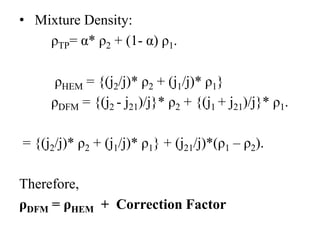
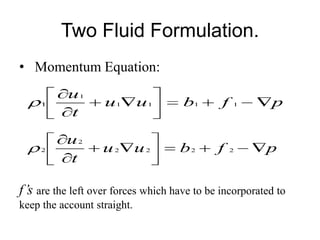
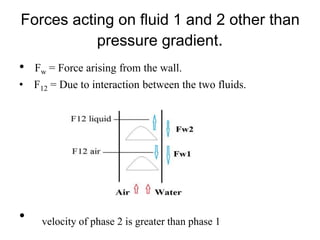
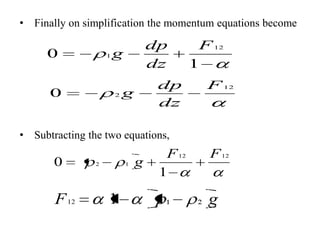
This document discusses the drift flux model (DFM), which is a separated flow model that focuses on the relative motion of phases rather than individual phase motion. The key assumption of DFM is that the dynamics of two phases can be expressed by the mixture momentum equation. DFM modifies mixture properties from homogeneous equilibrium model by correction factors. It provides equations for drift flux, mixture properties like density and phase velocities, and is applicable to various two-phase flows. However, it is not suitable for acoustic waves, choking phenomena, or high frequency instabilities.