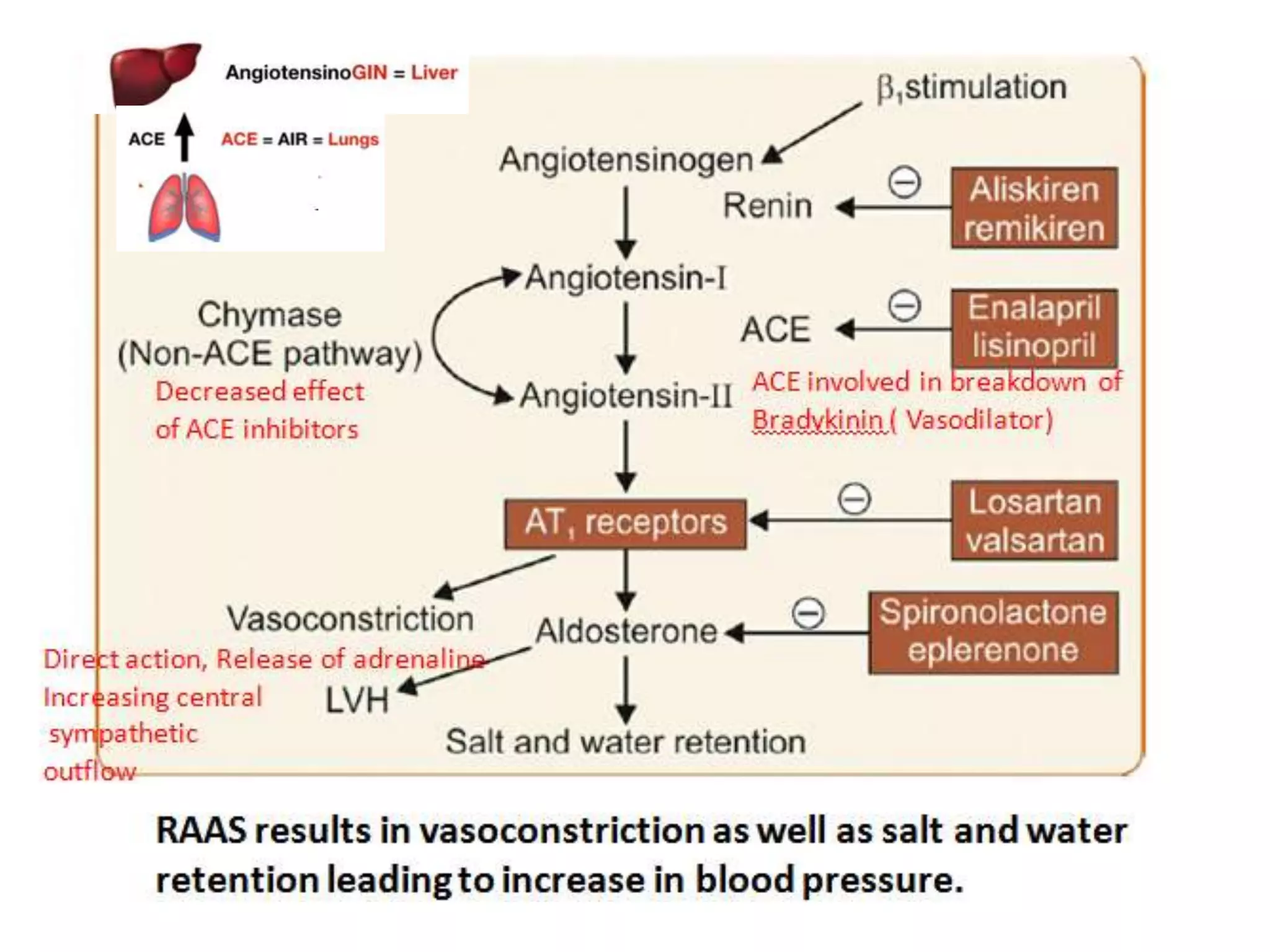
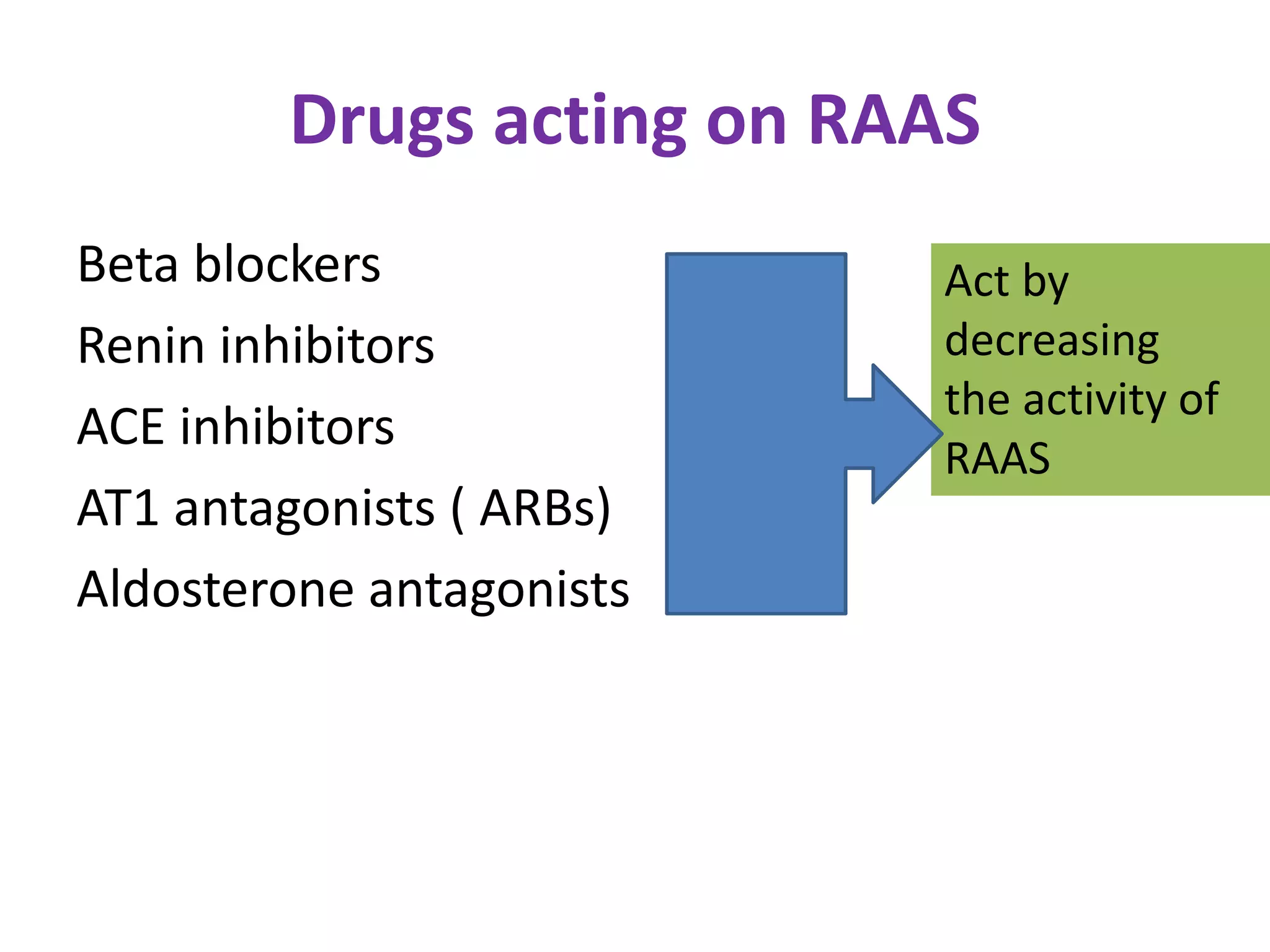
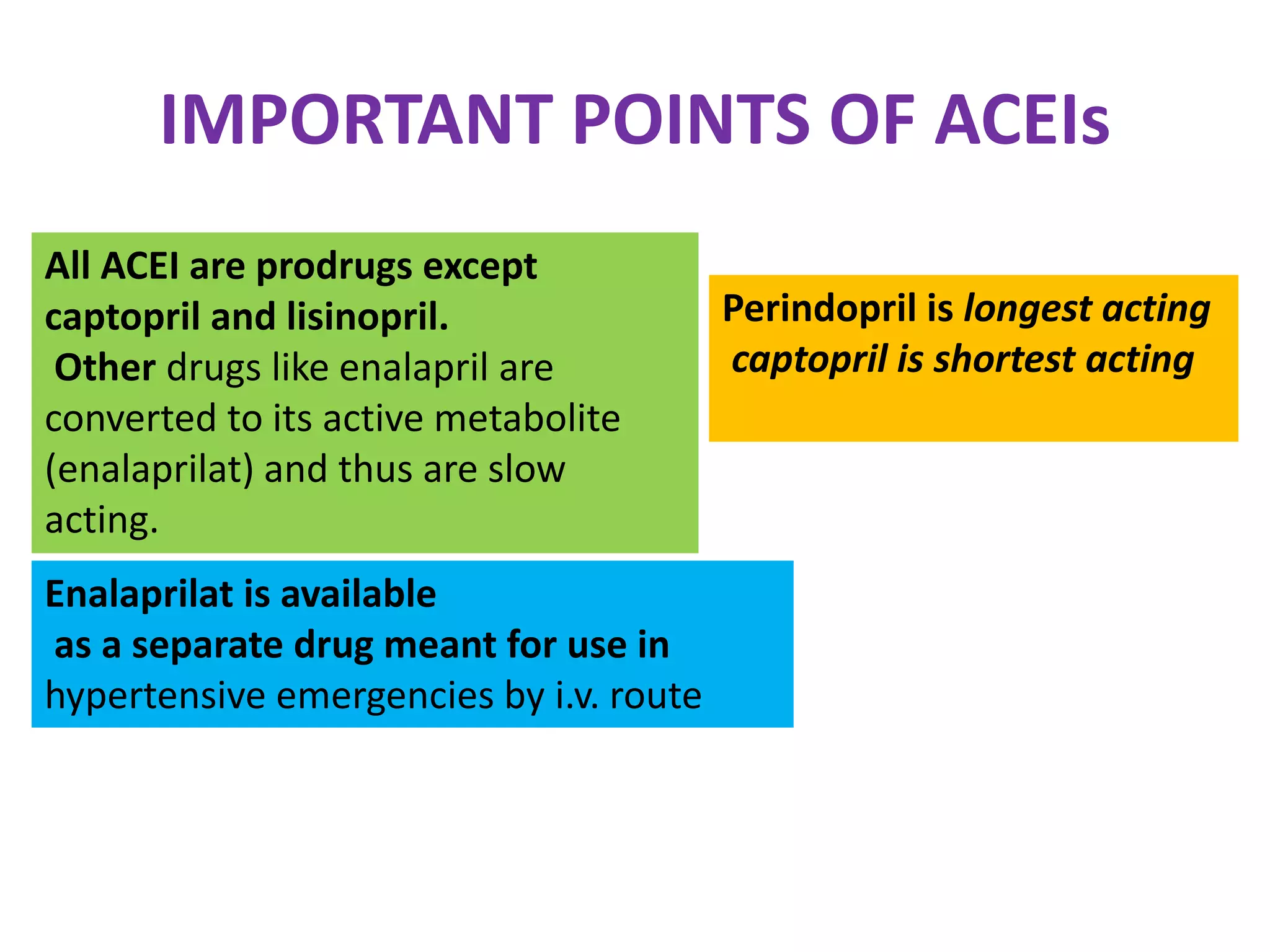
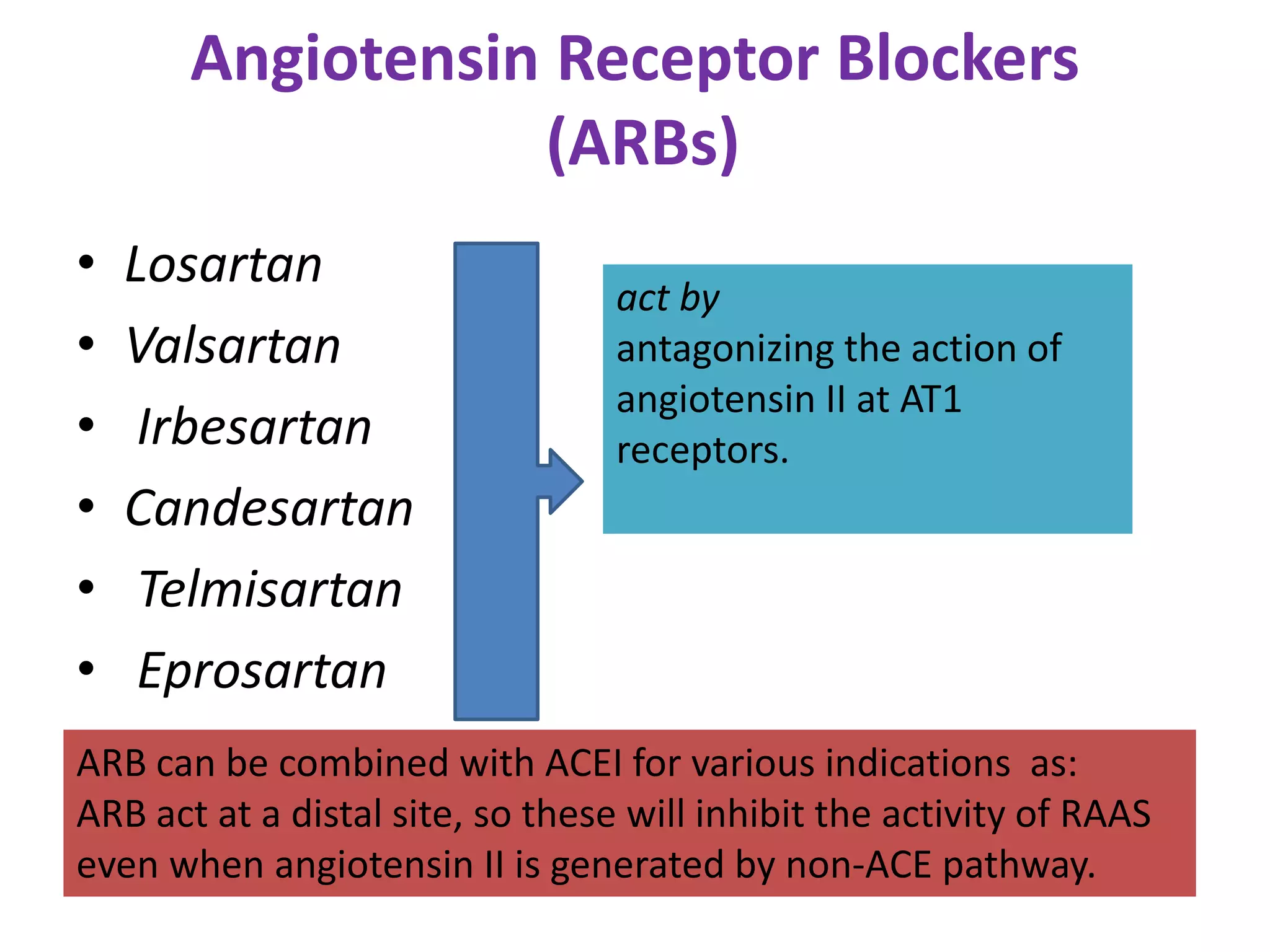
