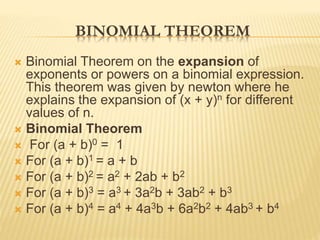
This document discusses the topic of combinatorics. It defines combinatorics as a branch of mathematics concerned with counting problems, arrangements, and derangements. The two main rules in combinatorics are the sum rule, which is used when events cannot occur simultaneously, and the product rule, which is used when events are independent. Examples of applying the sum and product rules to problems involving selecting students and choosing outfits are provided. The document also covers permutations, combinations, the binomial theorem, and binomial coefficients.