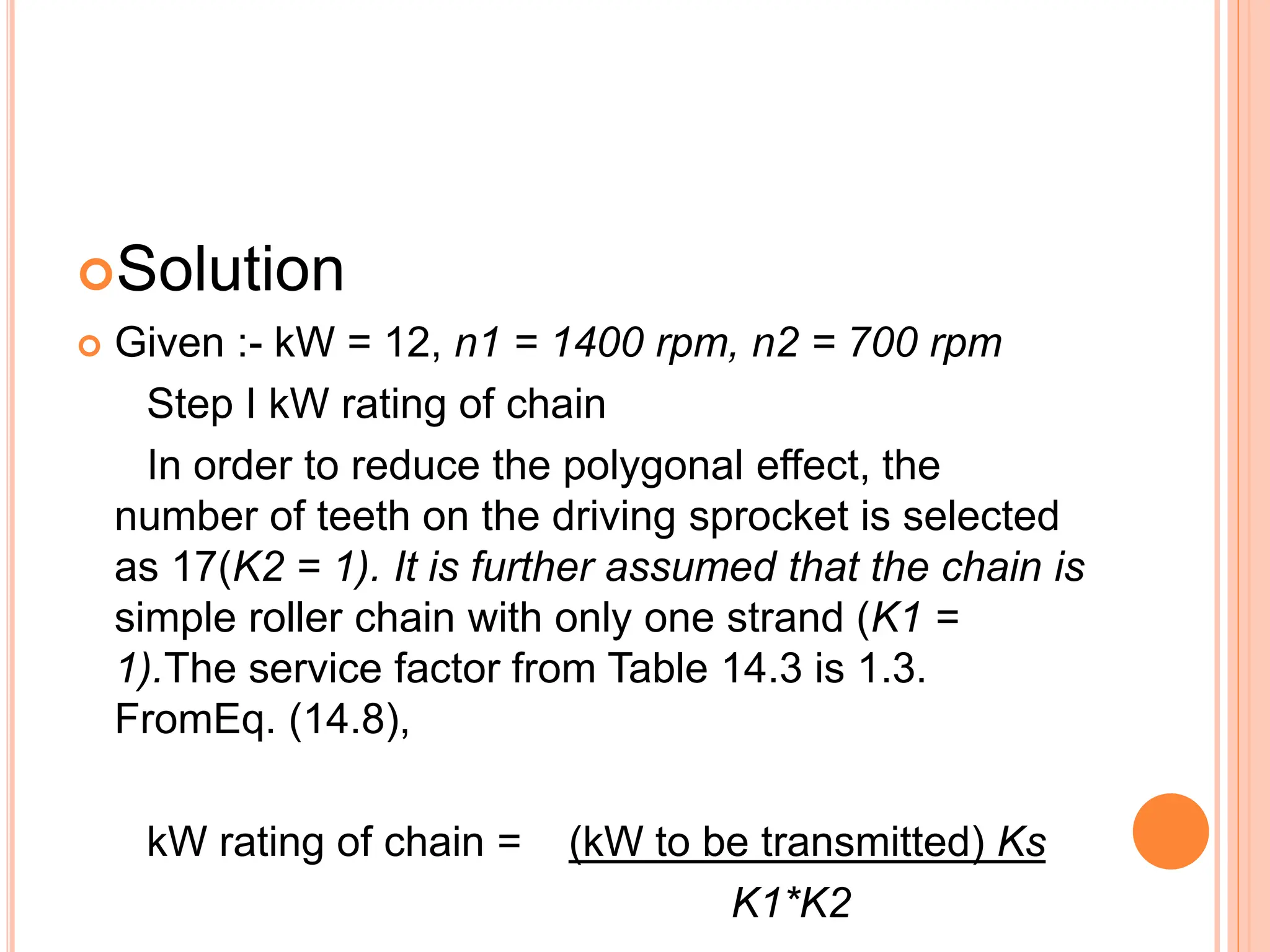
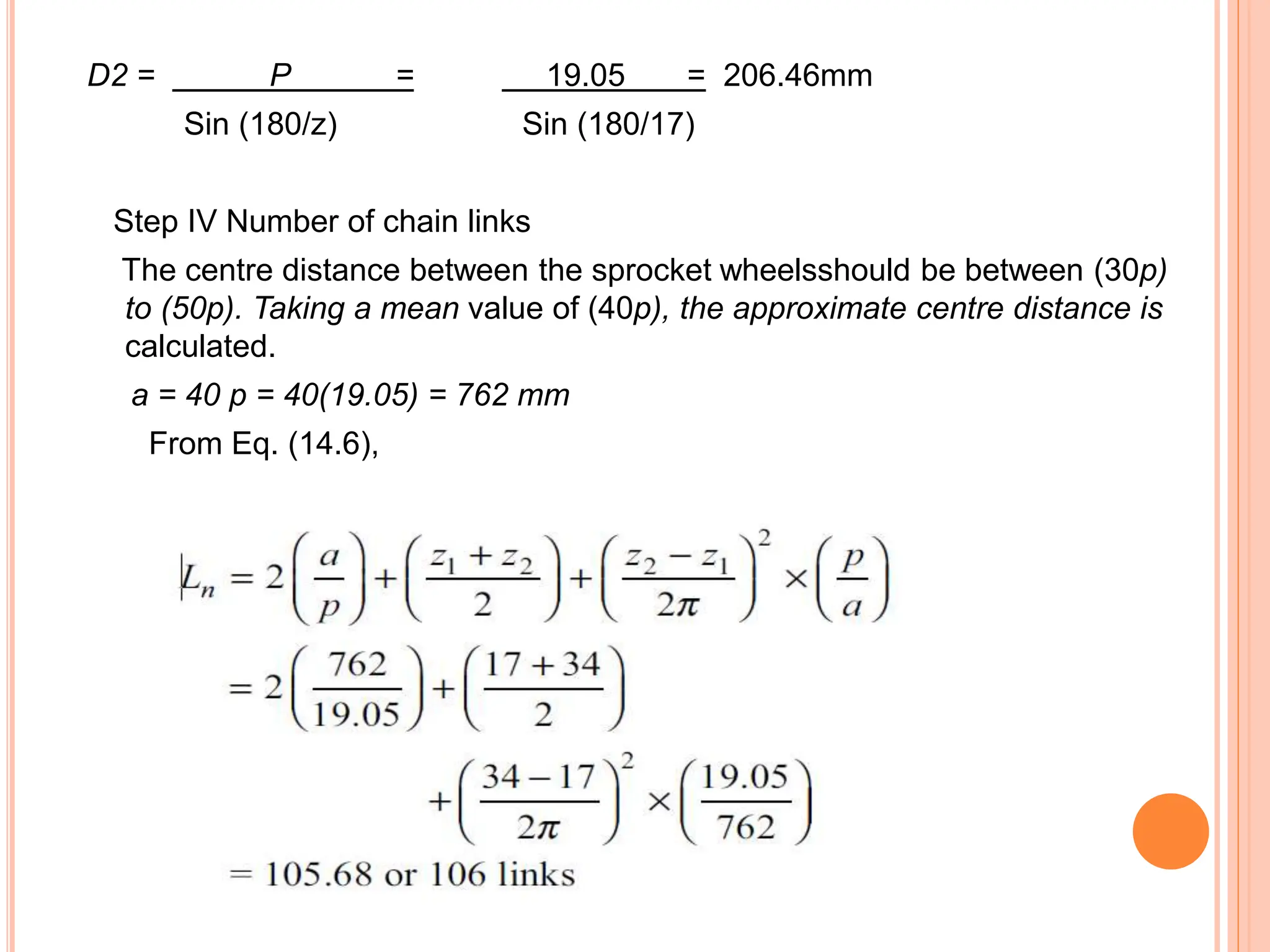
The document outlines a presentation on chain drives, detailing their introduction, types, advantages, disadvantages, and applications. It provides a specific design example for connecting an electric motor to a centrifugal pump using a roller chain, including calculations for dimensions and center distance. The principles and methods for selecting the appropriate chain, as well as a manufacturer’s catalog, are also discussed.