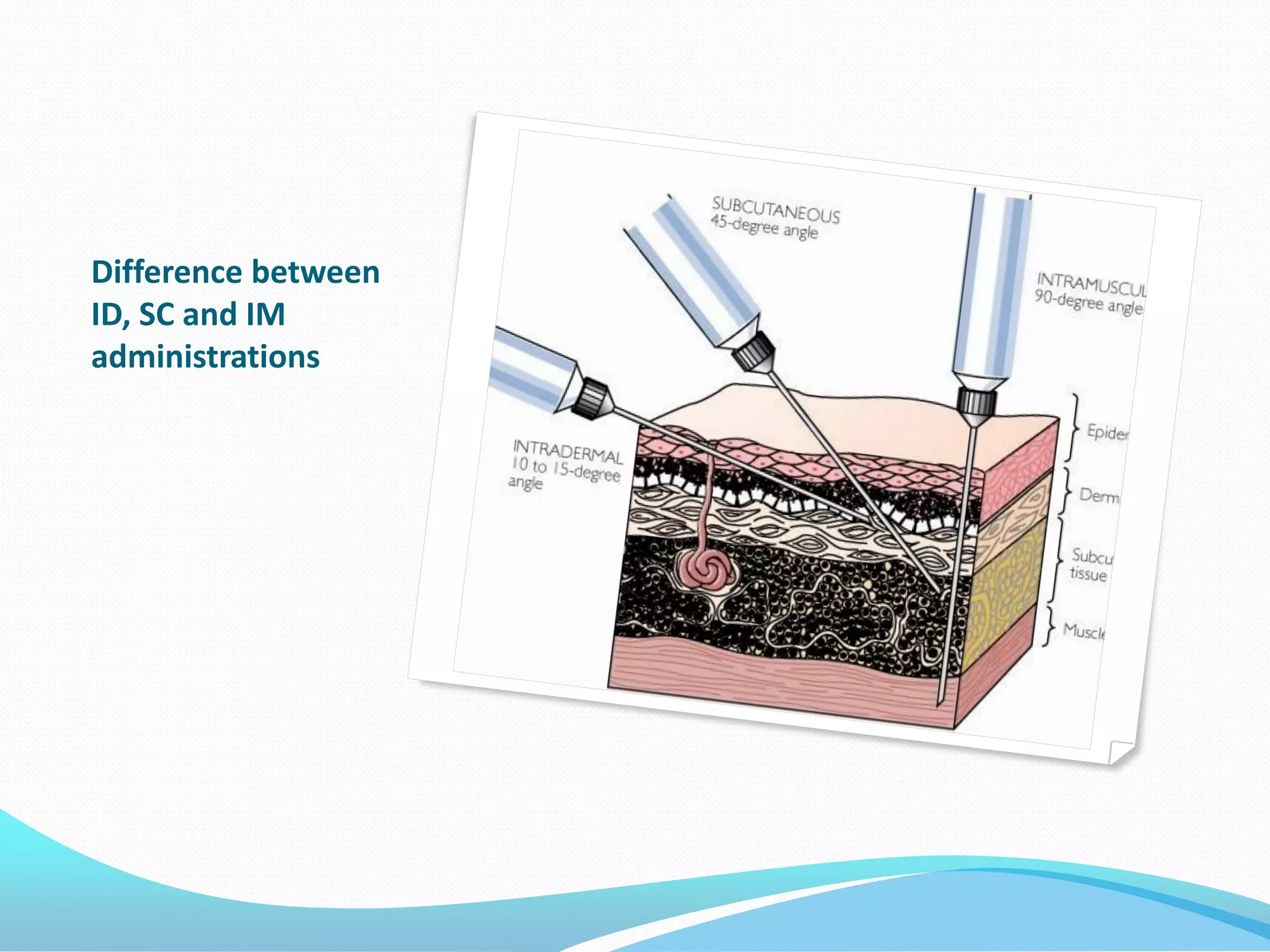
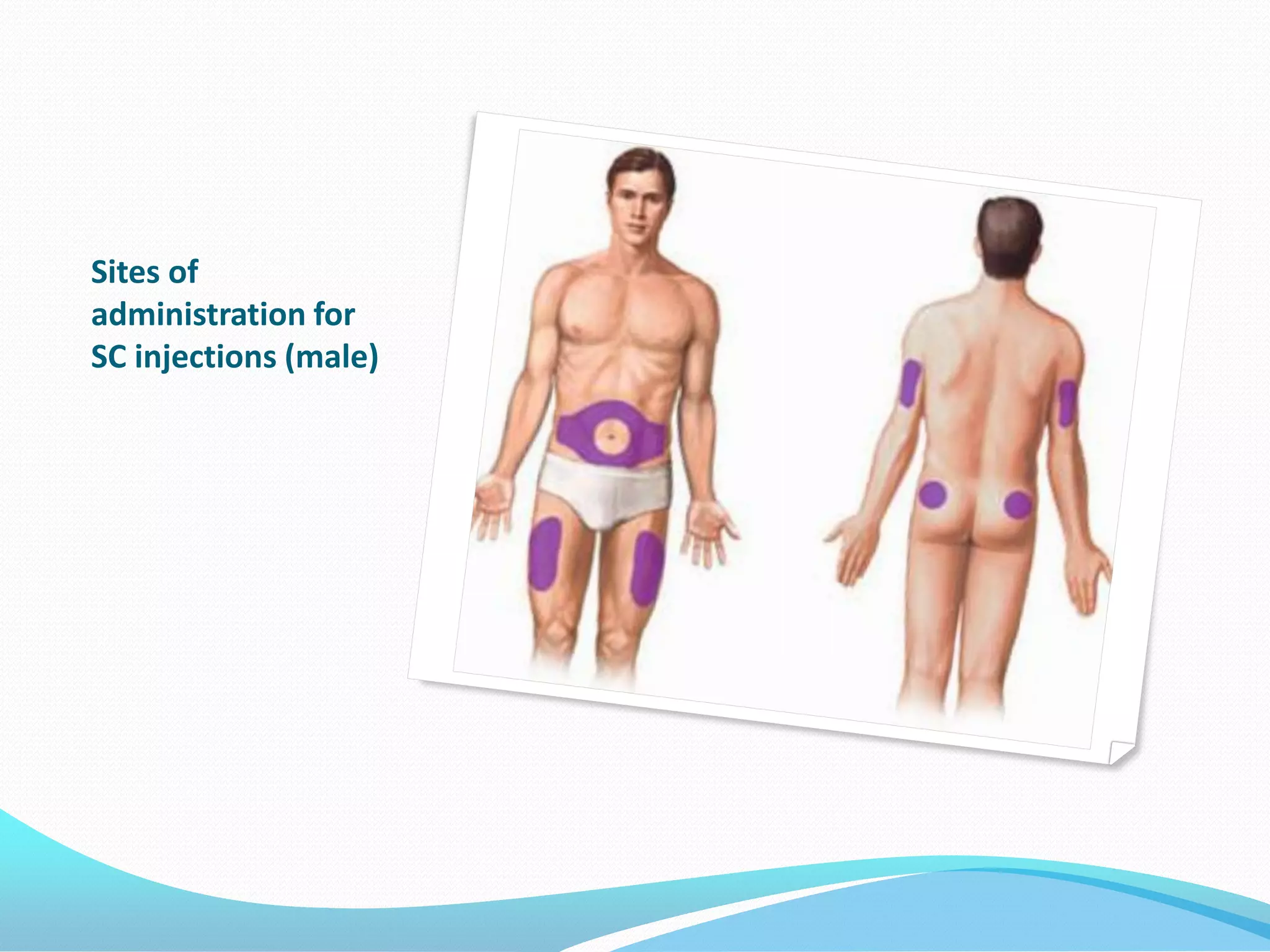
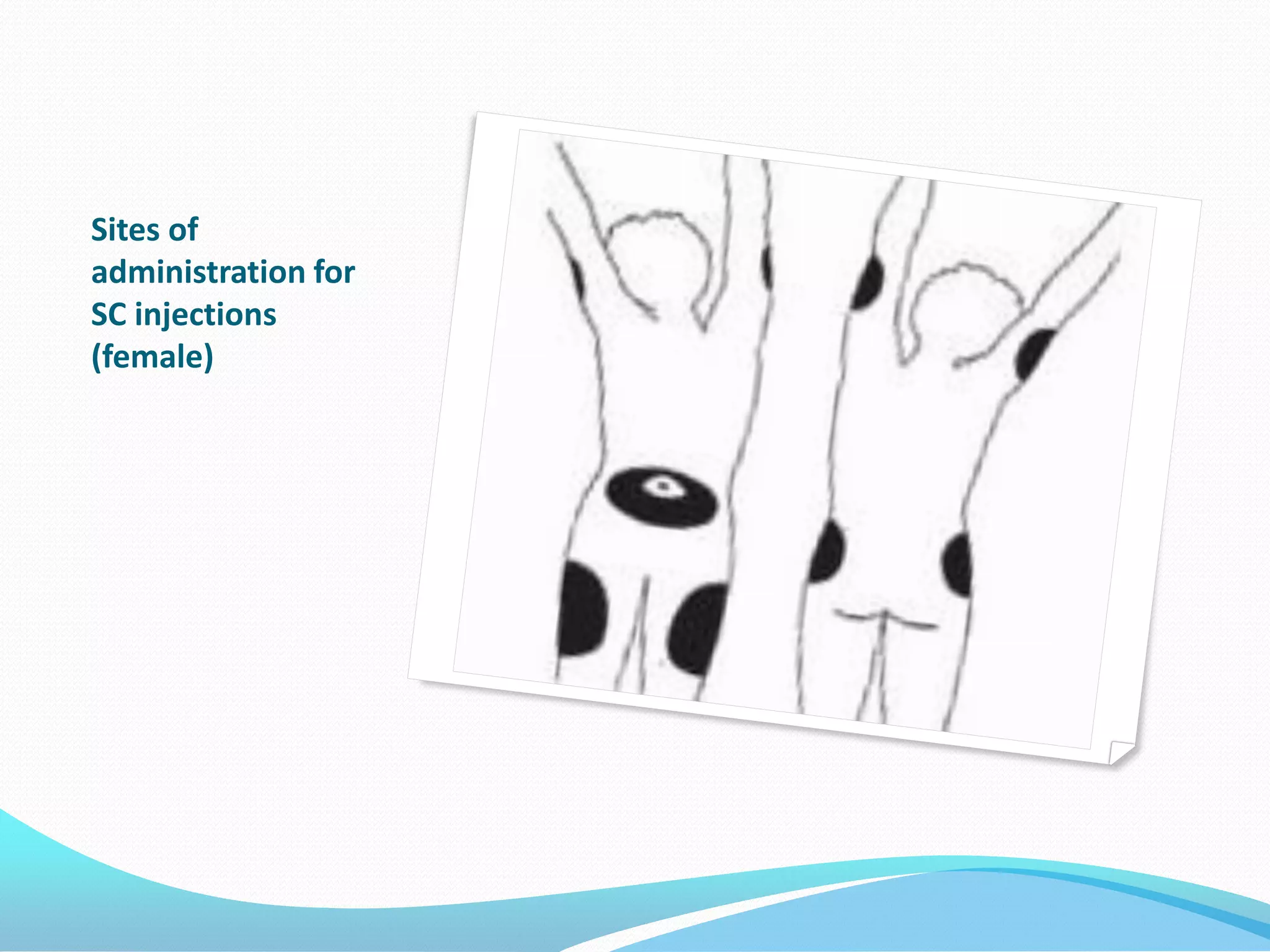
