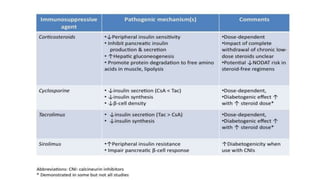
Many medications can cause drug-induced diabetes by increasing insulin resistance or affecting insulin secretion. Widely used medications like thiazide diuretics, beta-blockers, and statins weakly increase diabetes risk, while steroids, antipsychotics, immunosuppressants, protease inhibitors confer a high risk. Diabetes induced by medications may not always be permanent and blood glucose levels could return to normal after stopping the medication, but lifestyle changes are often needed to manage drug-induced diabetes.