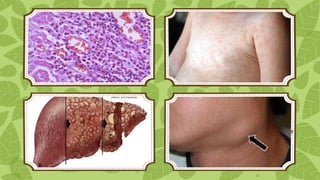
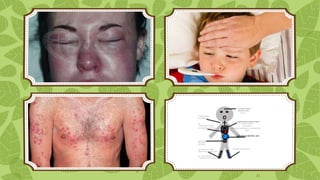
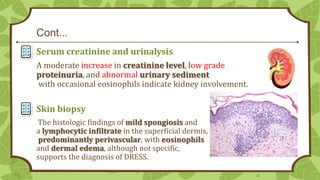
Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) is a severe adverse drug reaction caused by certain medications like carbamazepine. It involves a rash, fever, swelling of lymph nodes and organs like the liver, and high eosinophil counts. DRESS is diagnosed based on clinical features and test results showing eosinophilia, atypical lymphocytes, and elevated liver enzymes. Treatment involves promptly stopping the causative drug, supportive care, and sometimes corticosteroids. Complications can include autoimmune diseases or organ failure. Prognosis is generally good if the offending drug is identified and stopped early.