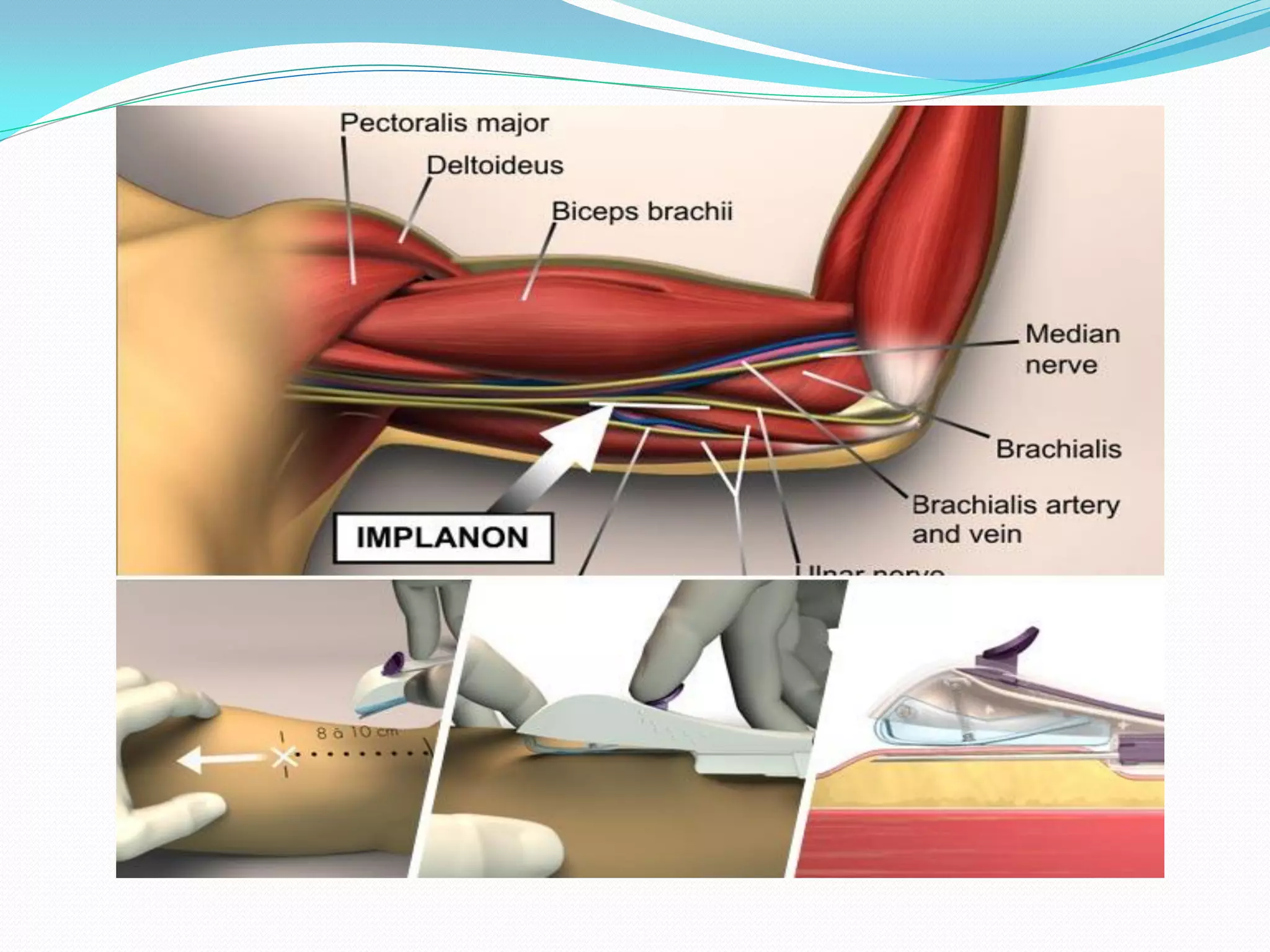
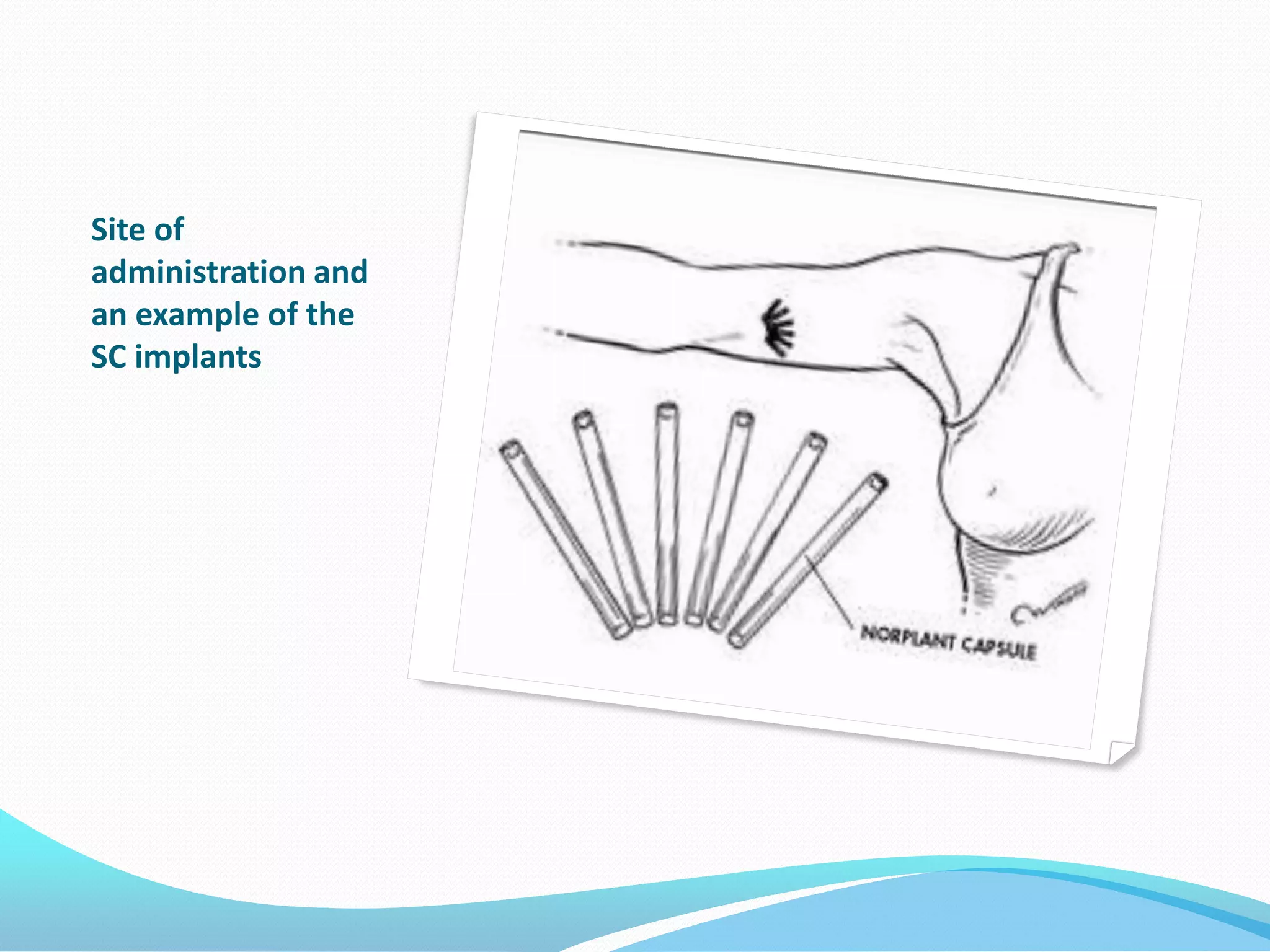
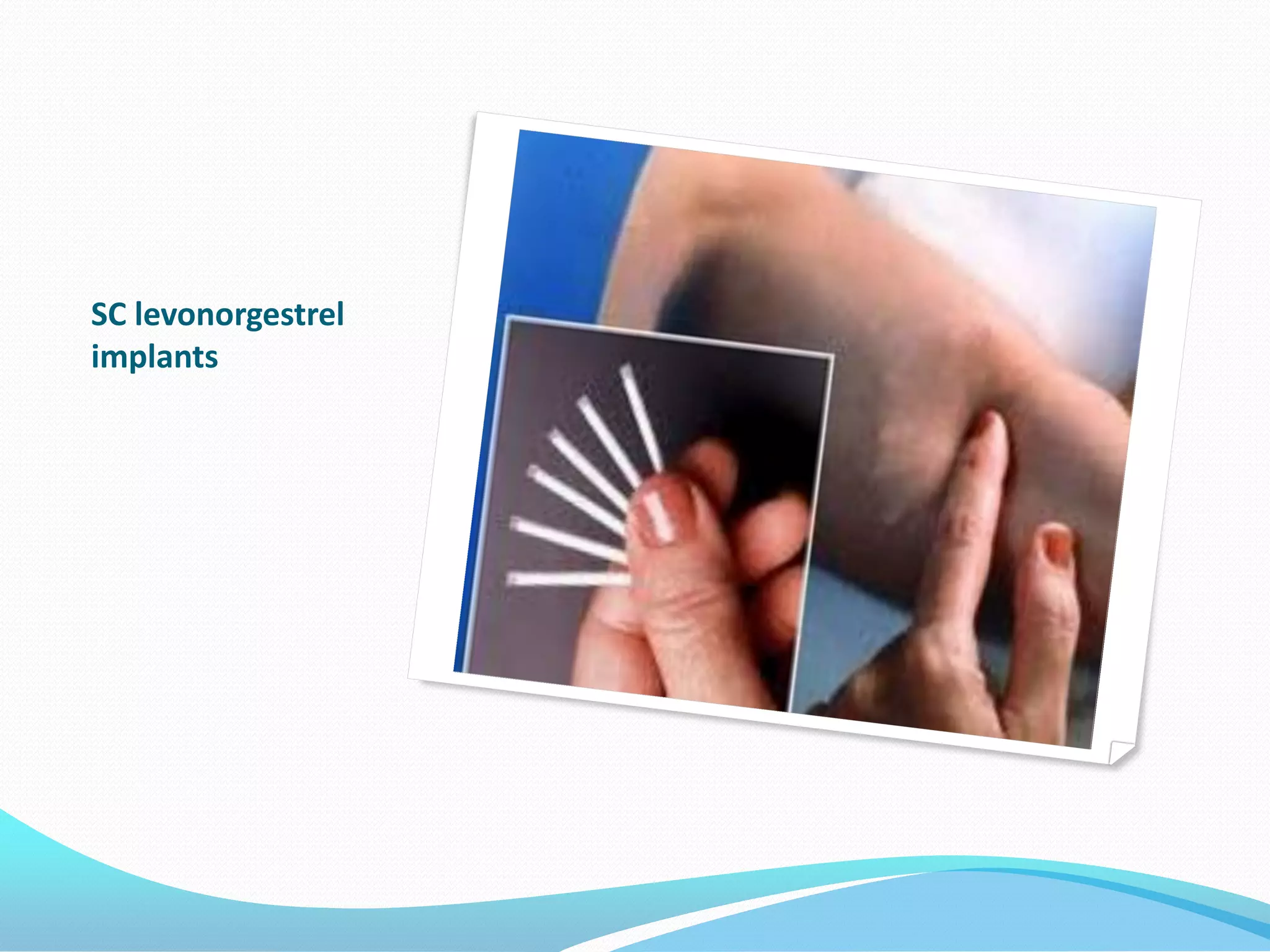
