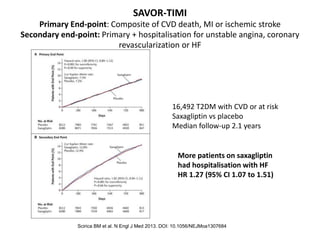
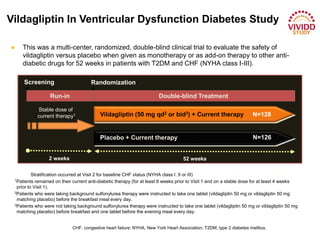
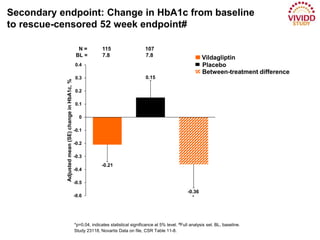
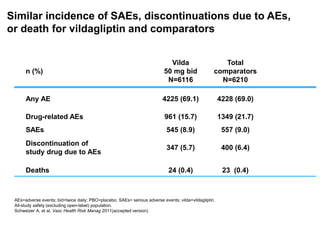
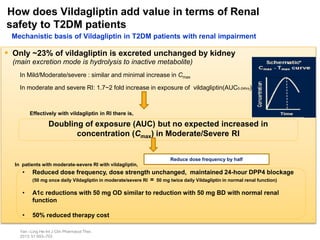
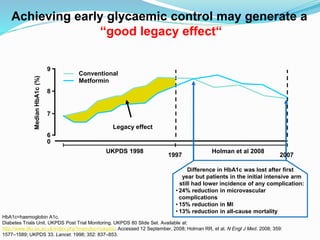
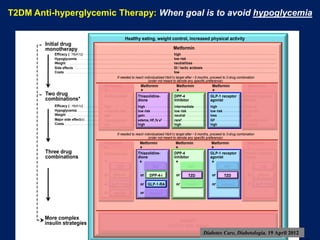
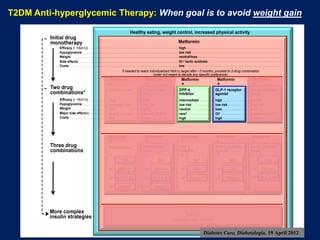
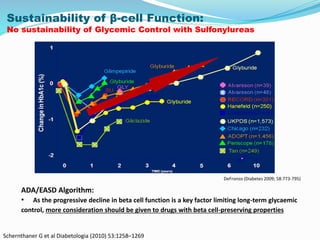
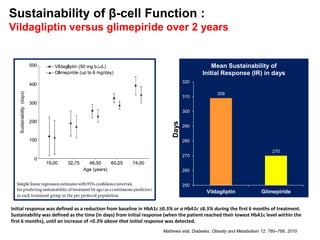
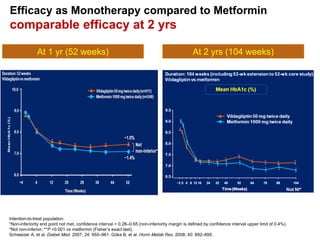
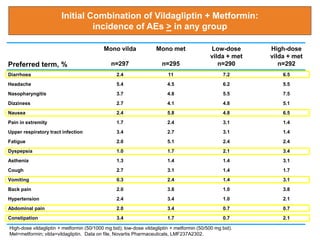
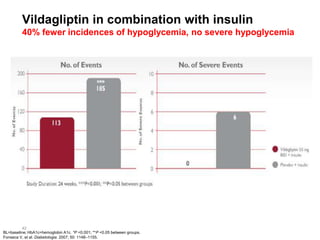
This document appears to be a slide presentation given by Dr. Faraz Farishta on diabetes management. It discusses diabetes as a global health problem and challenges in achieving optimal blood sugar control, including clinical inertia. It reviews guidelines on treatment goals and limitations of conventional oral therapies. It then discusses how DPP-4 inhibitors were developed to address multiple defects in type 2 diabetes by inhibiting the breakdown of GLP-1, an incretin hormone that stimulates insulin secretion. Data is presented on the efficacy and value of the DPP-4 inhibitor vildagliptin.





























![Odds ratio
[95% CI]
p-value
Major CV event1 0.71 [0.59, 0.86] < 0.001
Acute MI 0.64 [0.44, 0.94] 0.023
Stroke 0.77 [0.48, 1.24] 0.29
Mortality 0.60 [0.41, 0.88] 0.008
CV mortality 0.67 [0.39, 1.14] 0.14
Meta-analysis of 70 short- and medium-term trials, with 41,959 patients and mean
follow-up of 44.1 weeks
DPP4 inhibitor
better
Comparator
better
Cardiovascular Safety:
In a large meta-analysis of CV events, DPP-4is were better than the
comparator in terms of CV safety
AMI, acute myocardial infarction; CV, cardiovascular; DPP4i, dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors; MACE,
major CV events; MH–OR, Mantel–Haenzel odds ratio.
1.Analysis of MACE as serious adverse events supports the safety of DPP4 inhibitors, but does not
demonstrate their efficacy in reducing CV risk ion a long-term basis.
Monami M, et al. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013;15:112–120.
0.0 1.0 10.0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dpp4i-earlierthebetter1-150730112312-lva1-app6891/85/Dpp4i-earlier-the-better-1-43-320.jpg)