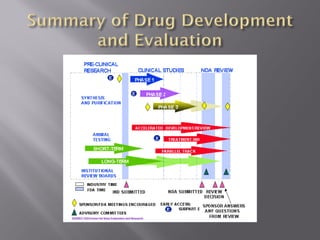
The document outlines the complex multi-step process of drug discovery and development from laboratory testing through FDA approval. It takes an average of 12 years and $350 million to get a new drug from initial discovery to pharmacy shelves. Drugs undergo preclinical testing followed by clinical trials in three phases with FDA review and approval required before market introduction. The FDA evaluates drugs based on evidence from clinical research to determine safety and efficacy.