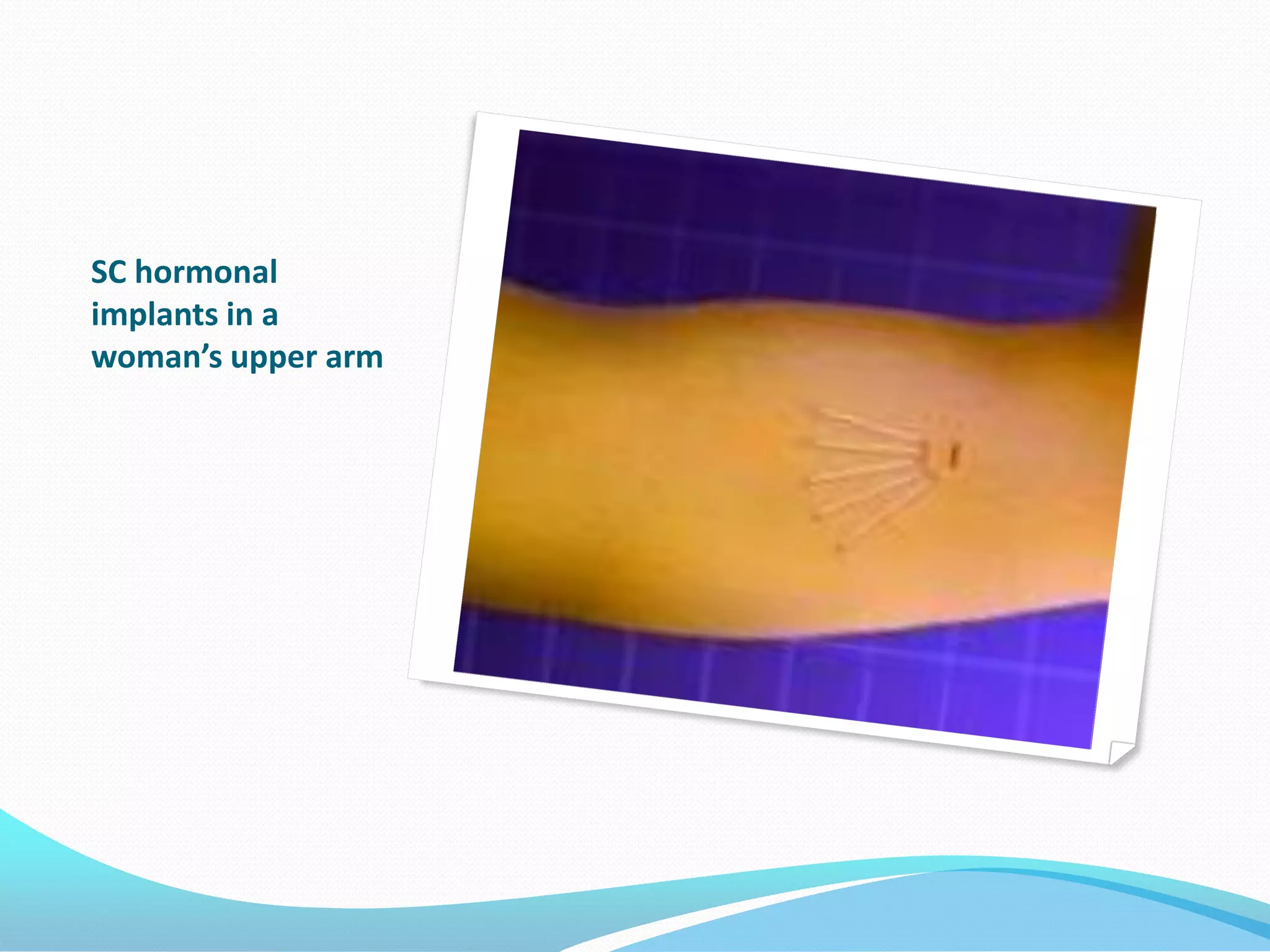
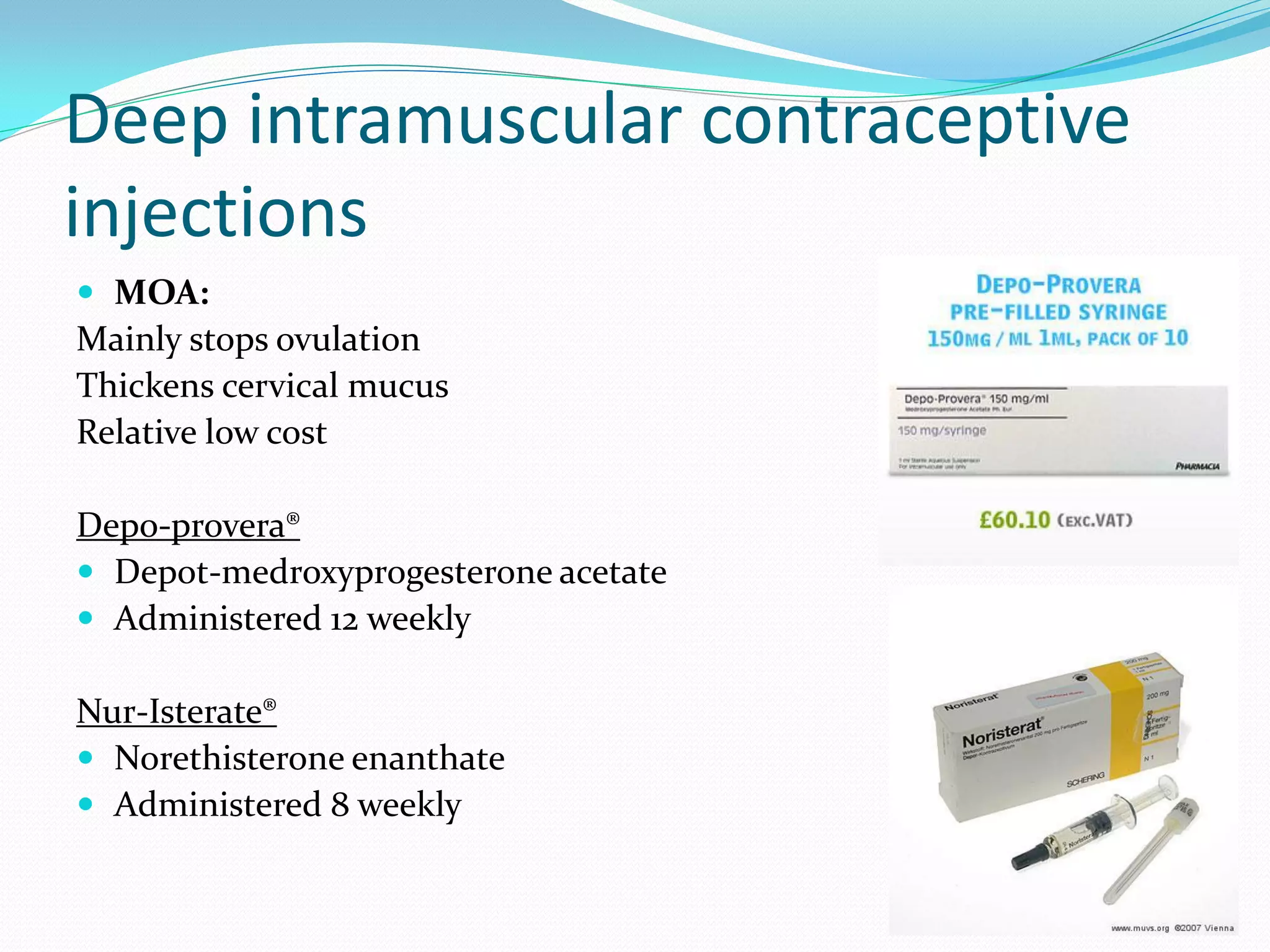
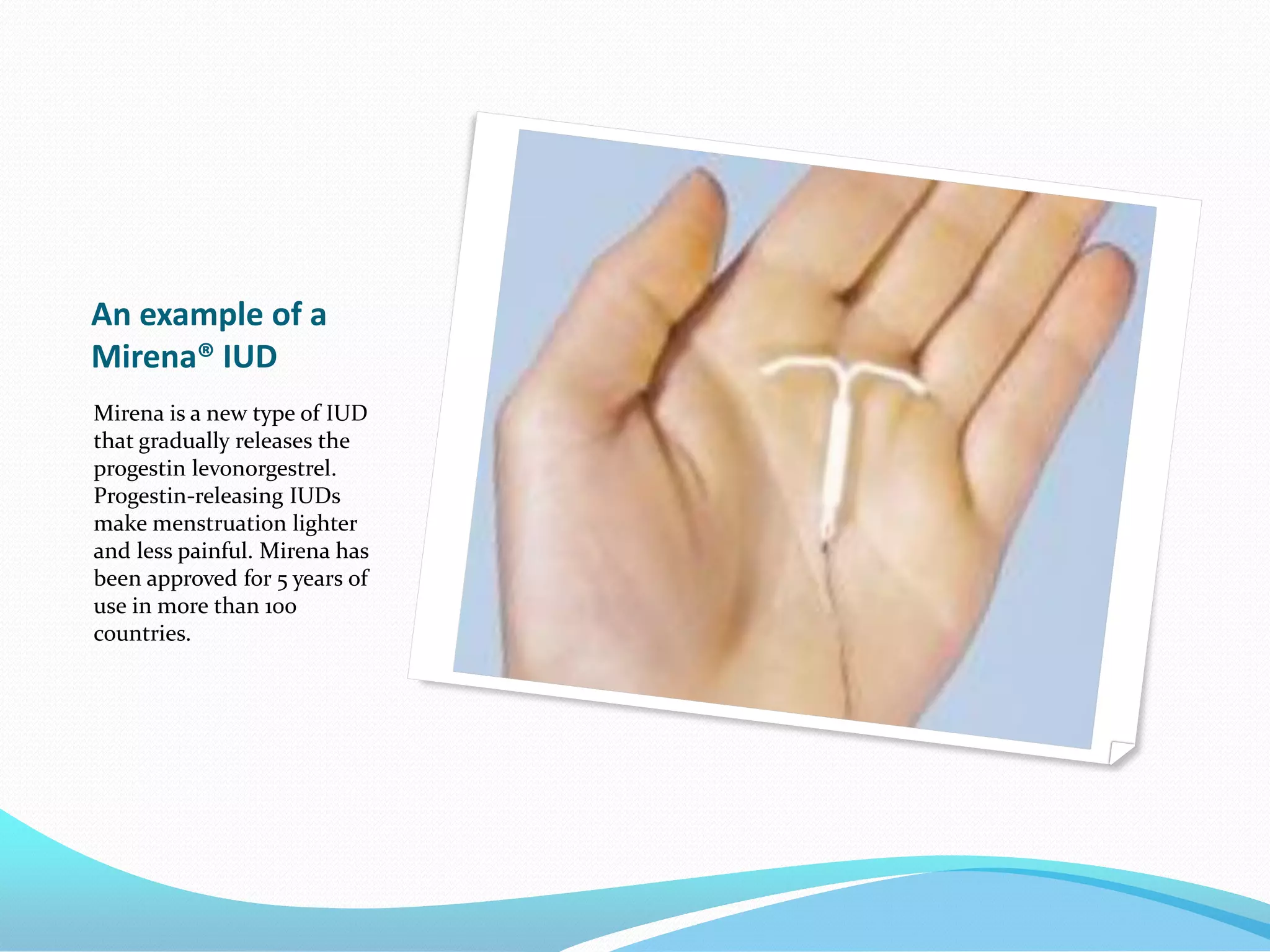
