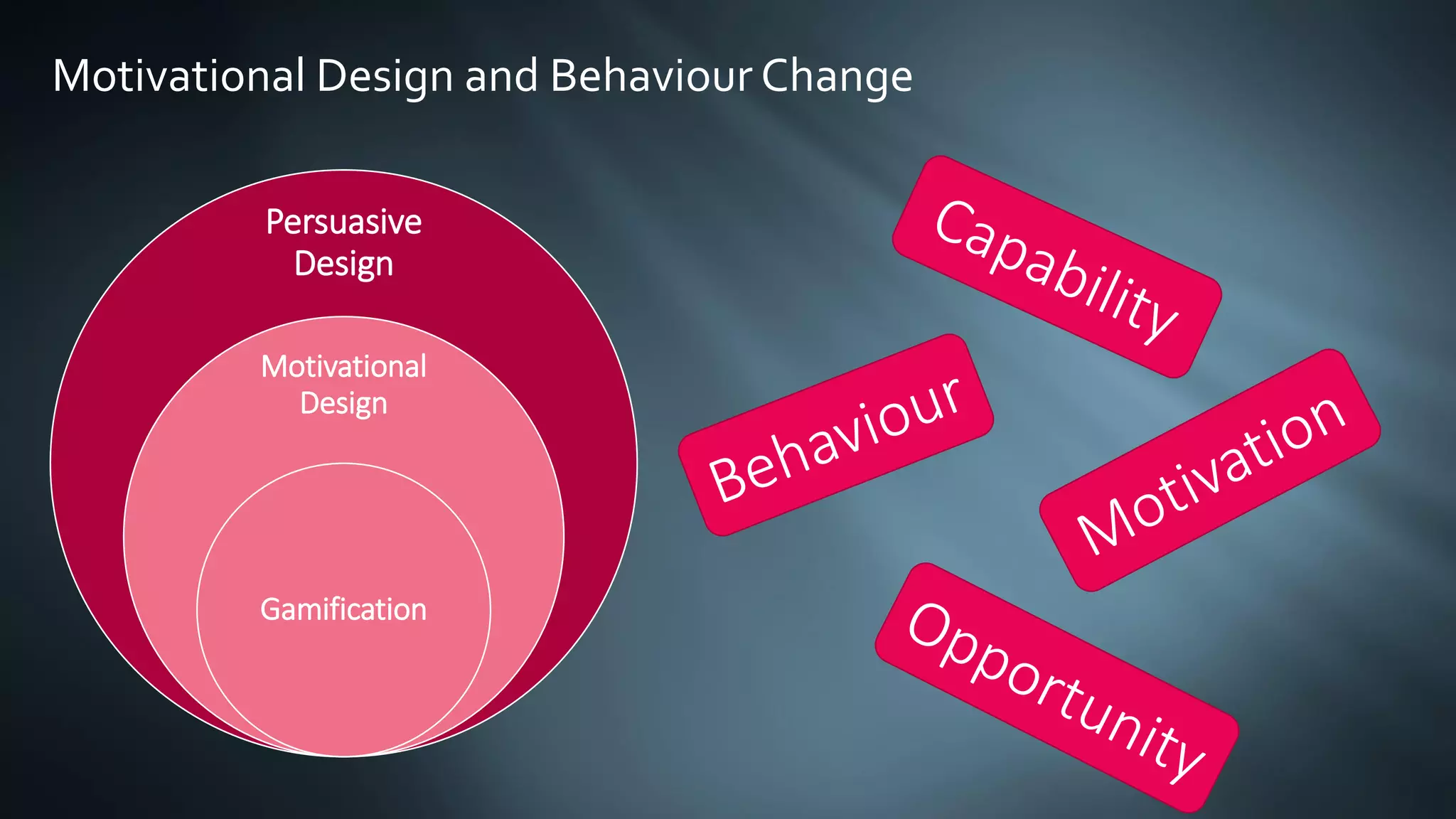
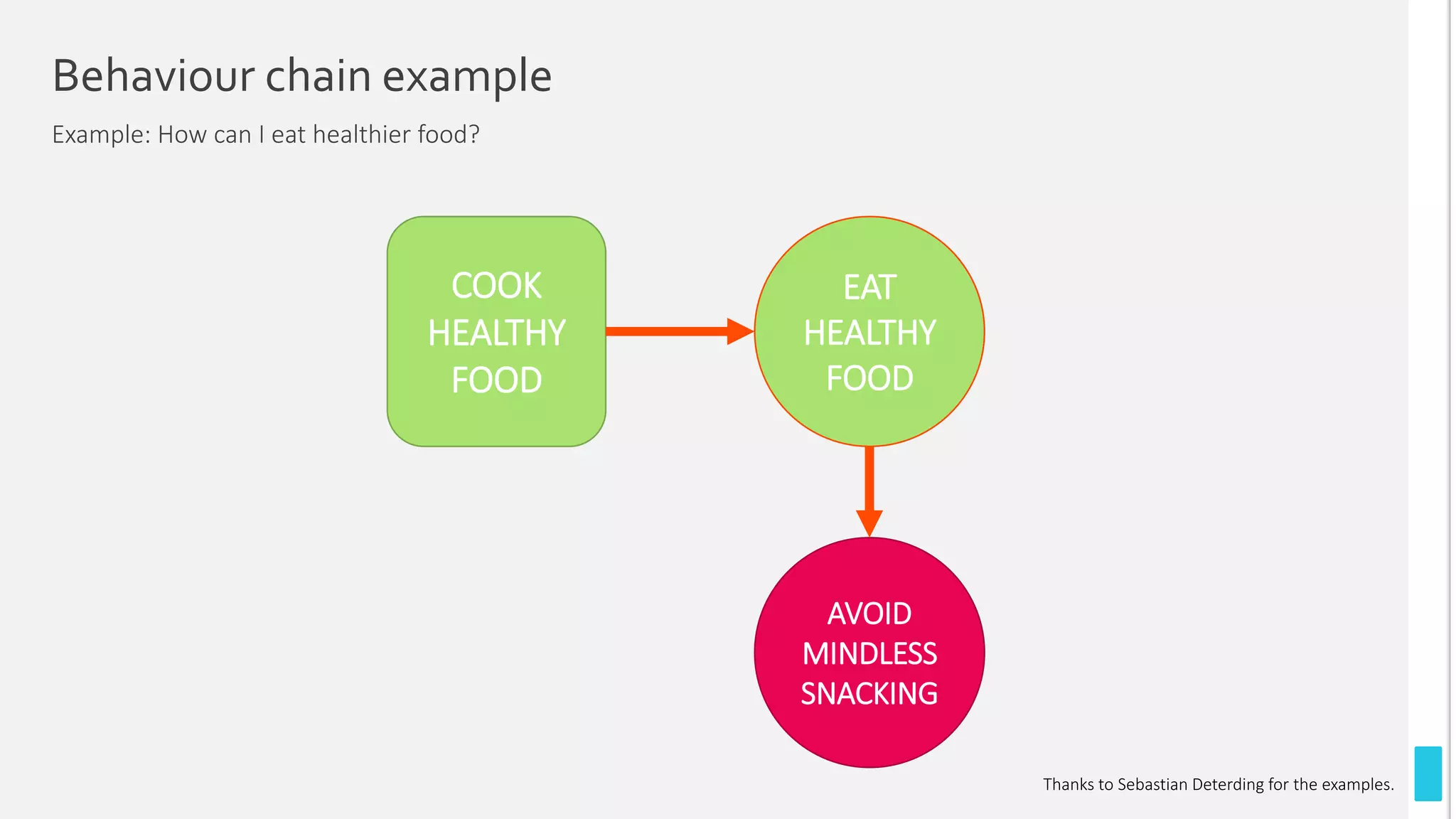
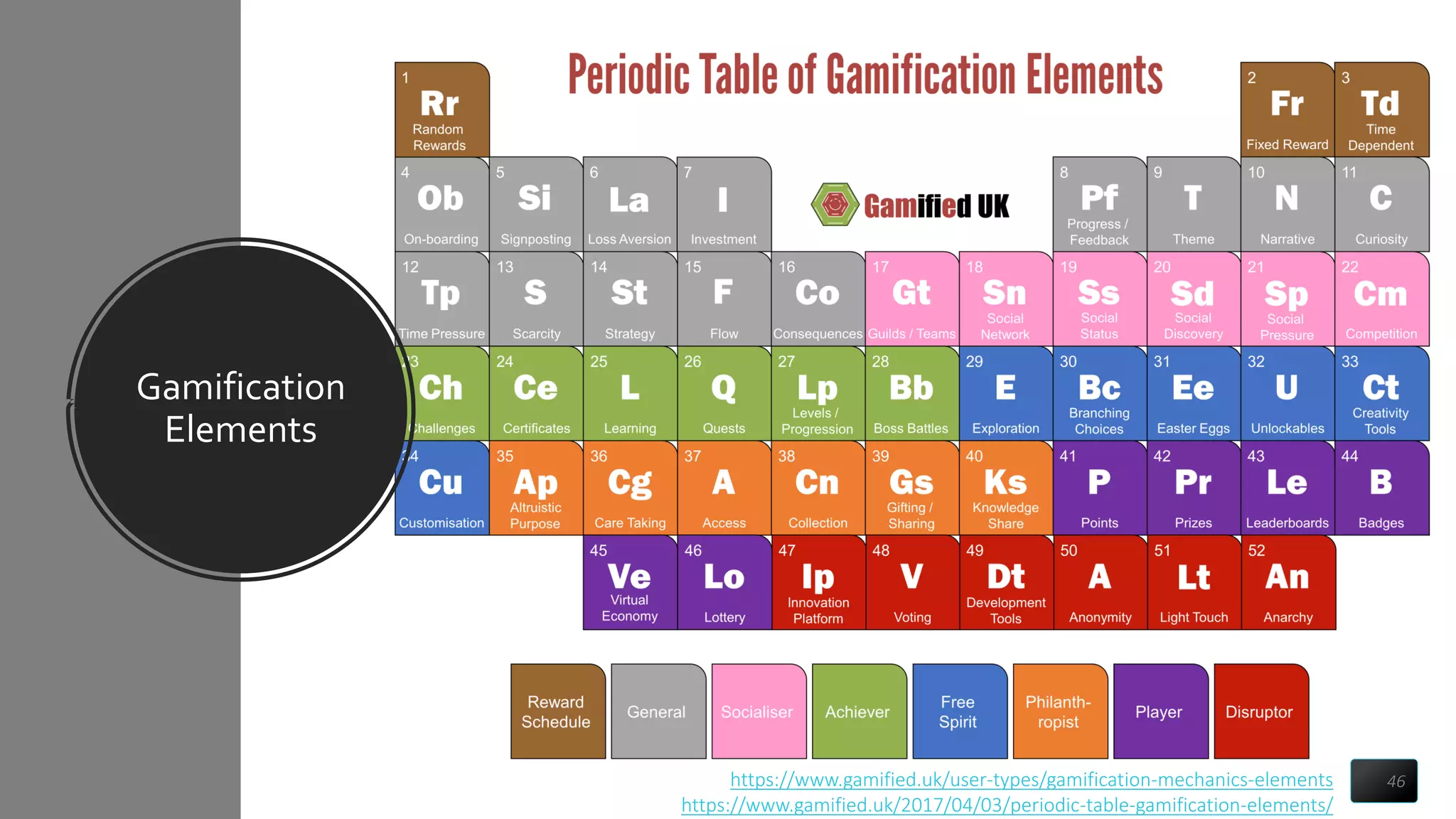
The document introduces gamification and game thinking, which use game design elements to enhance user engagement and solve motivational challenges. It outlines three main approaches: game thinking as a thought model, a user journey, and a design process, emphasizing the importance of understanding user needs and behavior change. It also highlights the stages of the user journey, focusing on building a core learning loop and creating repeatable activities to foster user mastery.