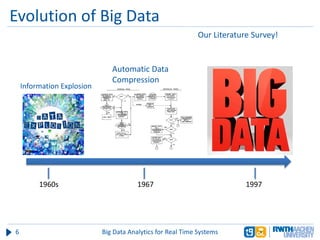
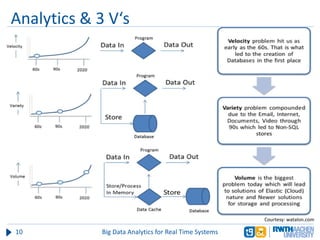
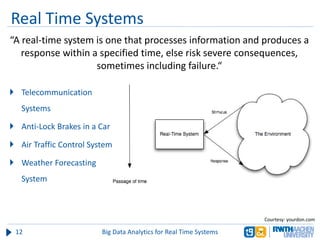
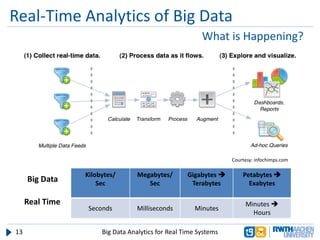
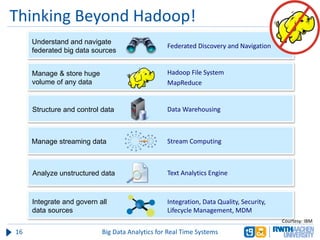
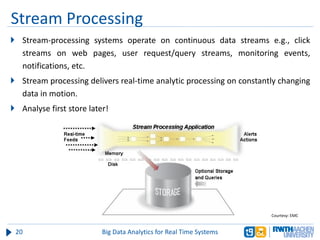
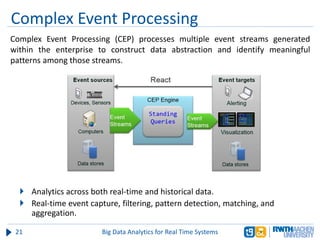
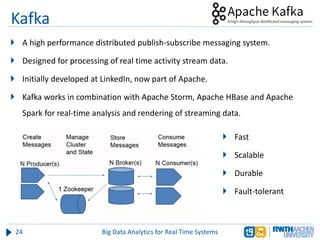
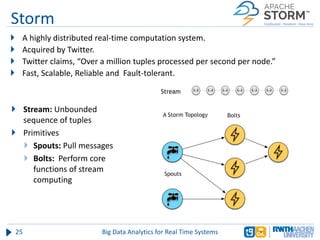
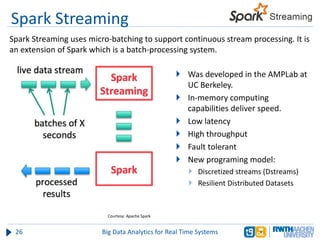
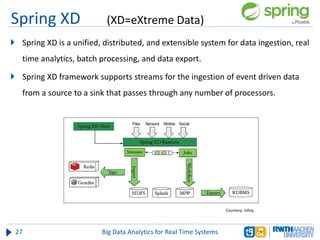
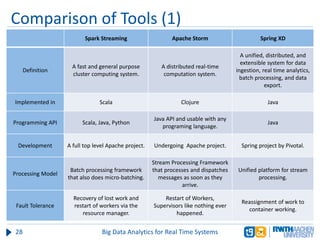
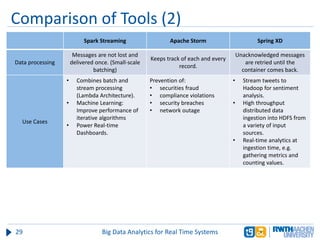
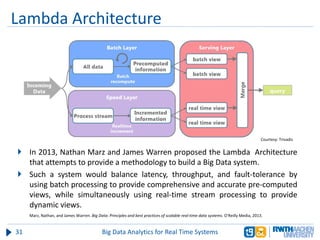
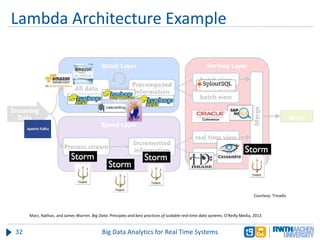
The document discusses big data analytics in real-time systems, highlighting its importance in uncovering patterns and trends from extensive datasets. It addresses challenges such as the need for sub-second response times and the limitations of traditional relational databases, while exploring various technologies and tools for real-time analytics, including stream processing and complex event processing. Use cases in sectors like healthcare, finance, and retail illustrate the practical application and future potential of these analytics.