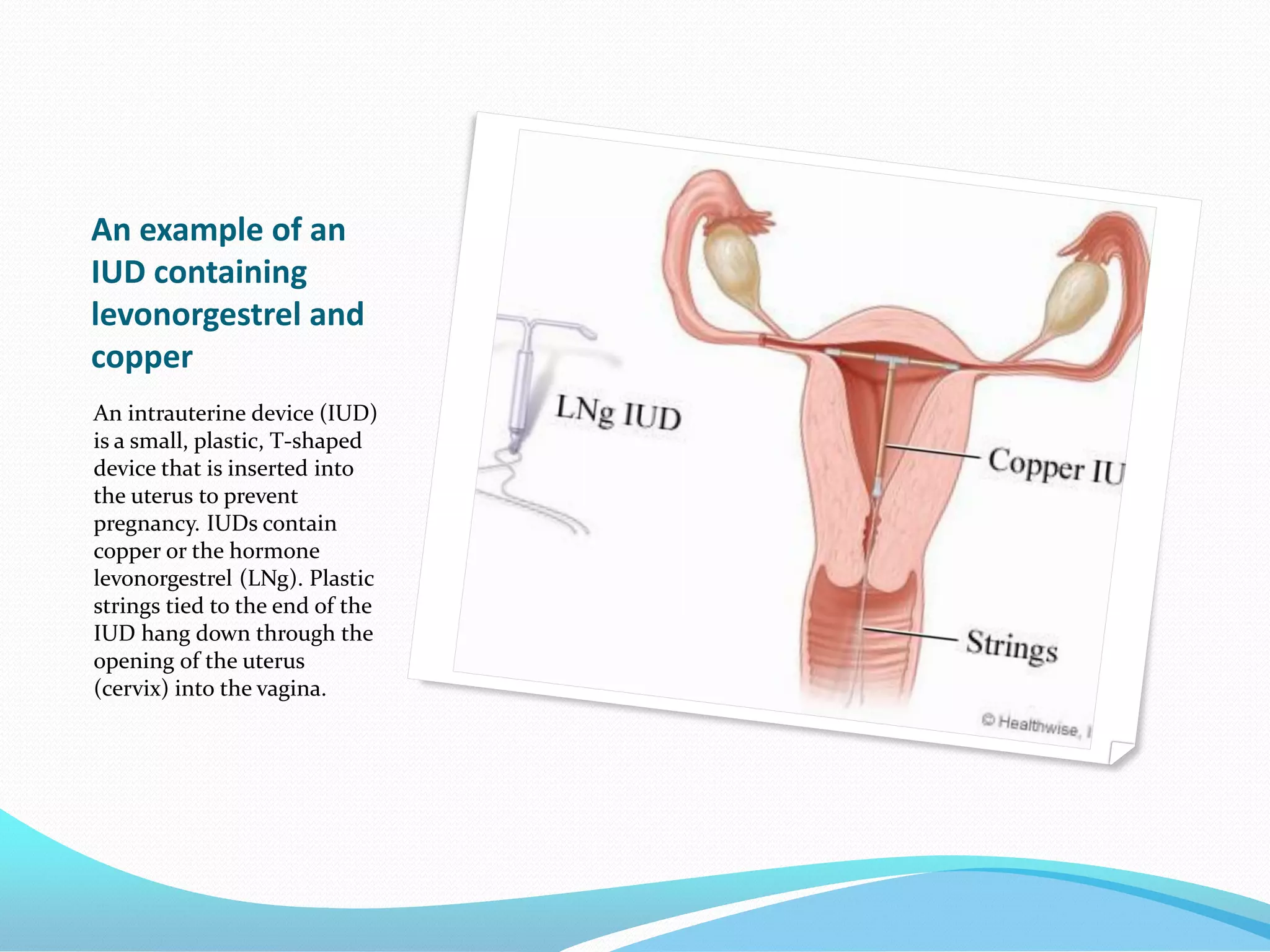
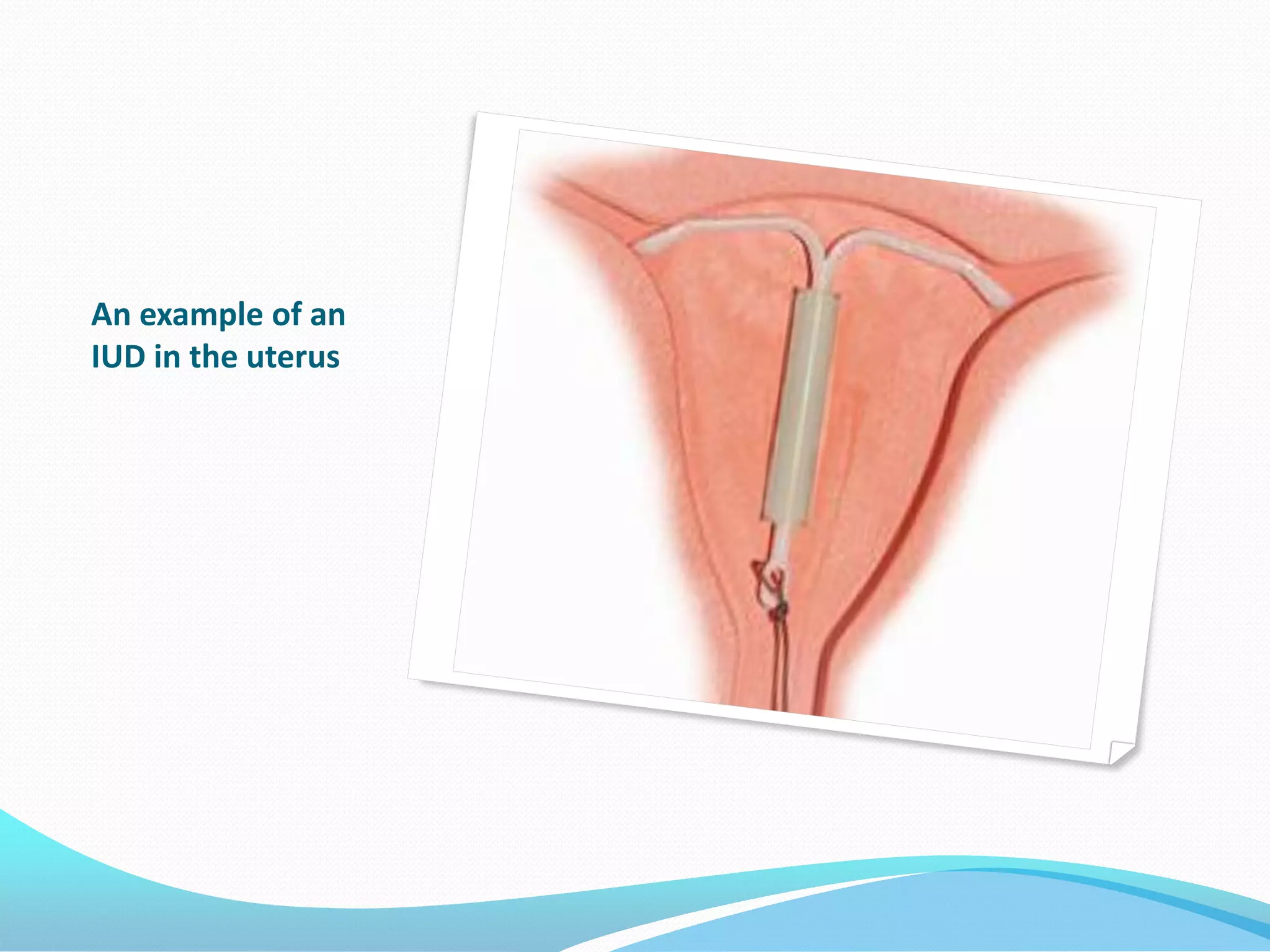
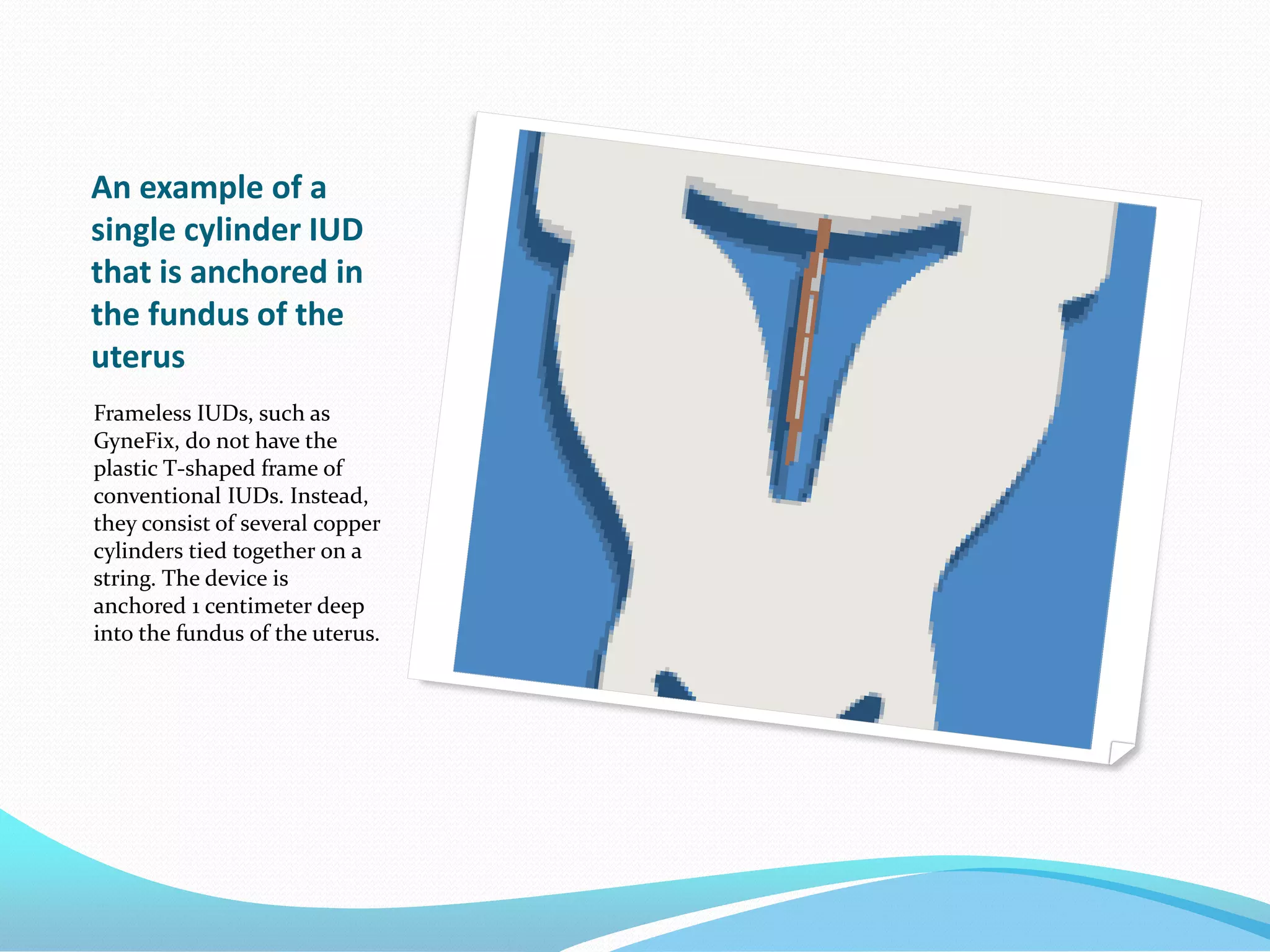
