1) The document discusses trends and challenges in the emerging field of the Internet of Things (IoT), which connects physical objects through internet connectivity and sensors.
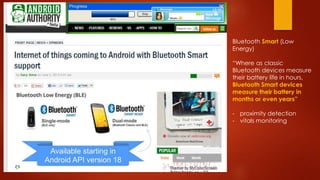
2) Key enabling technologies for IoT include RFID, NFC, barcodes, QR codes, IPv6, and Bluetooth Smart devices.
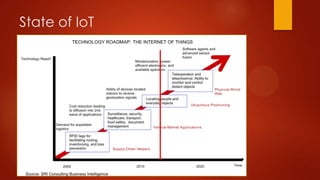
3) Major issues in implementing IoT on a large scale involve lack of standardization, managing the huge number of connected devices, ensuring real-time performance, and addressing privacy and security threats posed by interconnected devices.


![What is IoT ?
uniquely identifiable objects and their virtual representations in an
Internet-like structure [Ashton99]
“[…] the expanding interconnectedness of smart devices, ranging
from sensors in your shoe to jet engine monitors” [BusinessWeek]
Each object can be connected via other objects (usually via third
party) to exchange data.
Roots in the M2M.
The third age of the Internet](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/downoftheiot-140407135001-phpapp01/85/TRENDS-AND-CHALLENGES-IN-THE-DAWN-OF-INTERNET-OF-THINGS-ERA-3-320.jpg)
![What do we need ?
Key enabling technologies
RFID
NFC
Barcodes
2D codes: QR … or the more obscure ones: Aztec, Data Matrix, HCCB, PDF417
Digital watermarking: adding auth. data to a “signal”;
IPv6: there would be more IP addresses available than things.
“Every screen variant, mobile chip, and sensor known to man has been tuned to
work with Android” – [Jim Zemlin, Linux Foundation]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/downoftheiot-140407135001-phpapp01/85/TRENDS-AND-CHALLENGES-IN-THE-DAWN-OF-INTERNET-OF-THINGS-ERA-5-320.jpg)

![Implementation … issues
Lack of standardization;
Size: it’s going to be huge. From 50 to 100 trillion of moving things
[Waldner 2007];
Time constraints: “extremely hard real-time system”: billion of
simultaneous events.
Position tracking: things have to know their neighbors and interact
to them.
The shear quantity of data is way above what we can process
now … or not !?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/downoftheiot-140407135001-phpapp01/85/TRENDS-AND-CHALLENGES-IN-THE-DAWN-OF-INTERNET-OF-THINGS-ERA-8-320.jpg)


![Indoor location
iBeacon
Indoor spaces lack GPS and have poor GSM location;
“technology revolution that will rival the invention of the mouse and the graphical
user interface […]” [smh.com.au, ]
“Developers scramble to build services on top of beacons, analytics on top of
services, and brilliant user experiences and strategy at the top of the pyramid.”
[beekn.net]
http://estimote.com/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/downoftheiot-140407135001-phpapp01/85/TRENDS-AND-CHALLENGES-IN-THE-DAWN-OF-INTERNET-OF-THINGS-ERA-11-320.jpg)
![iBeacon technology
Bluetooth 4.0 (LE)
Geofencing three zones
Immediate: cm range (like NFC);
Near: a few meters
Far: more than 10 m
Micro-location awareness
“Apple iBeacons: With great power comes great potential to
annoy” [ZDNet]
iOS 7.1 : iBeacon is “opt-out” instead of “opt-in”
Beacons only transmit data apps. track people](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/downoftheiot-140407135001-phpapp01/85/TRENDS-AND-CHALLENGES-IN-THE-DAWN-OF-INTERNET-OF-THINGS-ERA-12-320.jpg)

![Industrial IoT - IIoT
Echelon IzoT;
Ex:
variable-speed compressor technology;
25–35% efficiency boost (Emerson)
Connect Nest with building scale air conditioning
1979 Modbus !!!
grid stabilization services
16$ billion market (vcharge-energy.com)
Automatic control of all devices during peak demands in the
grid;
“The Internet of Everything for cities” [CISCO, 2013] Weishaupt,
200,000 BTU/hr 37,000,000 BTU/hr](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/downoftheiot-140407135001-phpapp01/85/TRENDS-AND-CHALLENGES-IN-THE-DAWN-OF-INTERNET-OF-THINGS-ERA-14-320.jpg)
![Threats
“internet of things holds
promises but it also holds
dangers” [Rob van Kraneburg,
2011]
“the intelligence community
views Internet of Things as a rich
source of data” [Ackerman, 2012]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/downoftheiot-140407135001-phpapp01/85/TRENDS-AND-CHALLENGES-IN-THE-DAWN-OF-INTERNET-OF-THINGS-ERA-15-320.jpg)