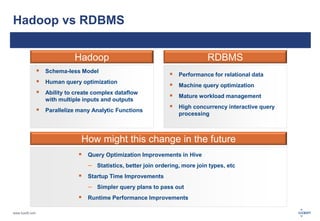
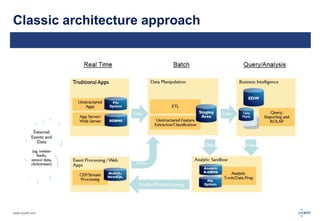
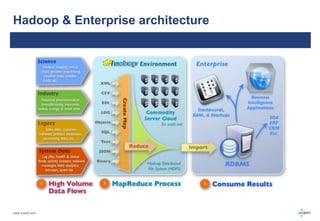
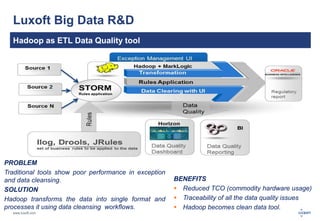
The document discusses big data and its challenges in processing, highlighting the limitations of traditional relational databases and the advantages of Hadoop as a solution. It outlines Hadoop's architecture, including key components like HDFS, HBase, and Hive, and contrasts it with RDBMS characteristics. The document emphasizes the future potential of query optimization and how Hadoop can improve data quality and management through its ETL capabilities.