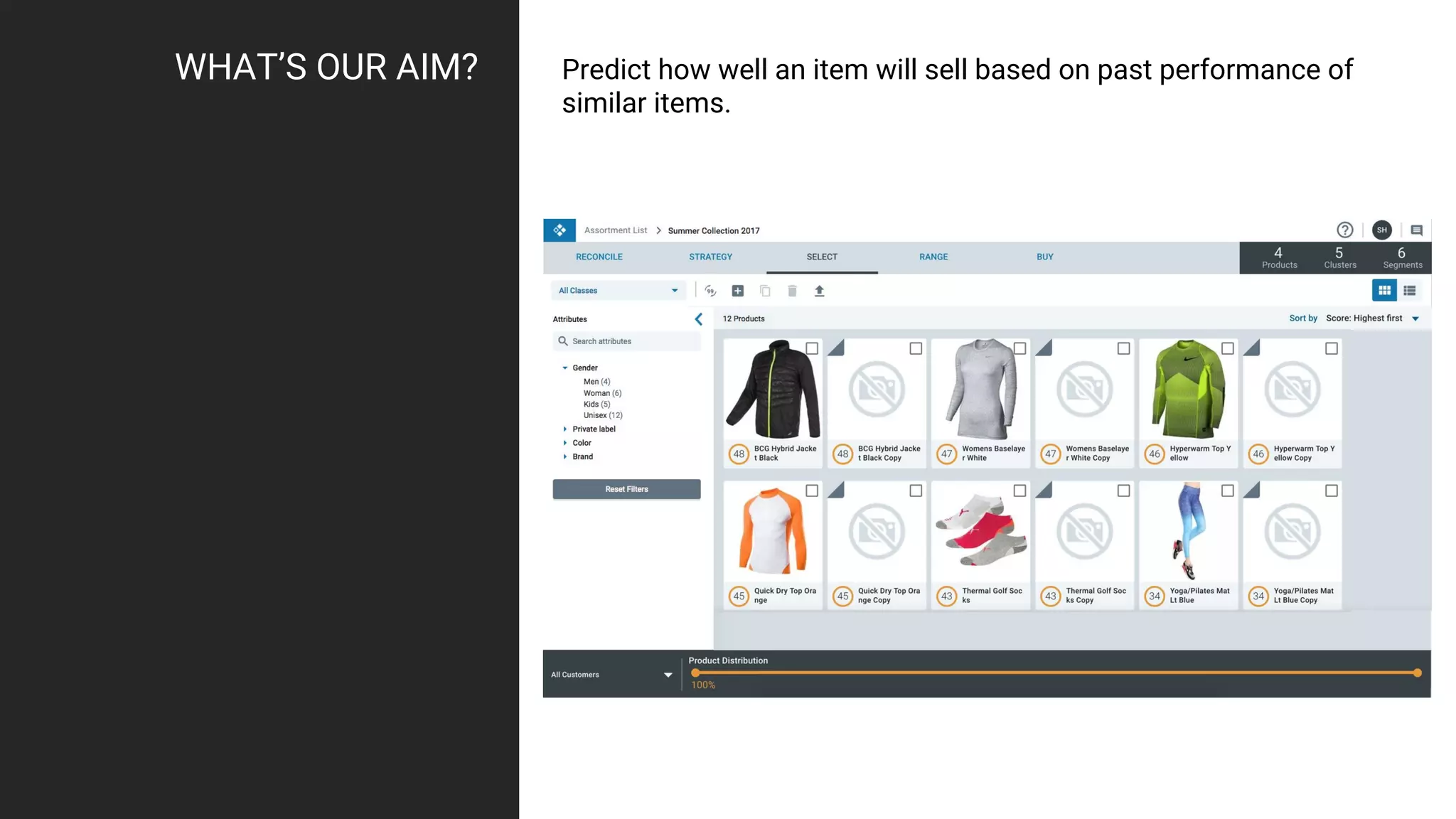
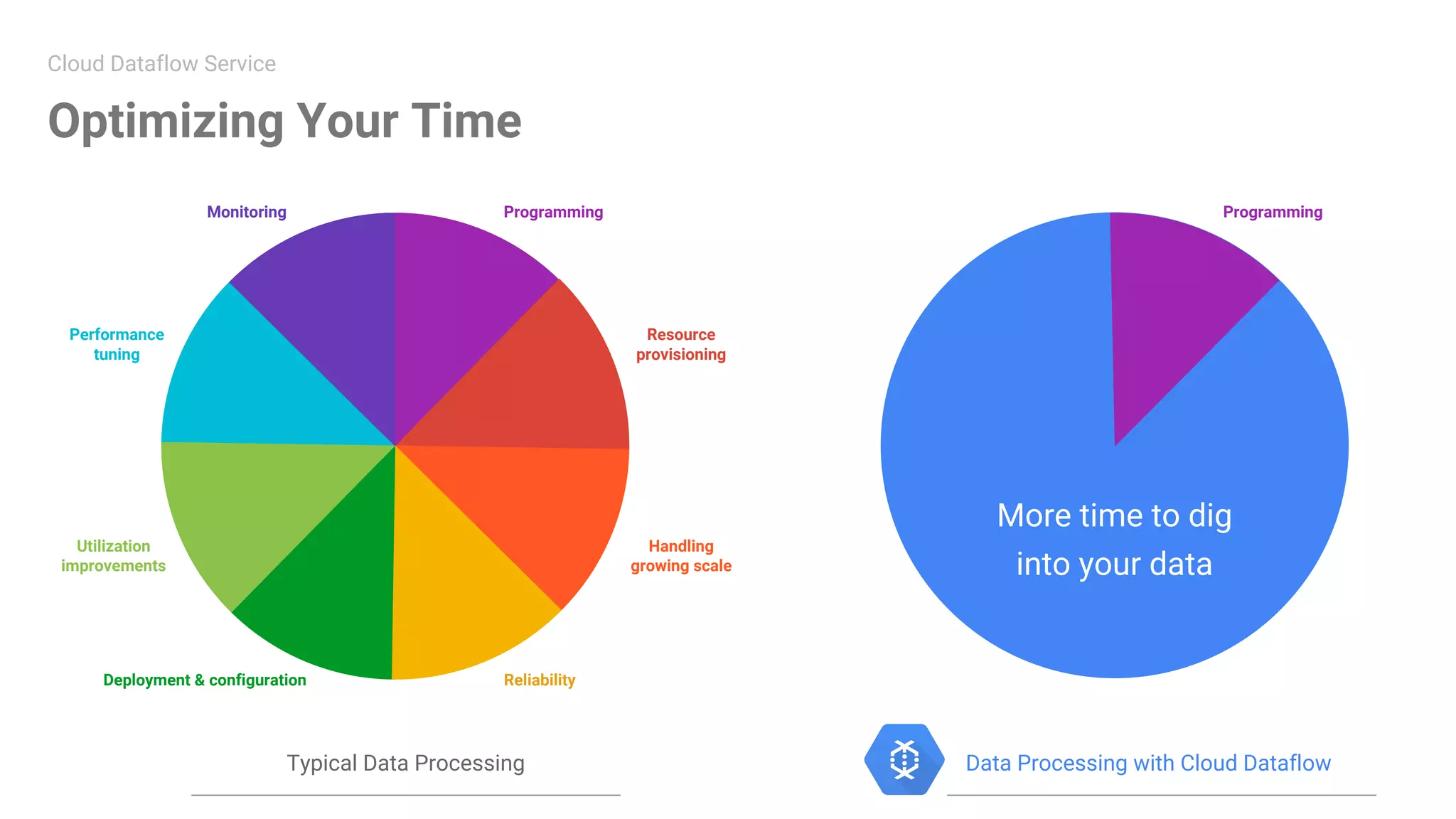
The document summarizes a meetup on