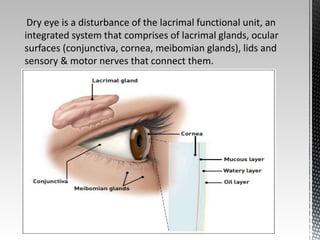
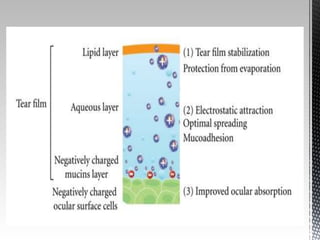
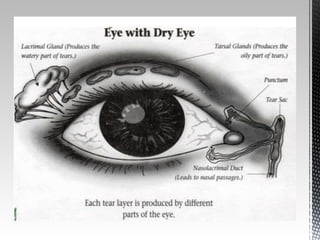
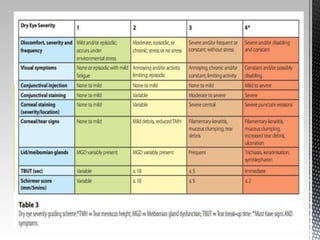
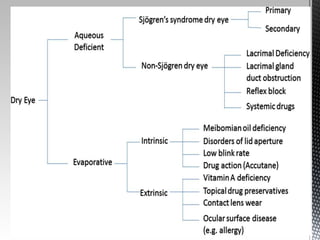
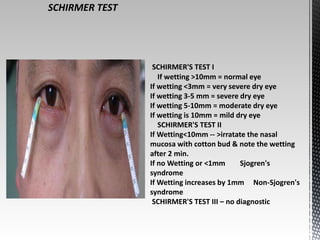
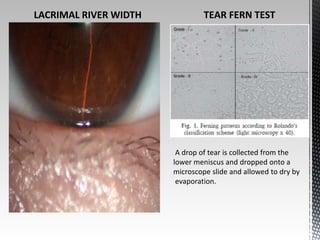
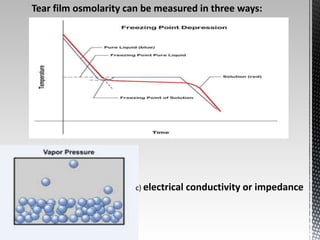
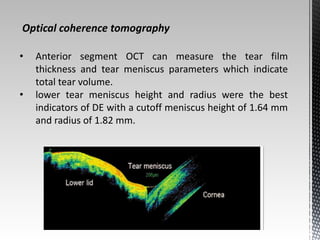
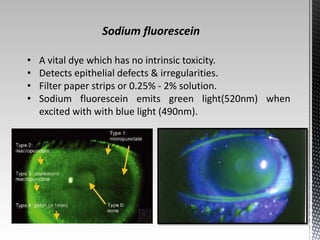
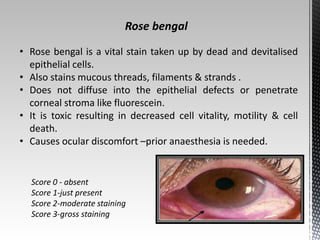
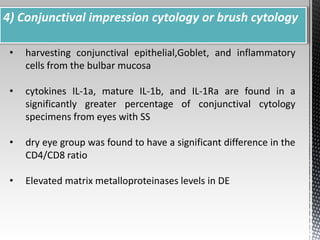
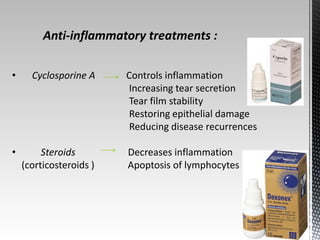
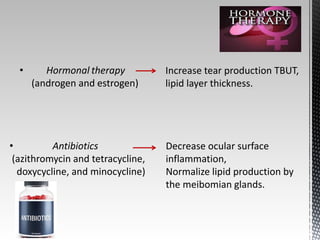
Dry eye disease is a multifactorial disease that results in discomfort and visual disturbance from tear film instability and damage to the ocular surface. It is characterized by increased tear film osmolarity and ocular surface inflammation. Diagnostic tests evaluate symptoms, signs of ocular surface damage, tear film breakup time, and tear osmolarity. Treatments include artificial tears, anti-inflammatory drugs like cyclosporine A and corticosteroids, essential fatty acids, and autologous serum for severe cases.