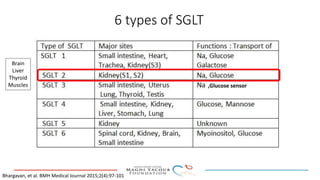
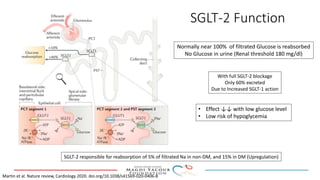
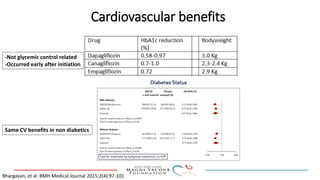
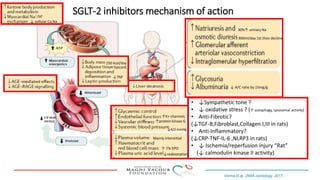
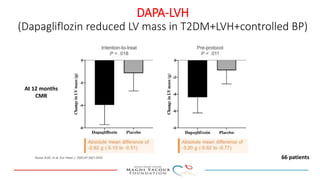
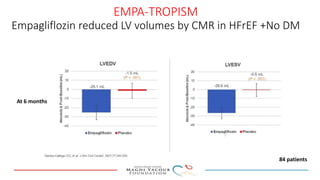
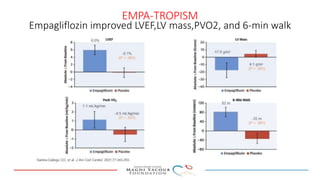
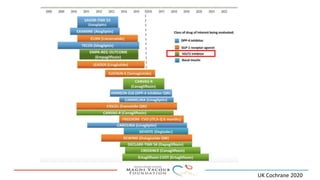
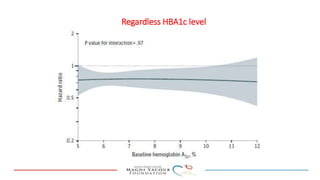
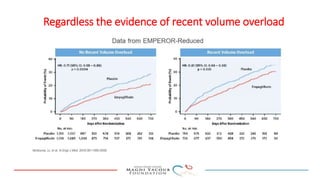
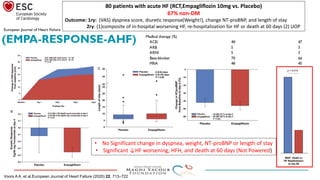
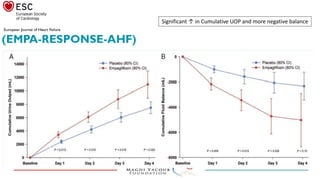
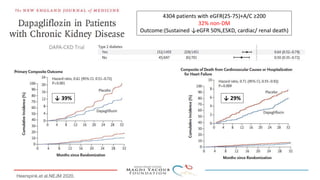
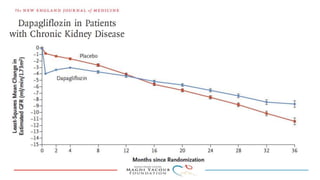
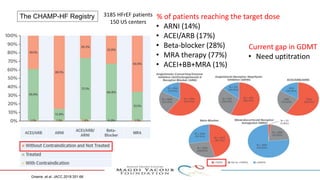
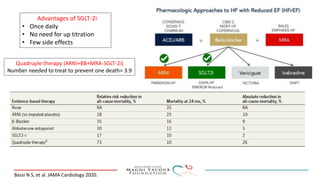
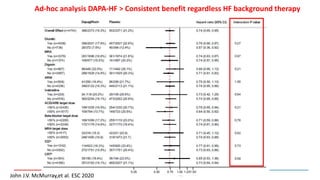
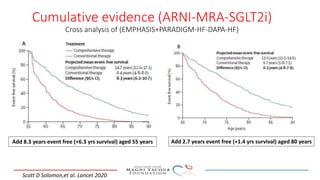
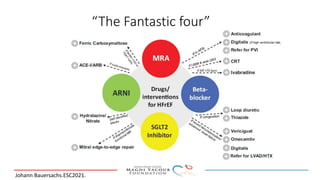
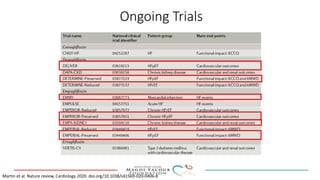
SGLT-2 inhibitors have shown promising cardiovascular and renal benefits:
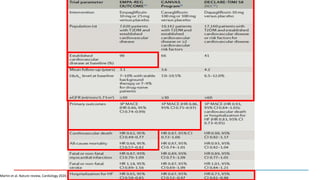
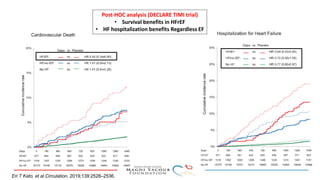
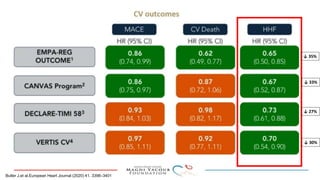
1) Trials have found SGLT-2 inhibitors reduce the risk of cardiovascular death in patients with type 2 diabetes and established cardiovascular disease, as well as reducing heart failure hospitalizations in those with diabetes and cardiovascular risk factors.
