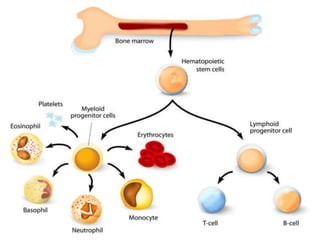
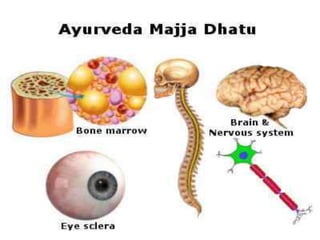
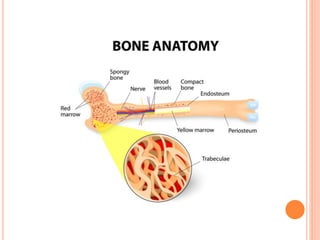
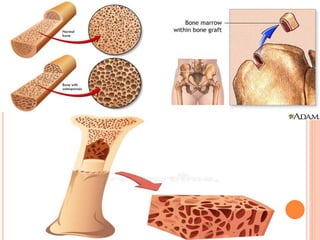
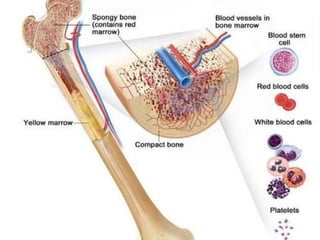
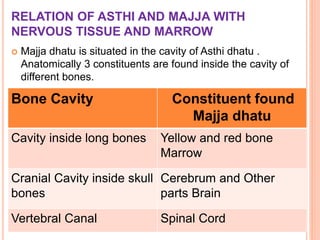
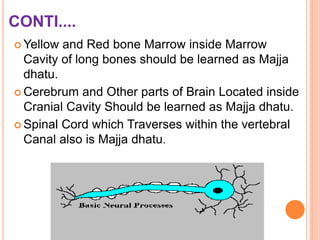
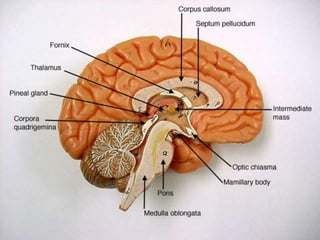
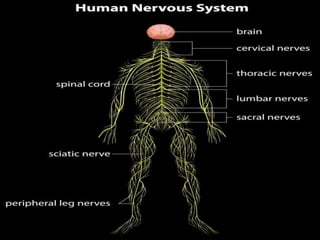
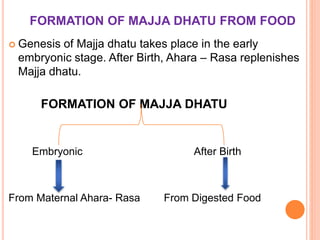
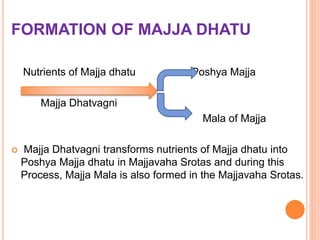
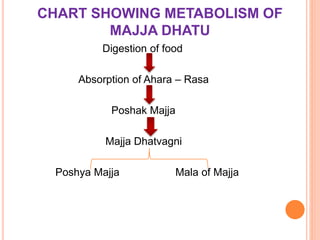
This document provides an overview of Majja Dhatu, the sixth dhatu (tissue) according to Ayurveda. It begins with an introduction and defines Majja Dhatu as the unctuous material found inside bone cavities. It describes the location of Majja Dhatu as being inside bones and its physiological importance in balancing the dryness of bones. It notes the clinical significance of the vertebral column and spinal cord as being part of Majja Dhatu. The document outlines the metabolism and waste products of Majja Dhatu and its functions in filling bone cavities.




















![PROPERTIES OF MAJJA DHATU
Majja dhatu is unctuous (Snigdha), Viscus (Picchila), soft
(Mridu) and Heavy (guru).
WASTE PRODUCTS OF MAJJA DHATU
¨ÉWÉ: ×Éä½ýÉä%ÊIÉÊ´É]Âüi´ÉSÉÉÆ*
(C.CHI.15/19)
xÉäjÉÊ´É]Âü i´ÉIÉÖSÉ×Éä½ýÉä| (S.SU.46/529)
• Sneha formed in the metabolism of Majja dhatu is called
as Mala (waste) of Majja dhatu.
• Netra Sneha- Oily secretion of eyes is called as Majja
Mala.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dr-180327192445/85/Dr-Sujit-Kumar-MD-Majja-Dhatu-PPT-34-320.jpg)








