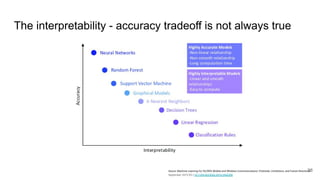
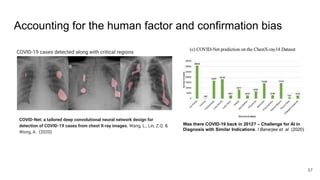
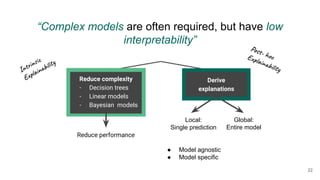
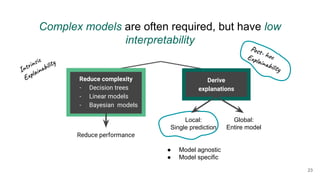
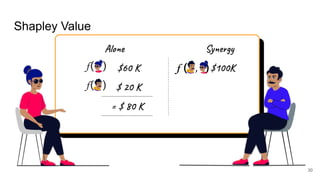
The document outlines the agenda for a Data Science, Design, and Technology meetup held on July 21, 2021, which includes topics on explainable AI and machine learning practitioners. It emphasizes the importance of interpretability in machine learning models, discussing tools and considerations for providing explanations to users. Key points include the need for collaboration with domain experts and proper data management to enhance model understanding and trust.










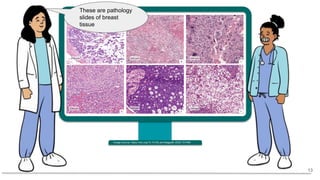
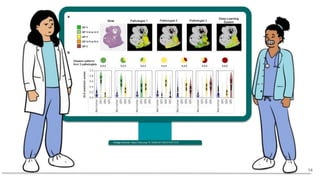











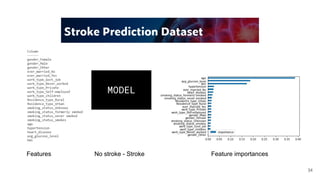
![35
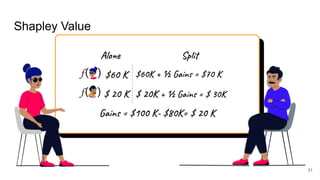
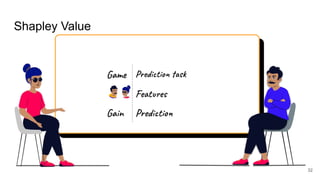
SHAP: SHapley Additive exPlanations
import shap
patient_id = 10
patient = X.loc[[patient_id]]
# %% Create SHAP explainer
explainer = shap.TreeExplainer(model)
# Calculate shapley values for patient
shap_values = explainer.shap_values(patient)
Age = 67
Sex = Male
[...]
BMI = 36
Gluc= 190.7
MODEL Prediction: Stroke](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dsdtmeetup202107-210723115717/85/DSDT-meetup-July-2021-35-320.jpg)
![36
SHAP: SHapley Additive exPlanations
# %% Visualize force plot
shap.initjs()
shap.force_plot(explainer.expected_value[1], shap_values[1], patient)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dsdtmeetup202107-210723115717/85/DSDT-meetup-July-2021-36-320.jpg)
![37
SHAP: SHapley Additive exPlanations
# %% Visualize force plot
shap.initjs()
shap.force_plot(explainer.expected_value[1], shap_values[1], patient)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dsdtmeetup202107-210723115717/85/DSDT-meetup-July-2021-37-320.jpg)
![38
SHAP: SHapley Additive exPlanations
# %% Visualize decision plot
shap.decision_plot(explainer.expected_value[1],shap_values[1],patient)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dsdtmeetup202107-210723115717/85/DSDT-meetup-July-2021-38-320.jpg)

![LIME: Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanation
instance to explain
Black-box model’s complex decision function
Source: Why Should I Trust You?": Explaining the Predictions of Any Classifier
arXiv:1602.04938 [cs.LG]
40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dsdtmeetup202107-210723115717/85/DSDT-meetup-July-2021-40-320.jpg)
![LIME: Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanation
Source: Why Should I Trust You?": Explaining the Predictions of Any Classifier
arXiv:1602.04938 [cs.LG]
Black-box model’s complex decision function
41](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dsdtmeetup202107-210723115717/85/DSDT-meetup-July-2021-41-320.jpg)
![LIME: Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanation
Source: Why Should I Trust You?": Explaining the Predictions of Any Classifier
arXiv:1602.04938 [cs.LG]
Surrogate model to explain locally
42](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dsdtmeetup202107-210723115717/85/DSDT-meetup-July-2021-42-320.jpg)

![LIME: Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanation
44
Source: arXiv:1602.04938 [cs.LG]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dsdtmeetup202107-210723115717/85/DSDT-meetup-July-2021-44-320.jpg)
![Explaining image data: LIME
45
Source: arXiv:1602.04938 [cs.LG]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dsdtmeetup202107-210723115717/85/DSDT-meetup-July-2021-45-320.jpg)

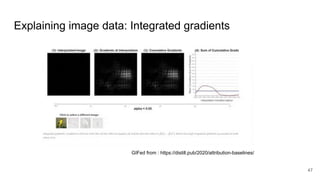

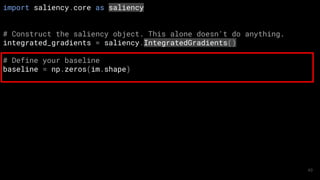
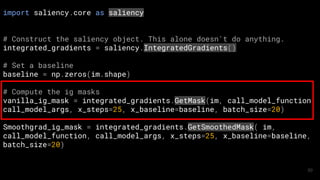
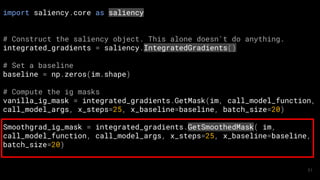


![# Construct the saliency object
xrai_object = saliency.XRAI()
# Compute XRAI attributions with default parameters
xrai_attributions = xrai_object.GetMask(im, call_model_function, call_model_args, batch_size=20)
####
# Show most salient 30% of the image
mask = xrai_attributions > np.percentile(xrai_attributions, 70)
im_mask = np.array(im_orig)
im_mask[~mask] = 0
ShowImage(im_mask, title='Top 30%', ax=P.subplot(ROWS, COLS, 3))
54](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dsdtmeetup202107-210723115717/85/DSDT-meetup-July-2021-54-320.jpg)