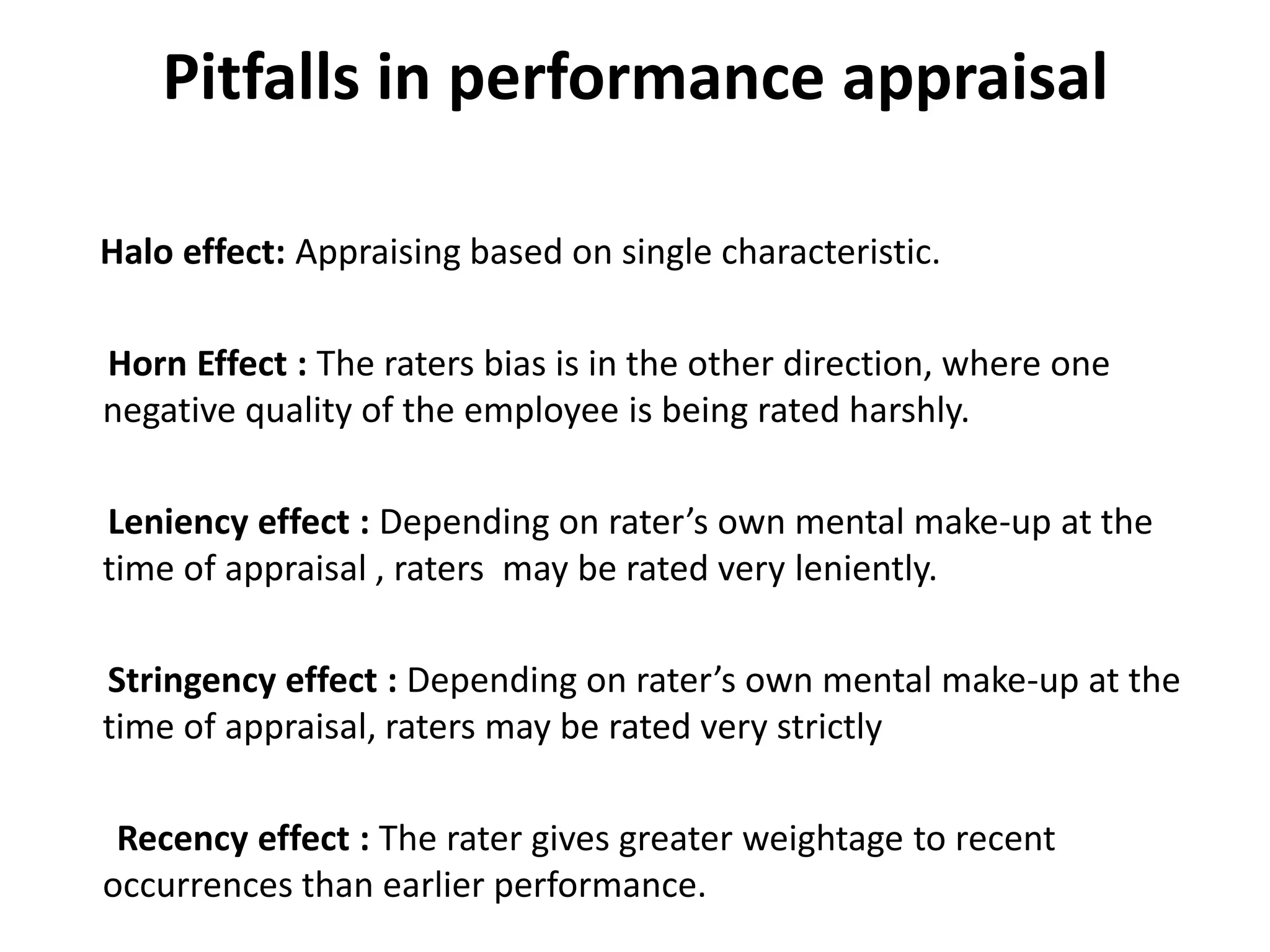
This document discusses performance appraisals, including definitions, objectives, processes, methods, and pitfalls. It defines performance appraisal as a formal assessment and rating of employees by managers, usually annually. The objectives are to set performance standards, evaluate performance, identify training needs, reward performance, and improve performance. Key methods discussed are management by objectives, 360-degree feedback, graphic rating scales, and behaviorally anchored rating scales. Pitfalls addressed include halo effects, leniency effects, and stereotyping.