The document outlines the agenda for a meetup focused on data science, design, and technology, featuring a talk by Dr. Lennart Nacke on gameful interaction design and games user research. It discusses various aspects of user experience (UX) in gaming and the importance of engagement through gameful design elements. The document also highlights upcoming events and opportunities for individuals interested in speaking or participating in related activities.





























![BIOMETRIC STORYBOARDS
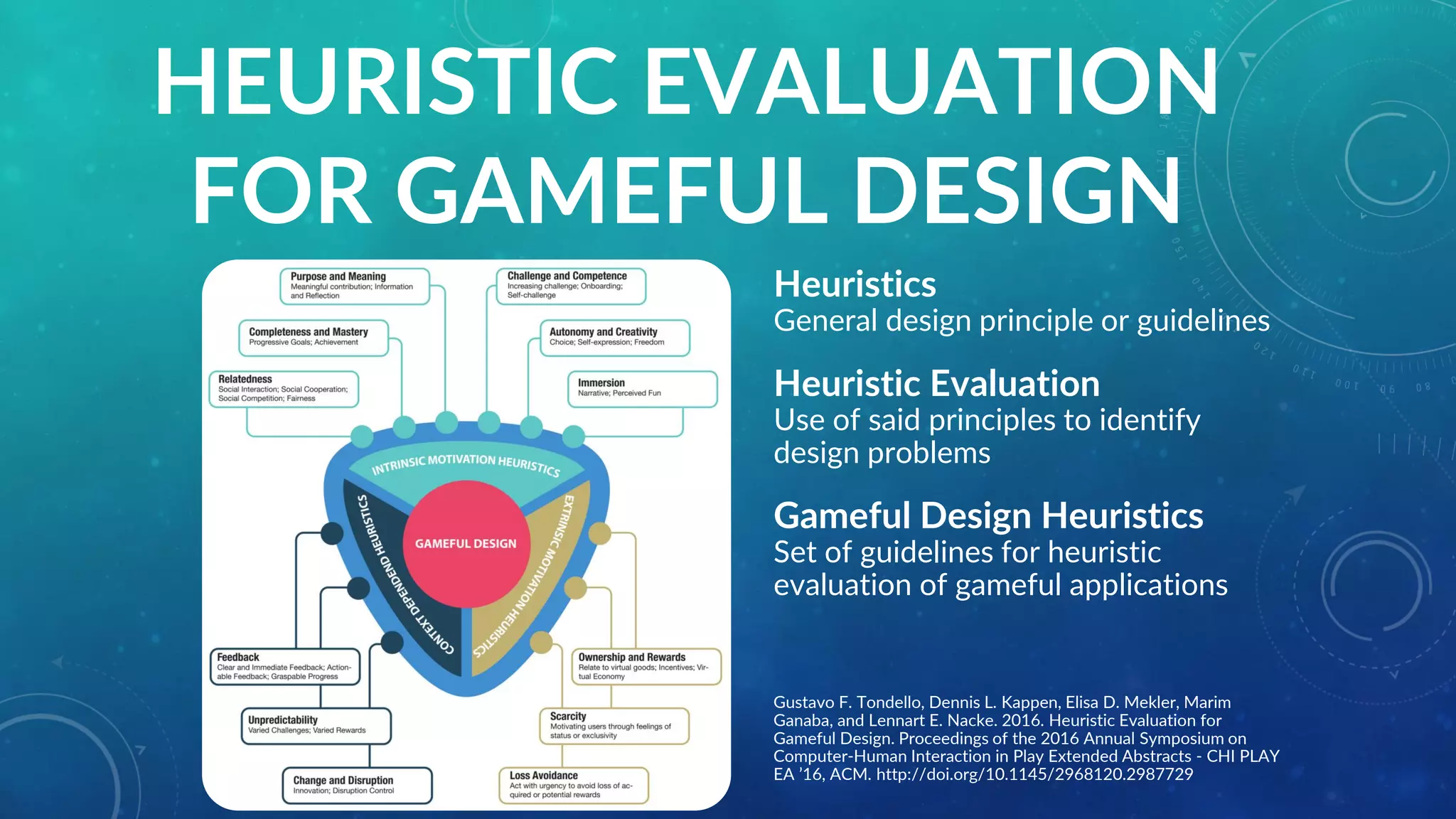
• Comparison study (N=24) of different player testing
approaches
• A single User Experience (UX) graph
• Intended UX
• Actual UX
• Players rated the gameplay quality of the BioSt User Test (UT)
game and fun and visuals of both UT games significantly higher
than the Non-UT game
• “The BioSt UT team had the most significant changes in their
version […] they […] polish existing mechanics.”
Pejman Mirza-Babaei, Lennart E. Nacke, John Gregory, Nick Collins, and Geraldine Fitzpatrick. 2013. How does it play better?: exploring user
testing and biometric storyboards in games user research. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems
(CHI '13). ACM, New York, NY, USA, 1499-1508. DOI=10.1145/2470654.2466200](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dsdtmeetupfebruary2018-190219181206/75/DSDT-Meetup-February-2018-32-2048.jpg)