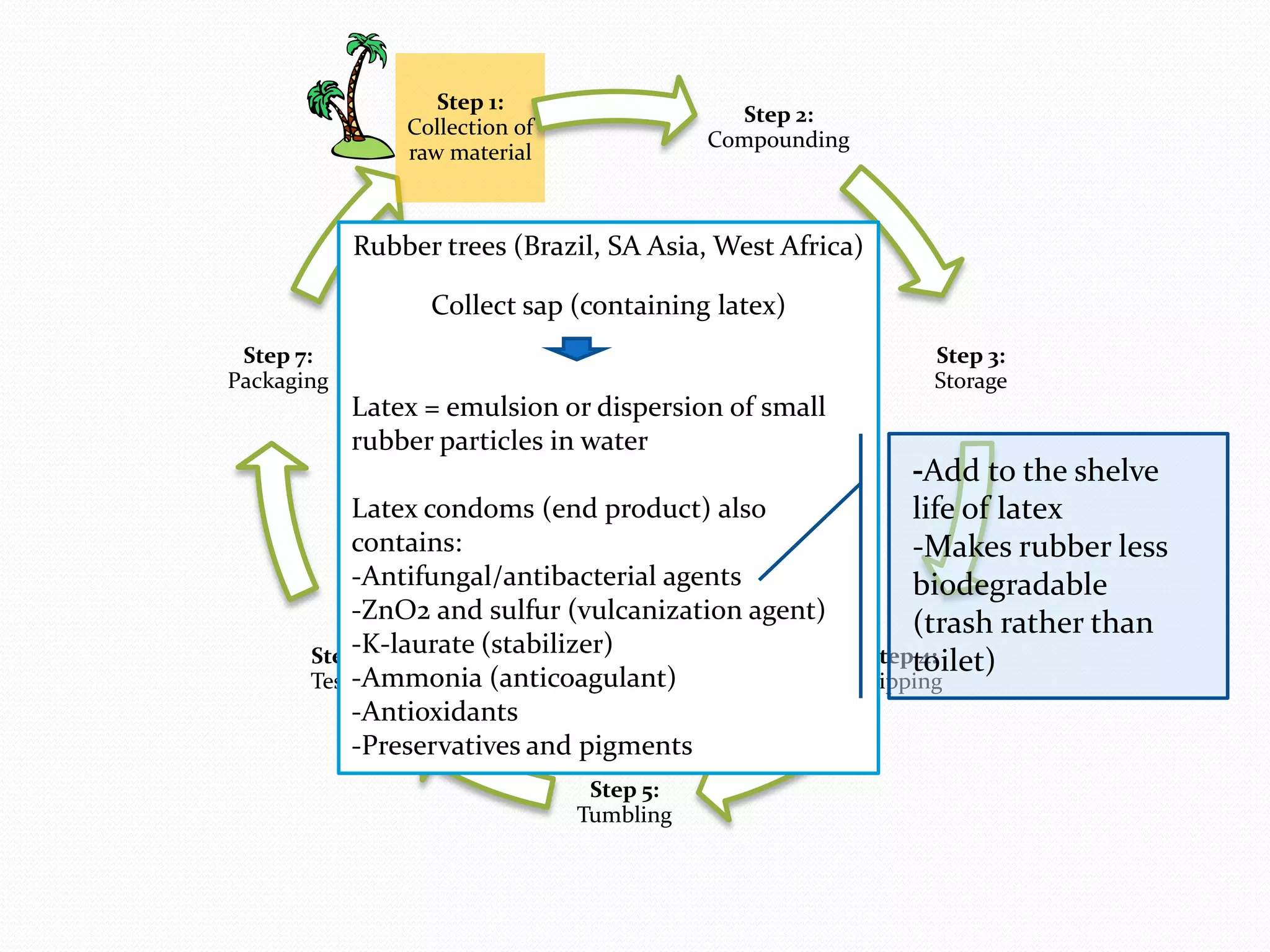
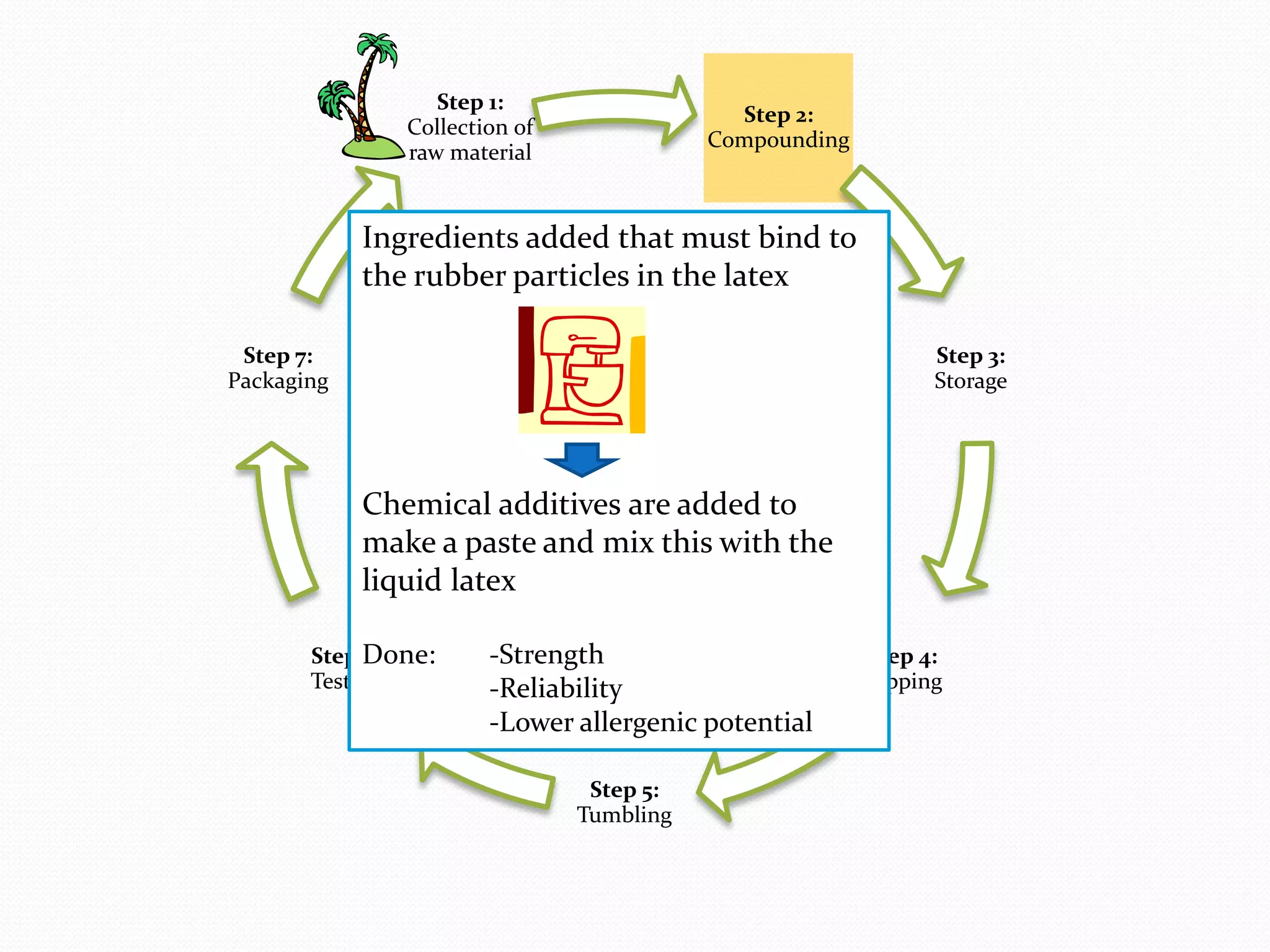
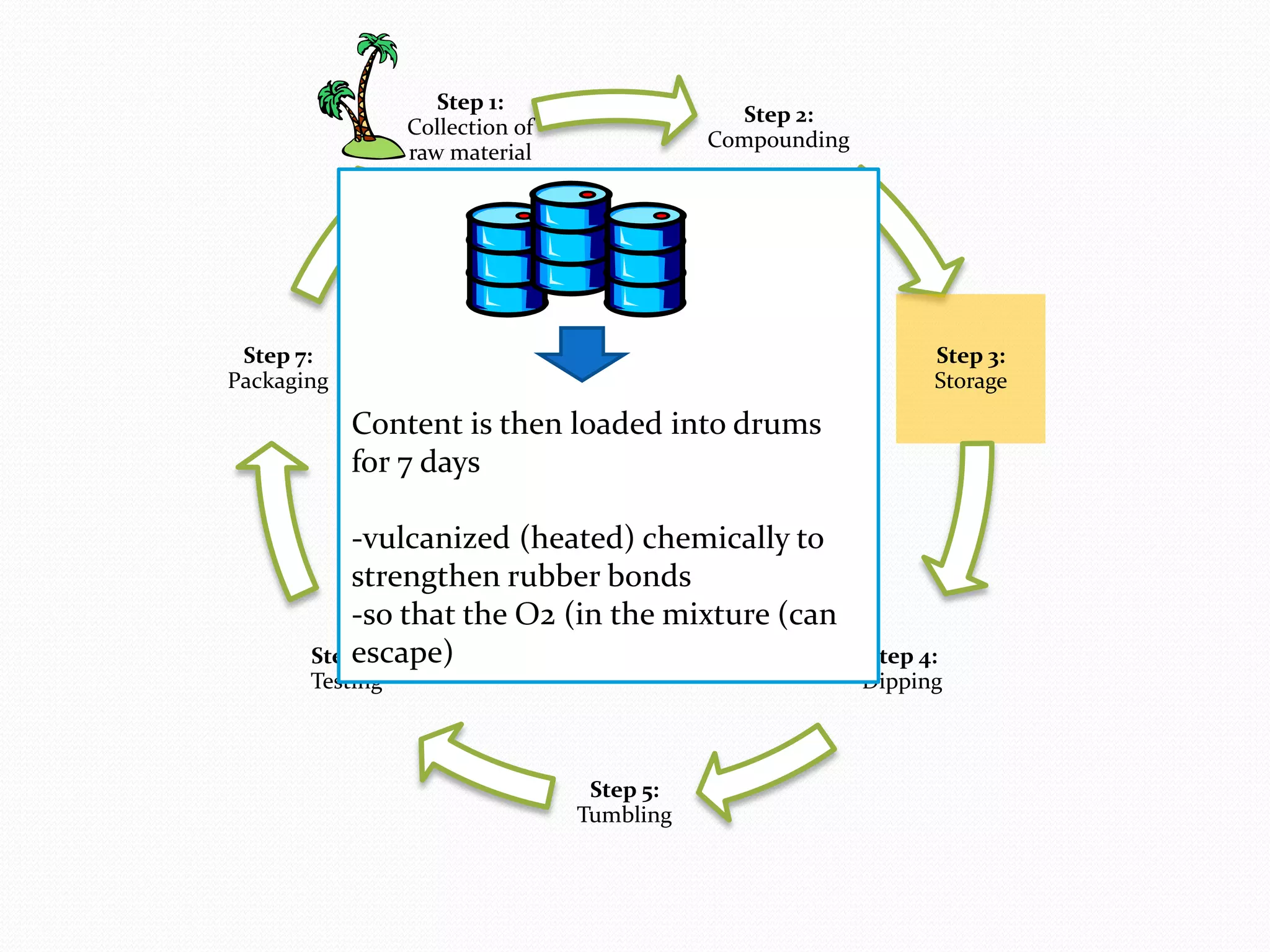
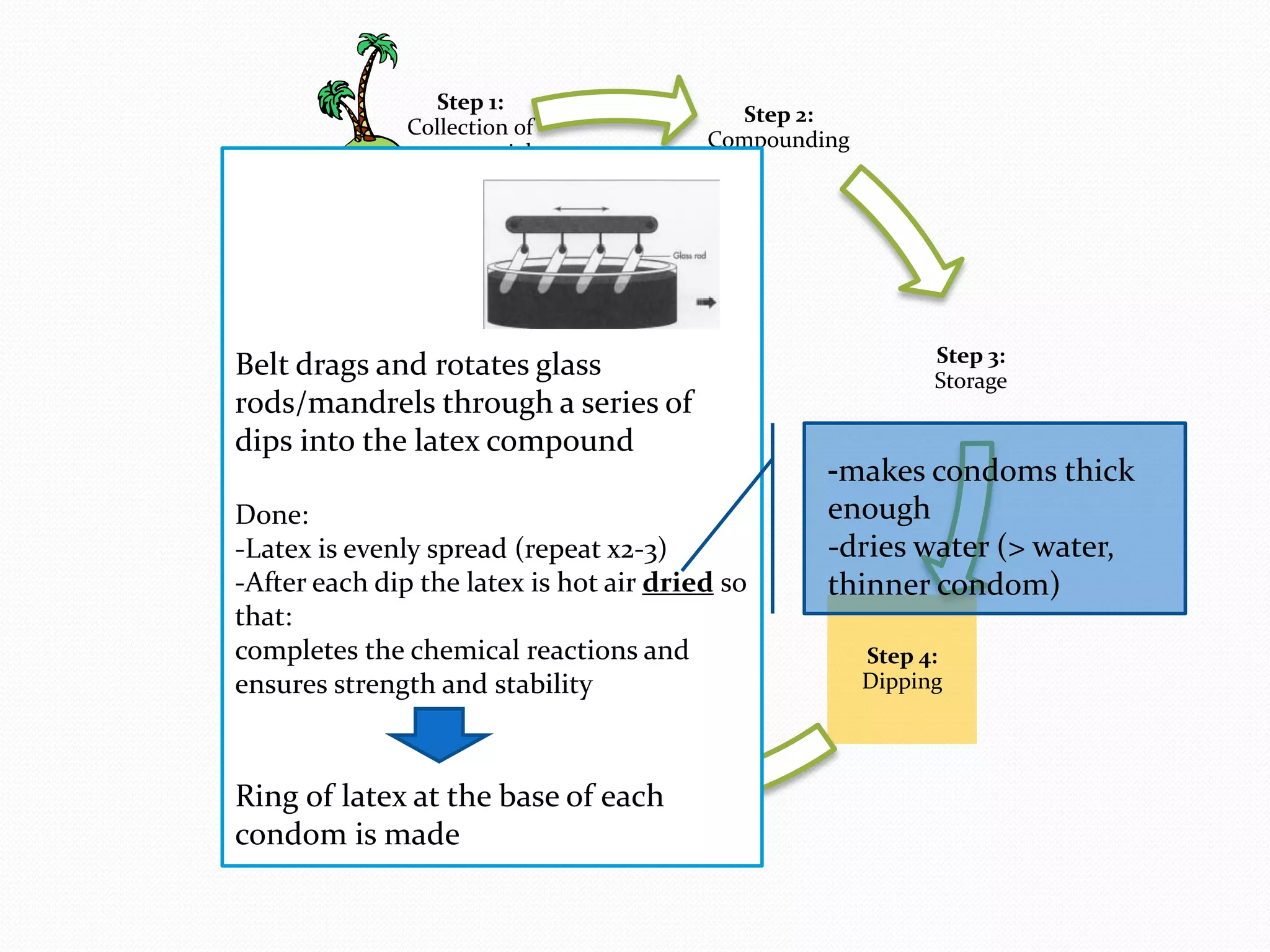