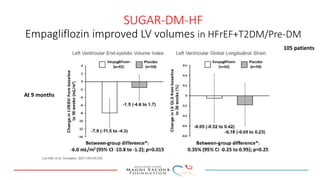
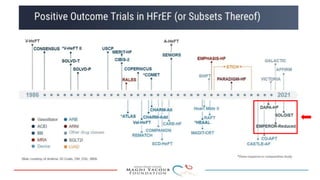
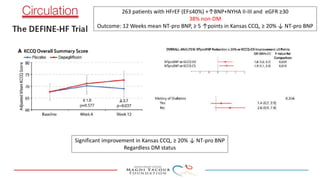
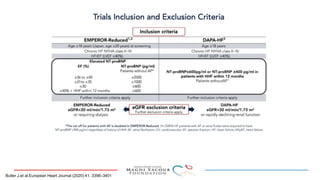
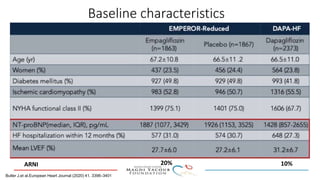
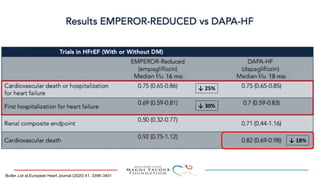
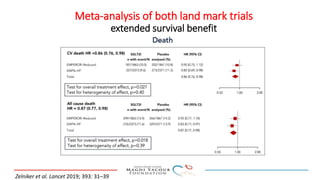
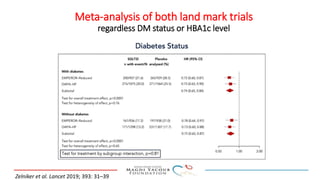
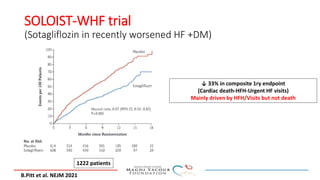
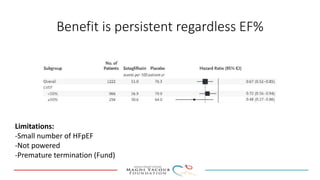
2) Studies also show SGLT-2 inhibitors improve outcomes for patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, reducing rates of heart failure hospitalization and mortality regardless of diabetes status or background heart failure therapies.
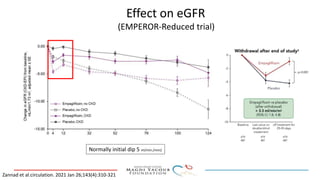
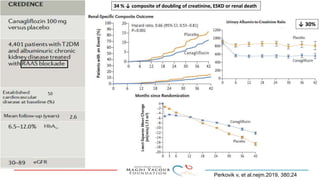
3) SGLT-2 inhibitors were also found to reduce the risk of renal death or progression to end-stage kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes and macroalbuminuria.