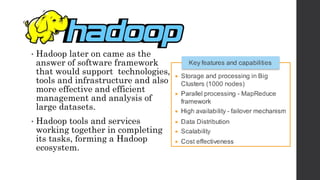
The document introduces big data, highlighting its characteristics, types, and the challenges of managing large datasets with traditional tools. It discusses the Hadoop ecosystem as a solution for processing and analyzing big data, with components like HDFS, MapReduce, and various data storage alternatives. Additionally, it explores the importance of big data analytics in business, particularly in social media and commerce, and poses questions to assess the need for big data solutions.