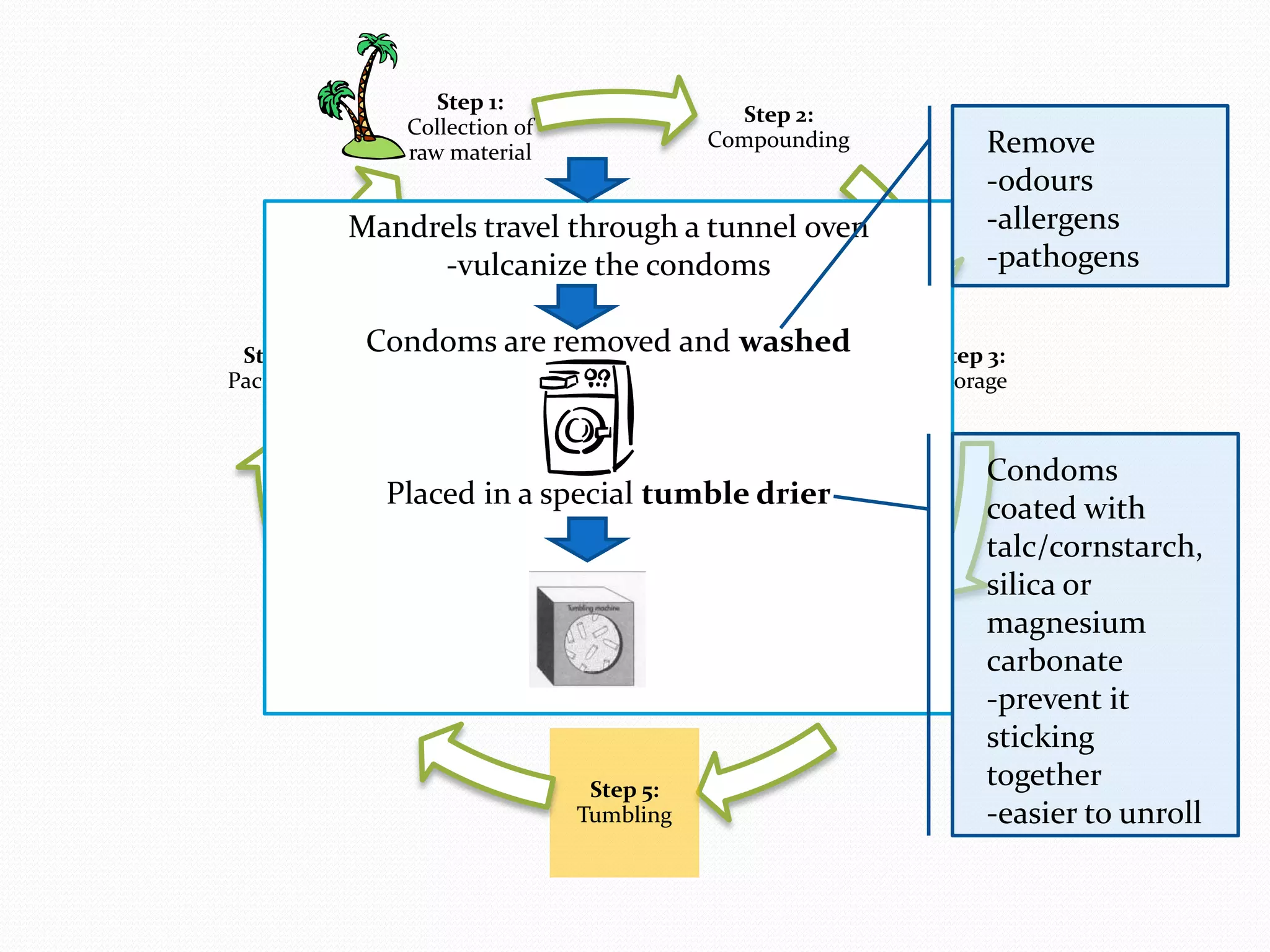
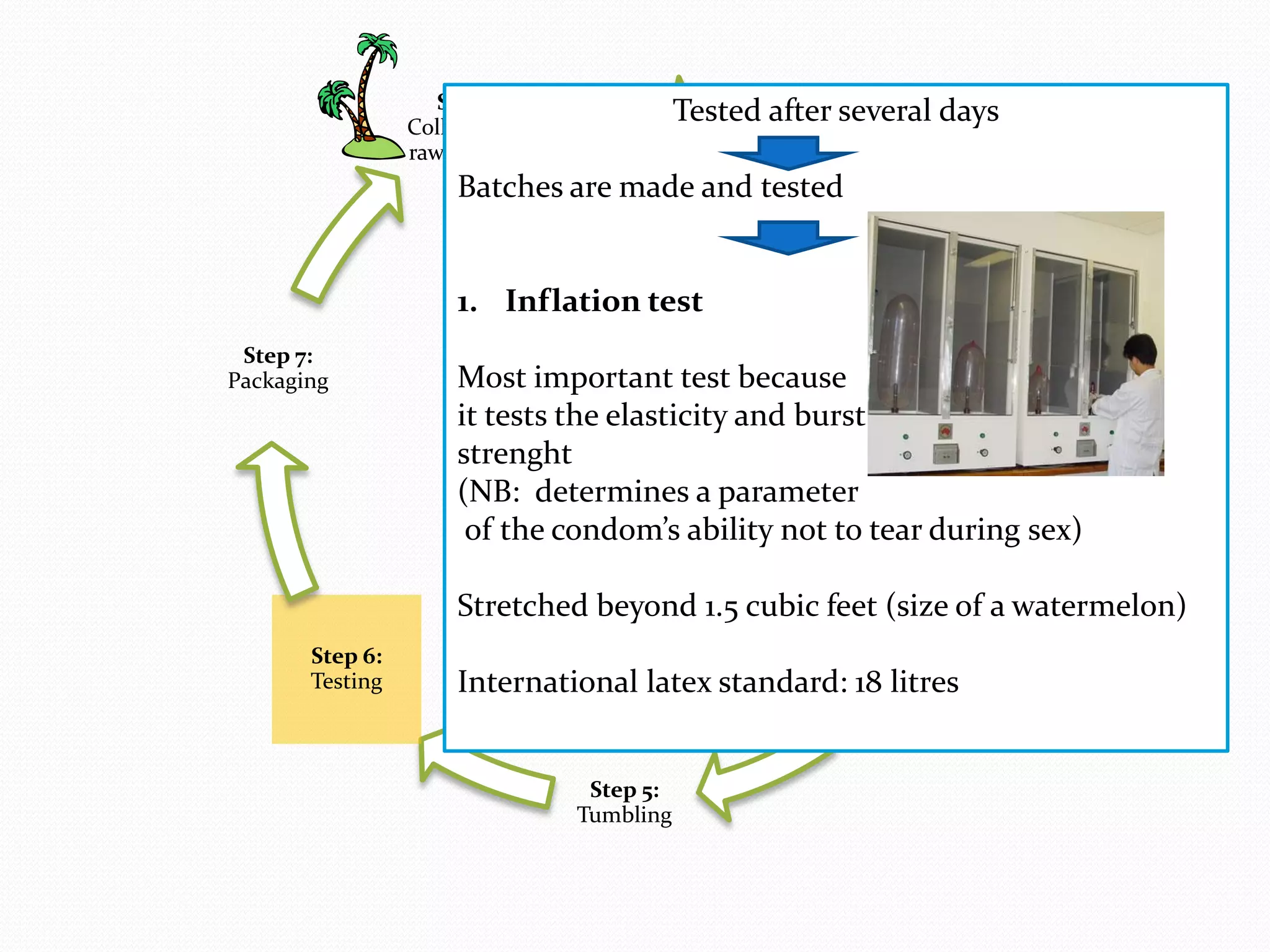
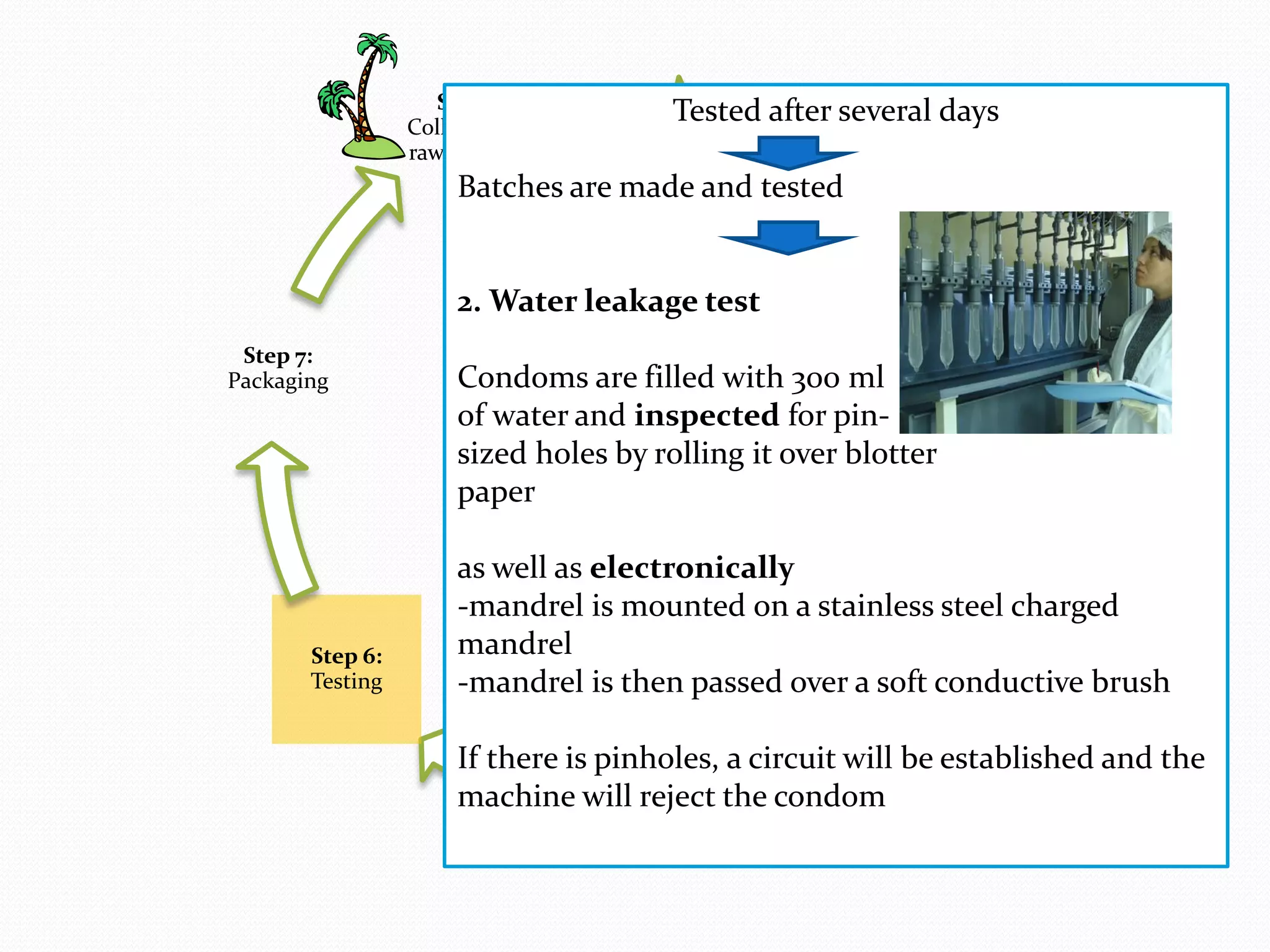