data streaming and machine learning with Google Cloud Platform. The meetup consisted of two presentations:
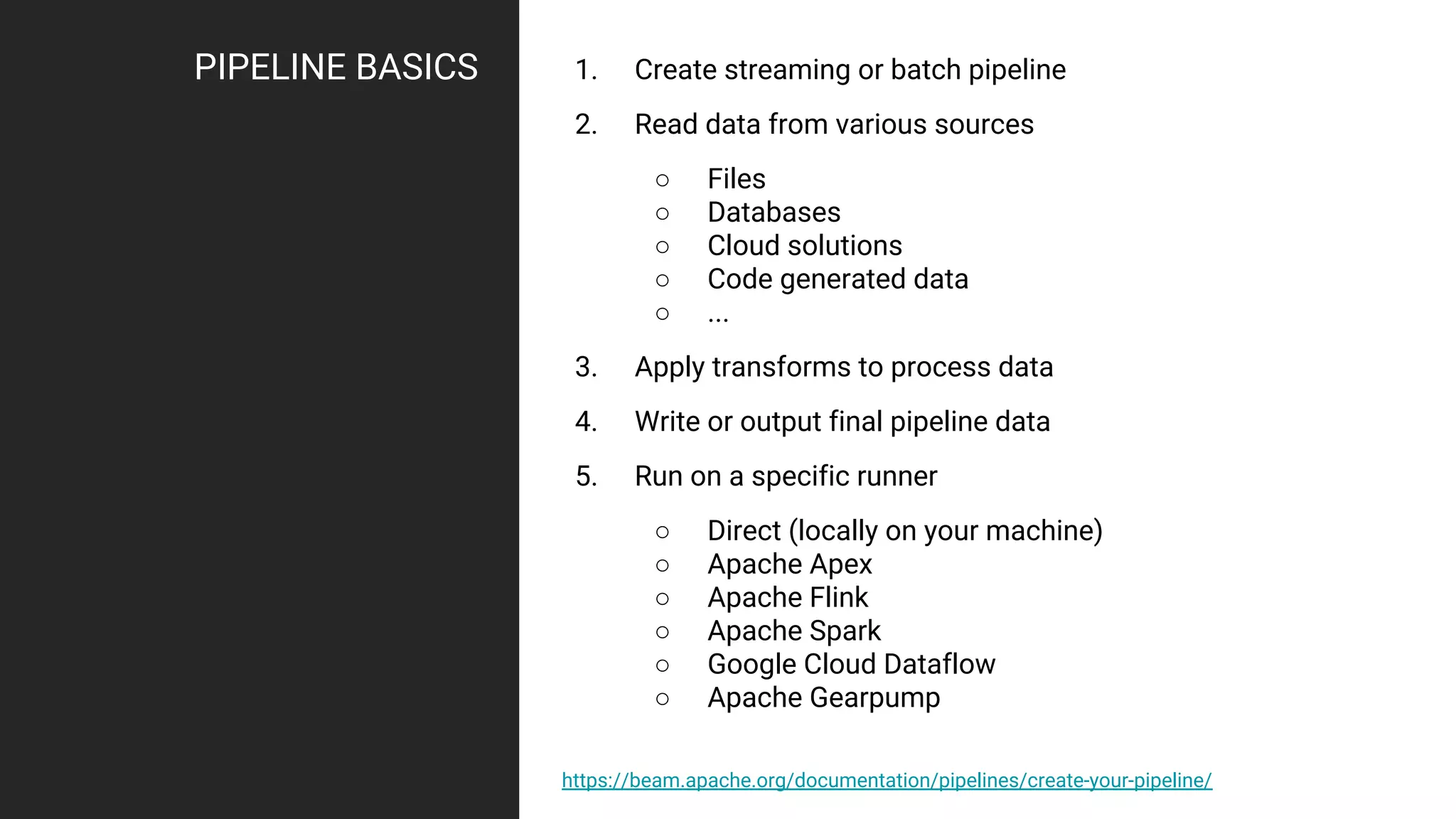
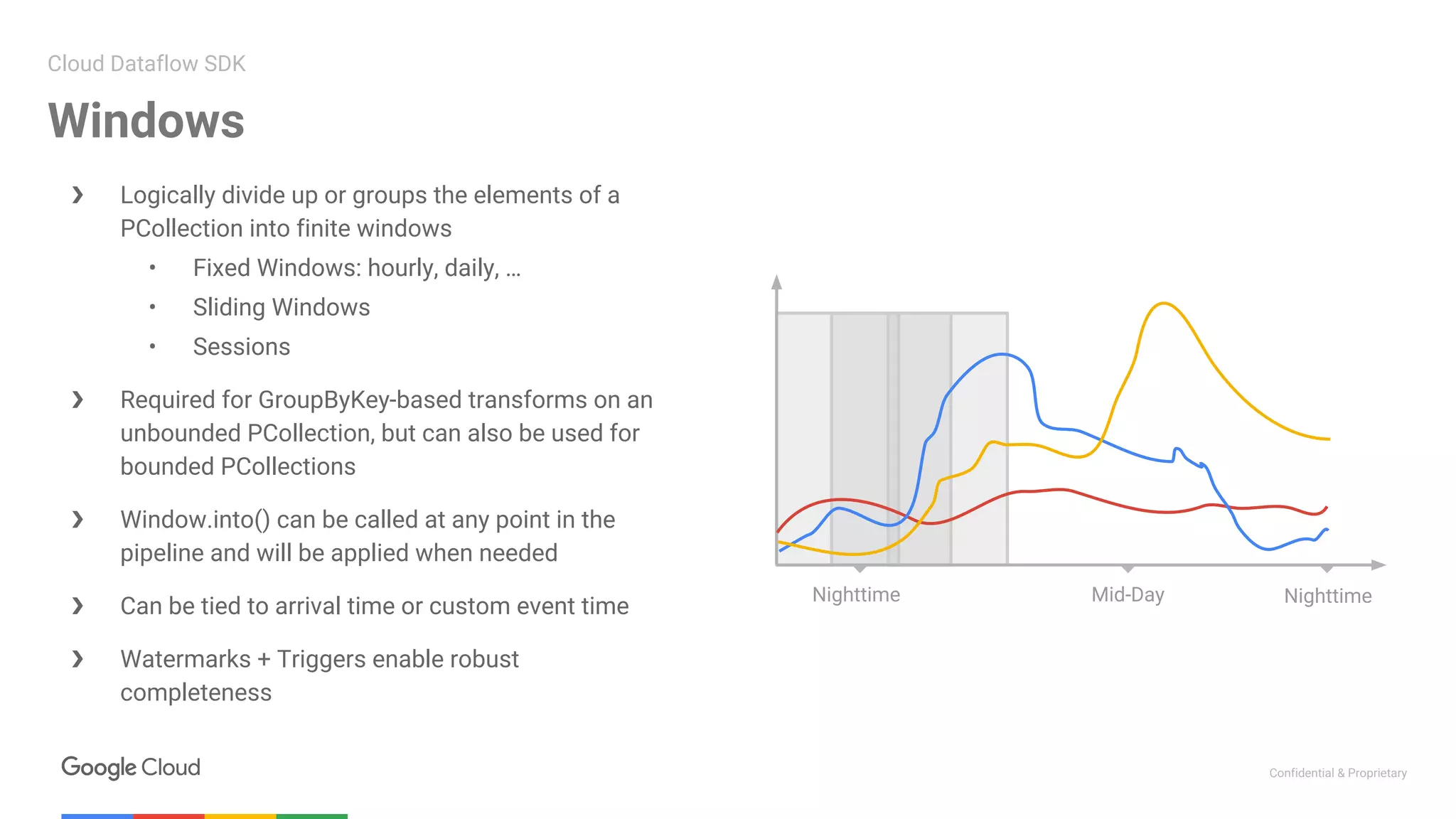
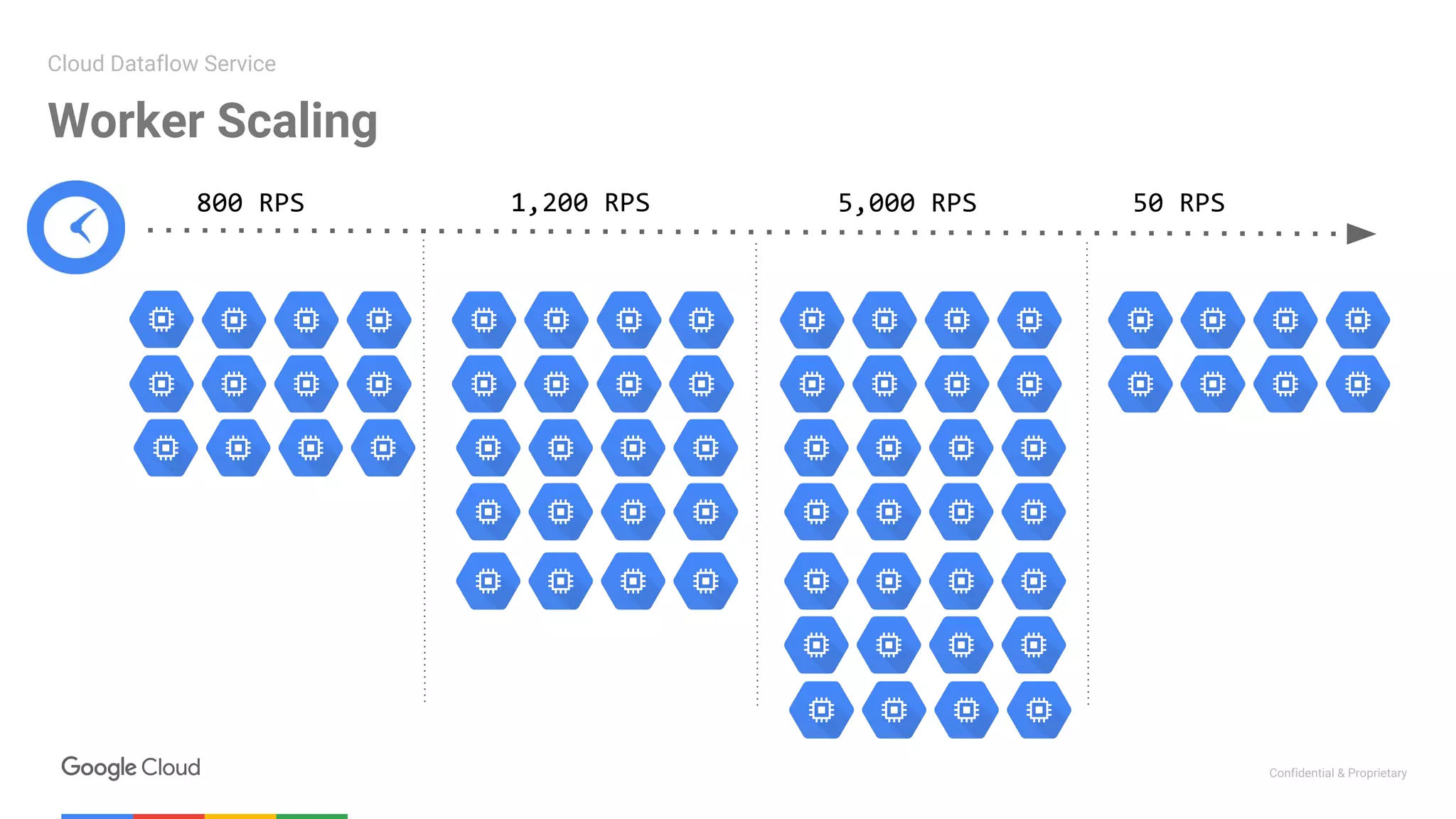
1. The first presentation discussed using Apache Beam (Dataflow) on Google Cloud Platform to parallelize machine learning training for improved performance. It showed how Dataflow was used to reduce training time from 12 hours to under 30 minutes.