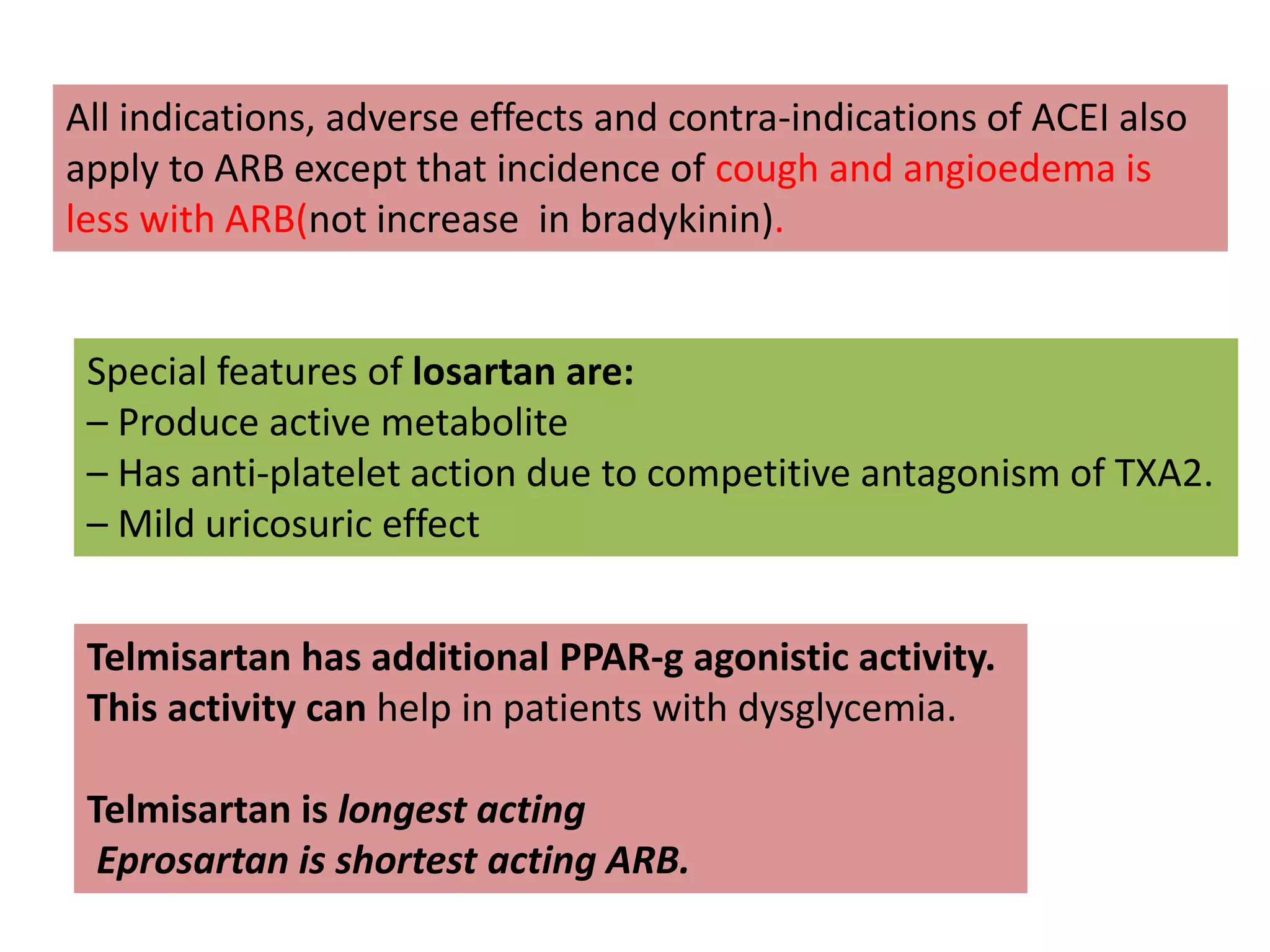
The document discusses various classes of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors, including renin inhibitors, ACE inhibitors, ARBs, and aldosterone antagonists, highlighting their mechanisms of action and uses in treating hypertension and other cardiovascular conditions. It also addresses potential side effects, contraindications, and specific characteristics of different drugs, such as the effects of ACE inhibitors on bradykinin levels and the unique qualities of telmisartan. Additionally, it contains multiple-choice questions to test understanding of these pharmacological agents.