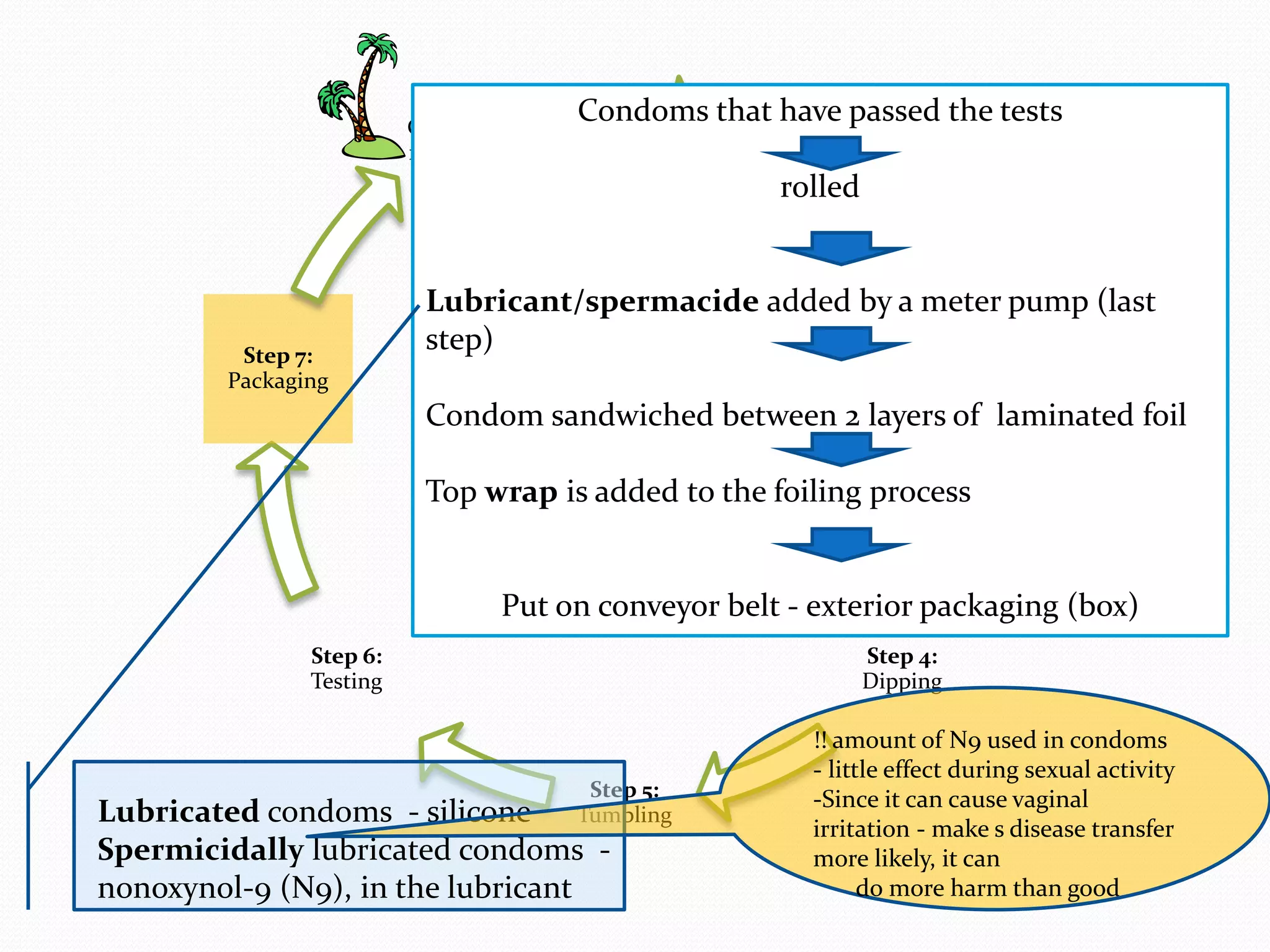
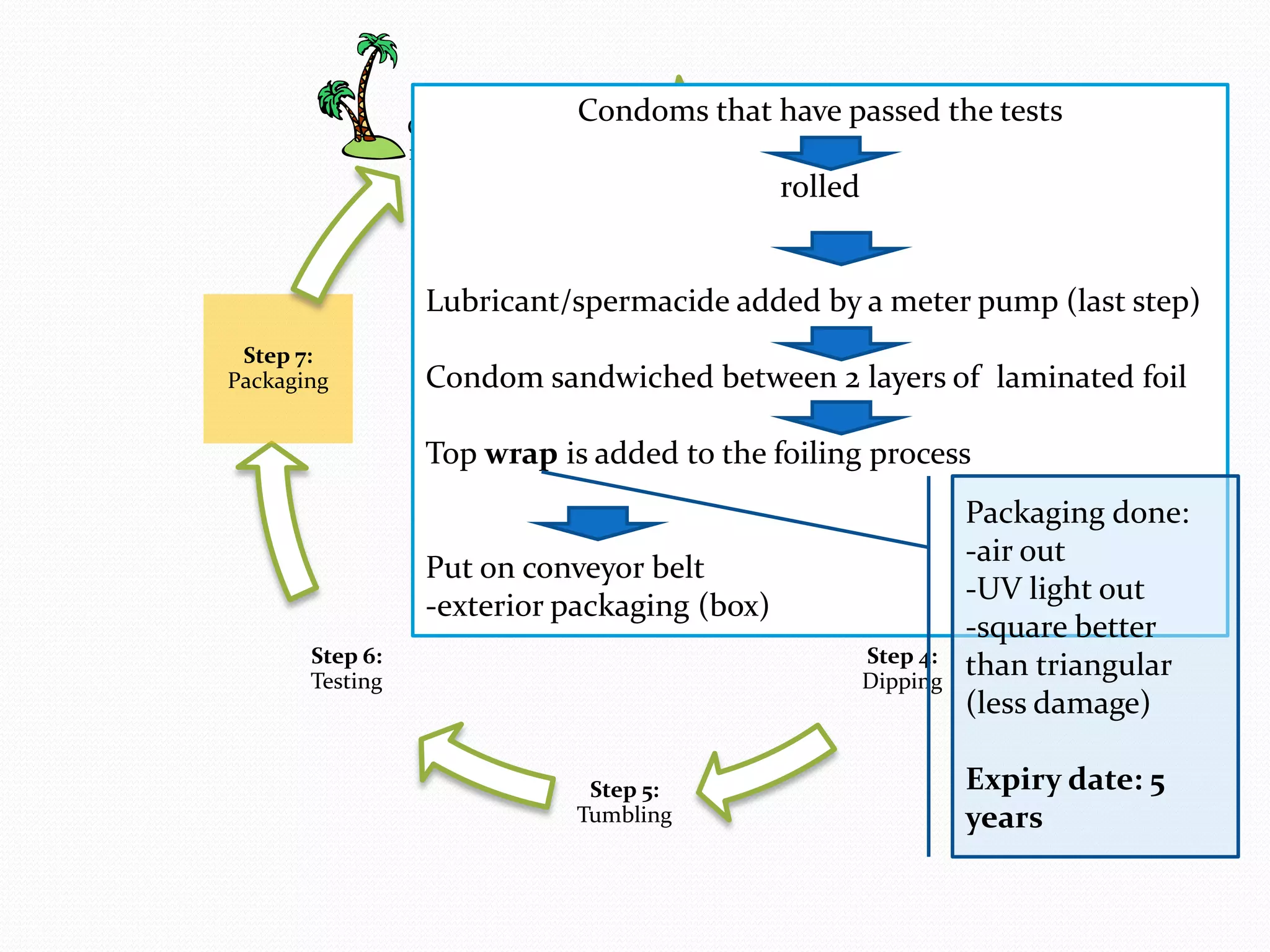
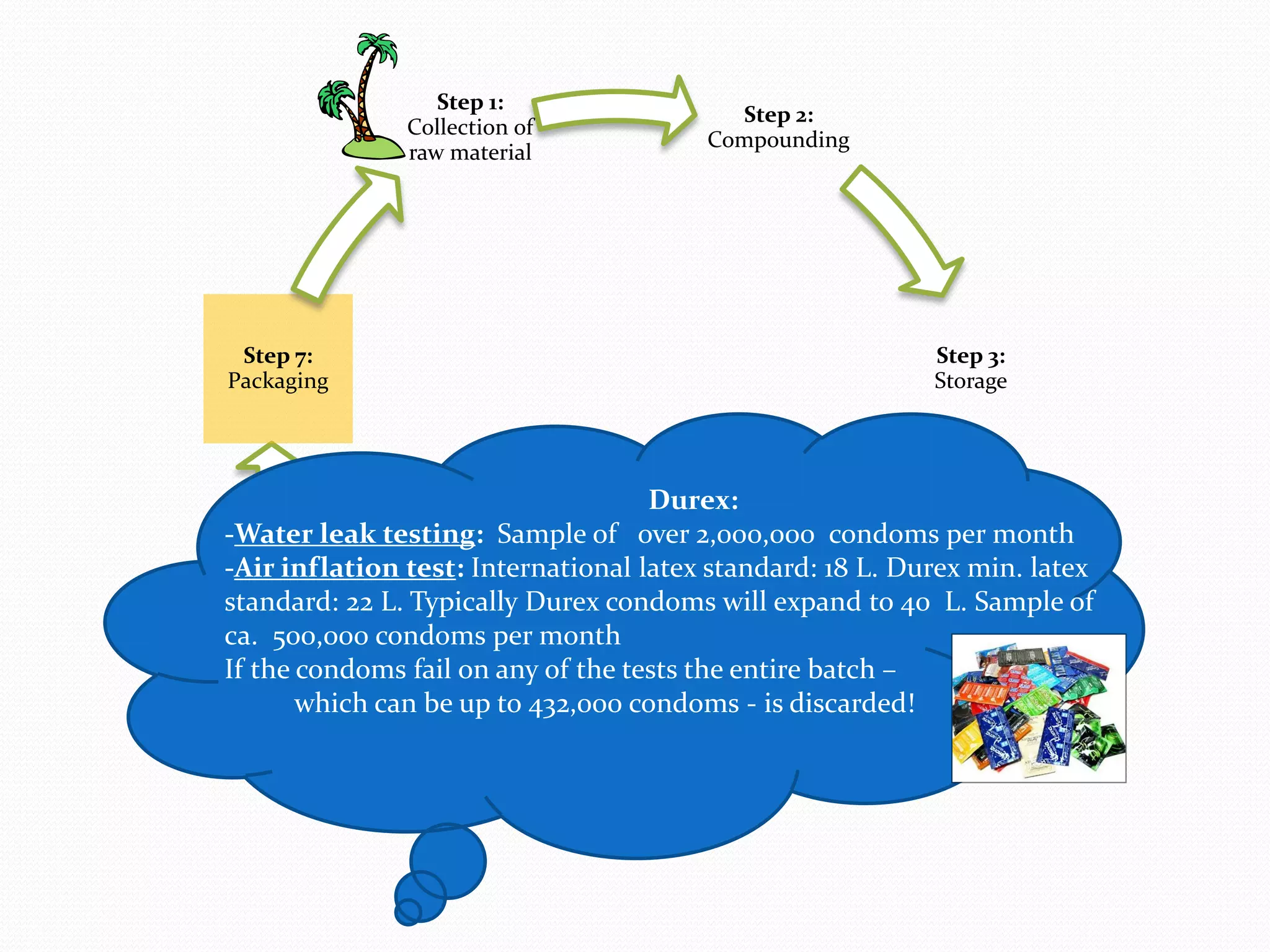