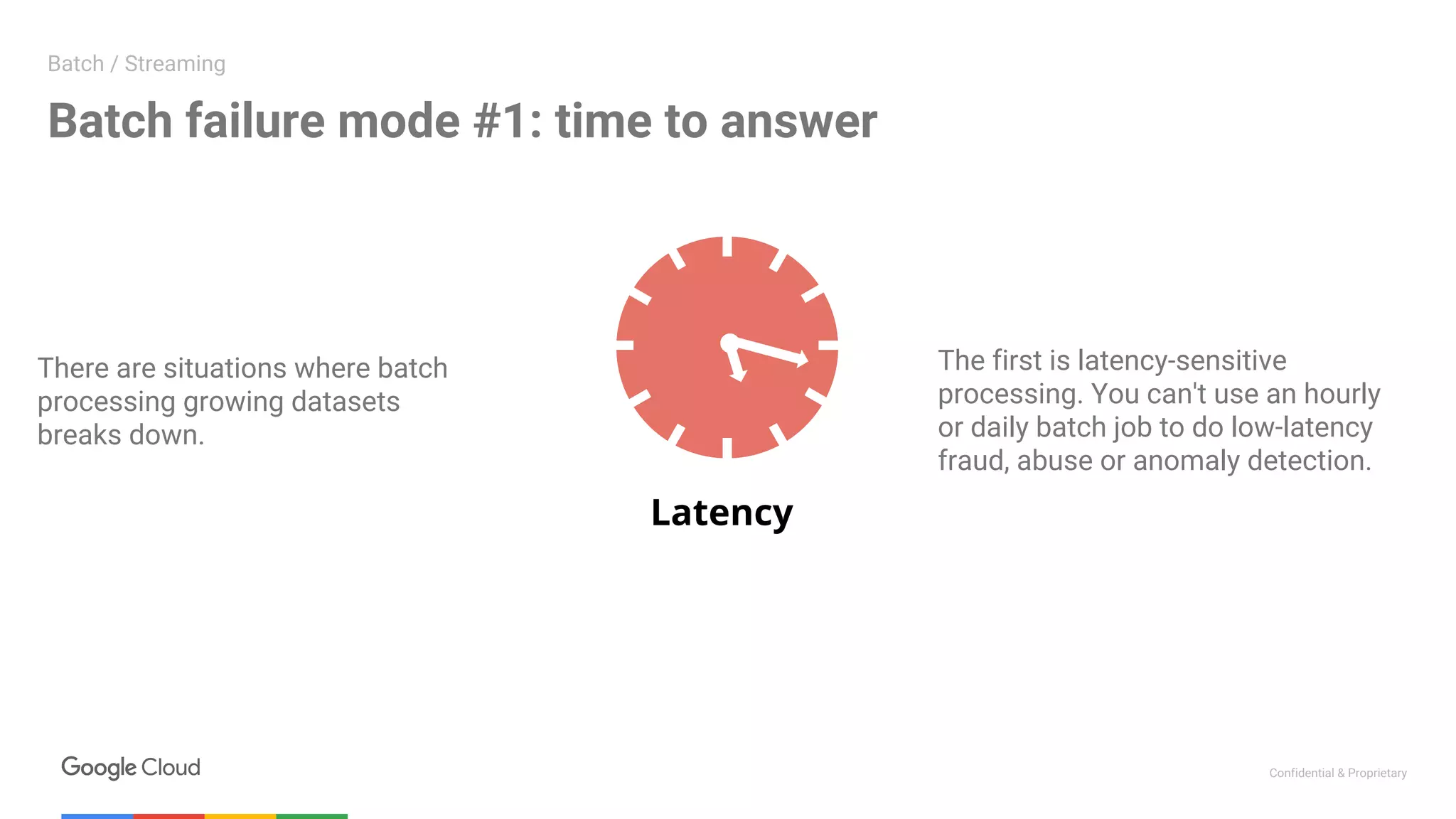
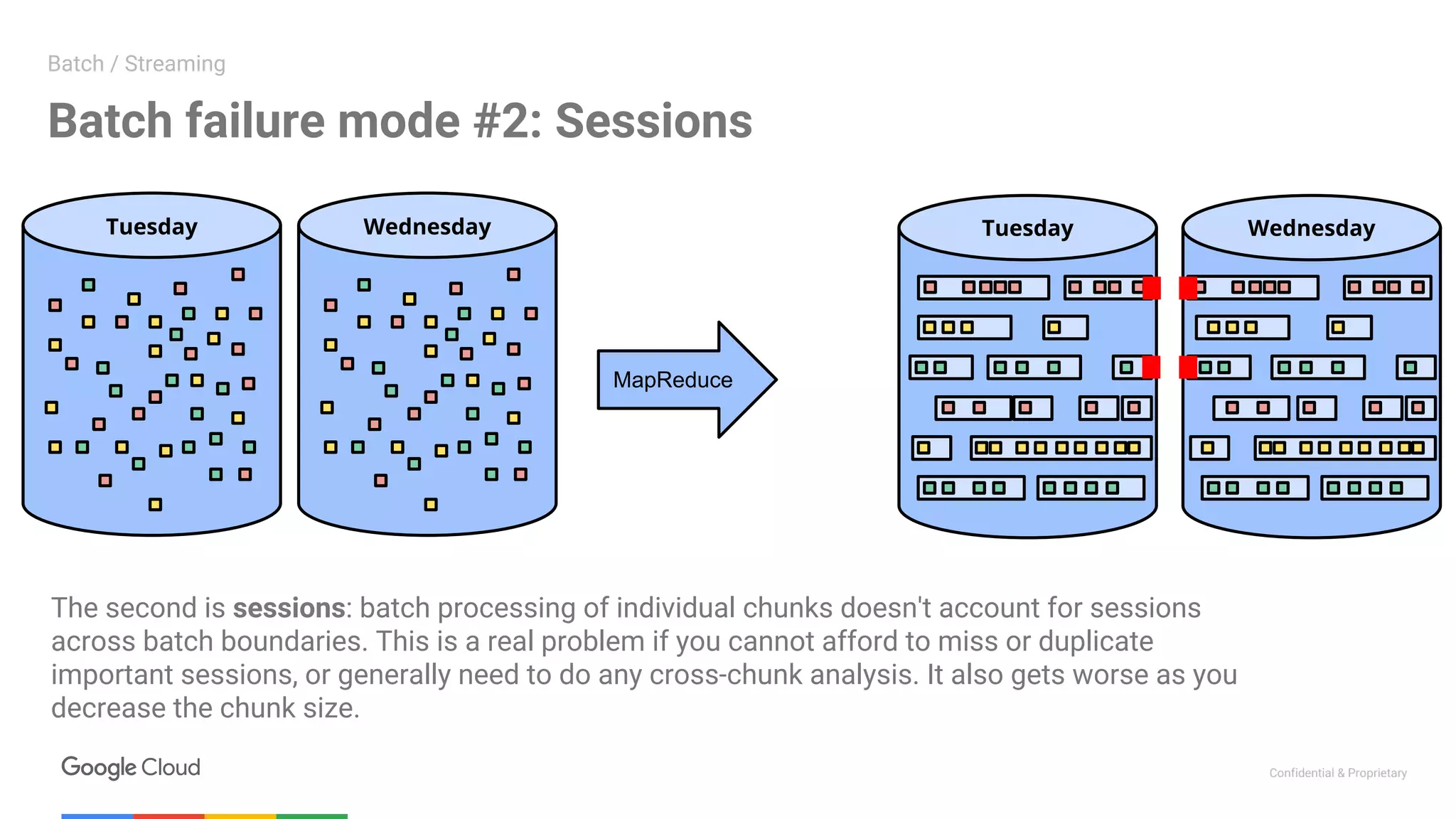
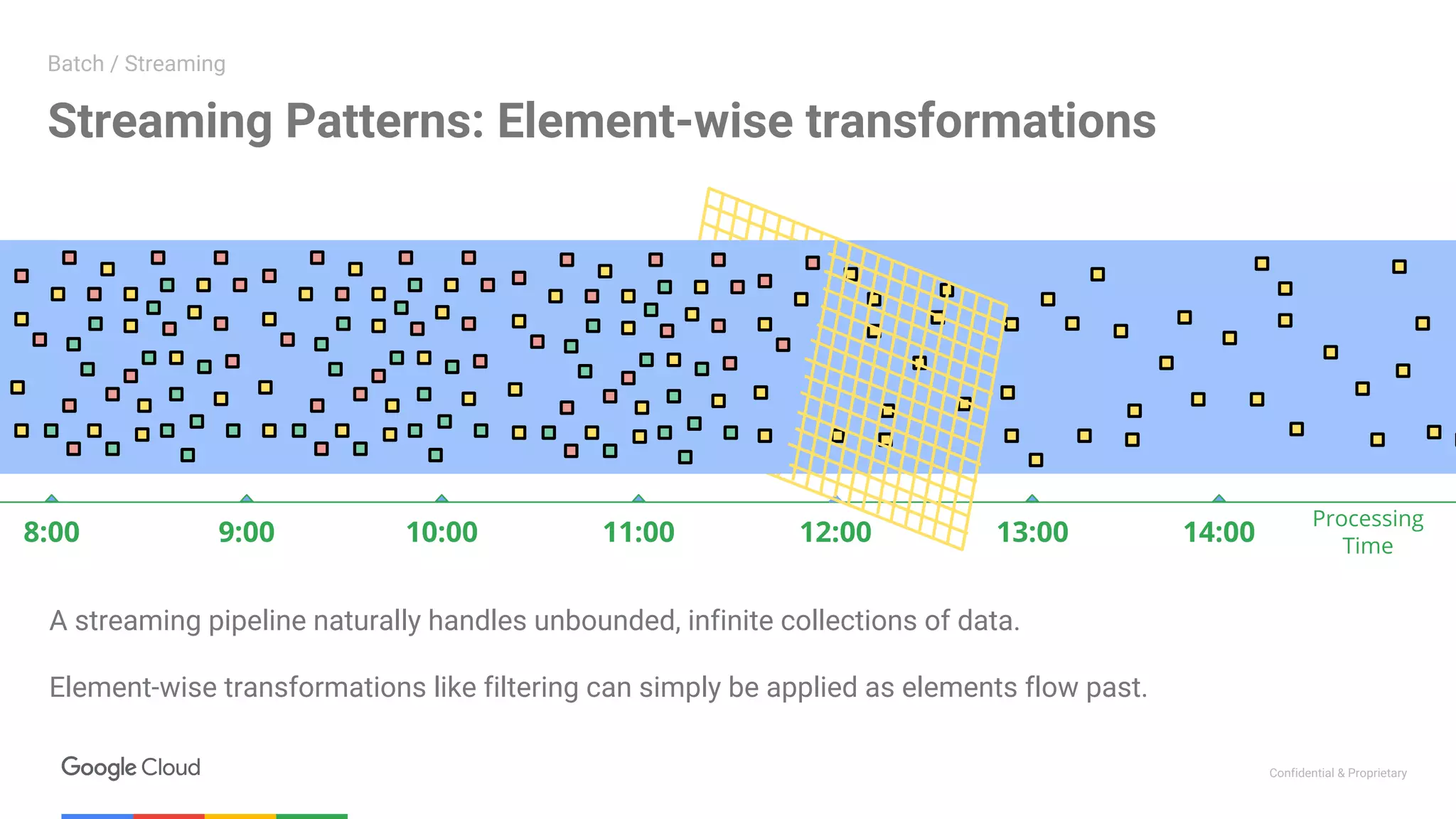
2. The second presentation demonstrated building a streaming pipeline for sentiment analysis on Twitter data using Dataflow. It covered streaming patterns, batch vs streaming processing, and a demo that ingested tweets from PubSub and analyzed them using Cloud NLP API and BigQuery.