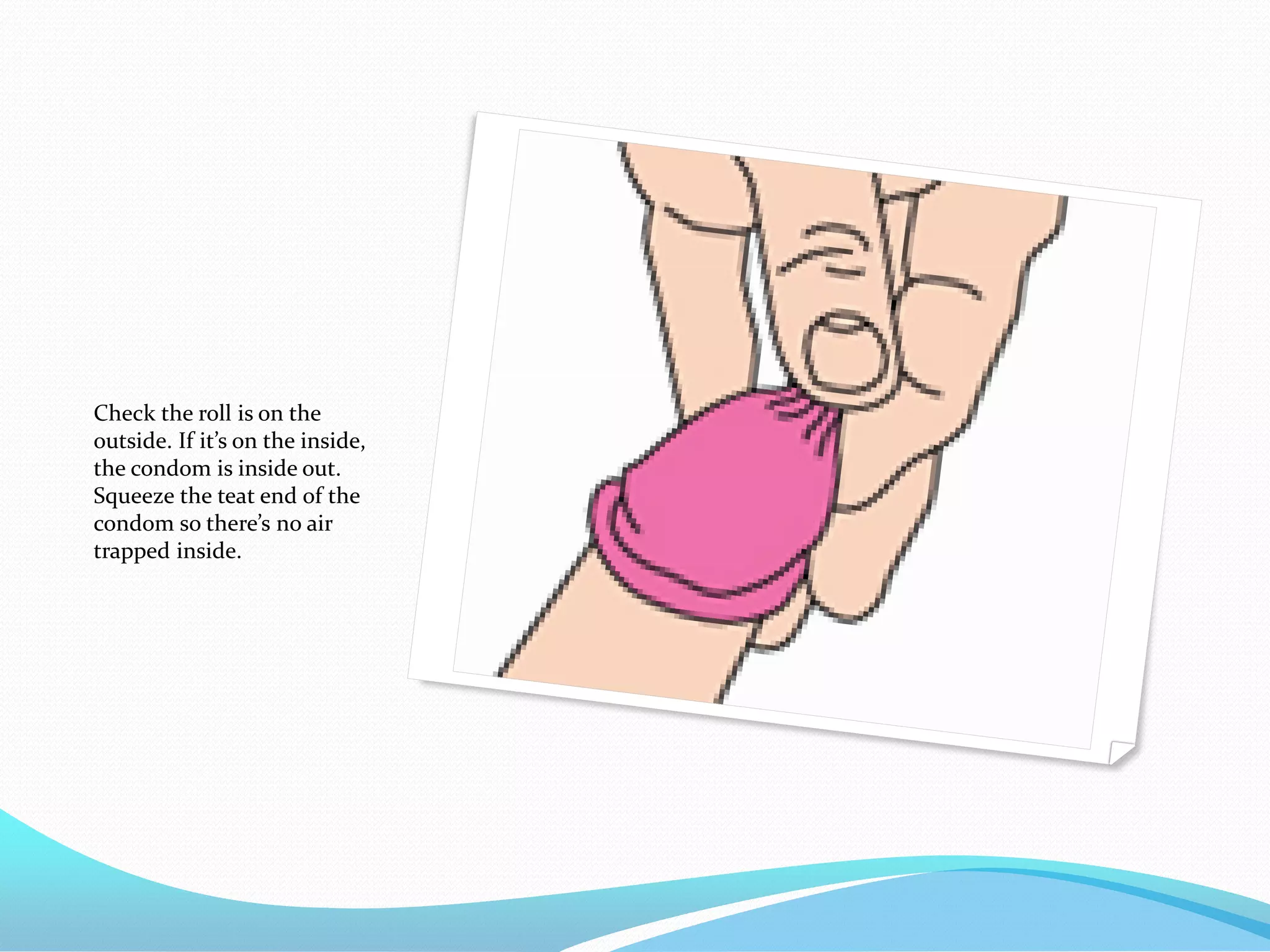
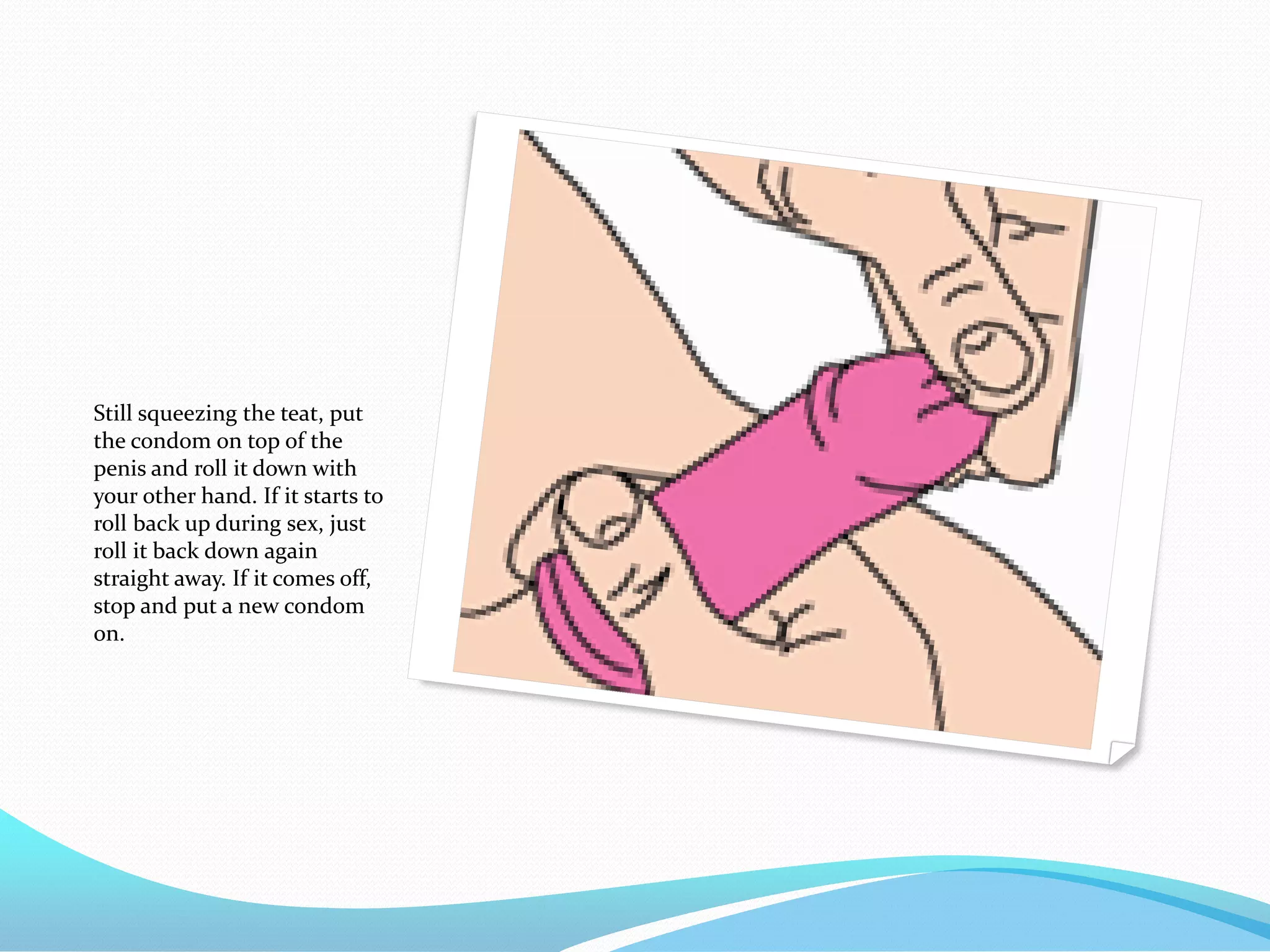
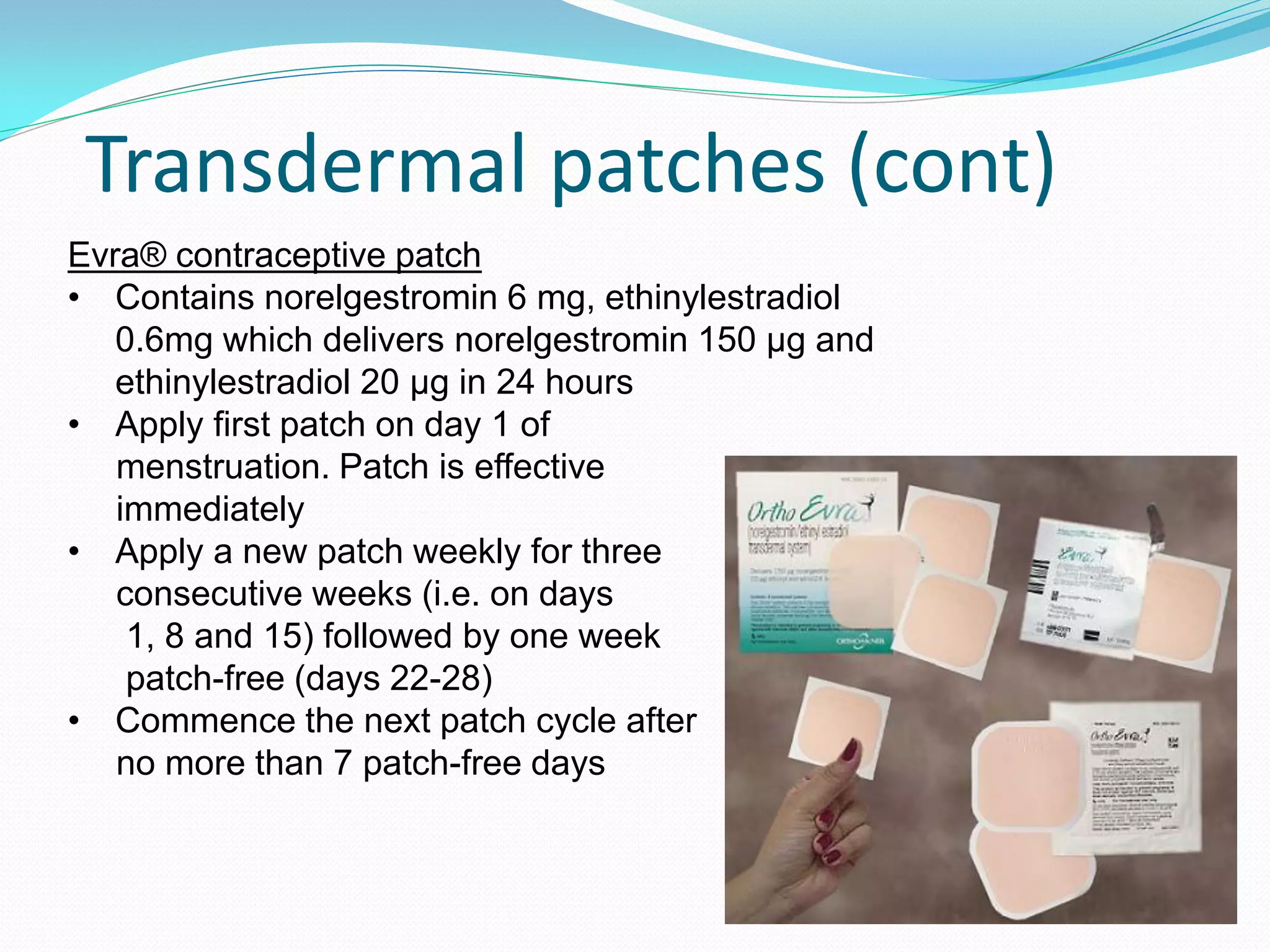
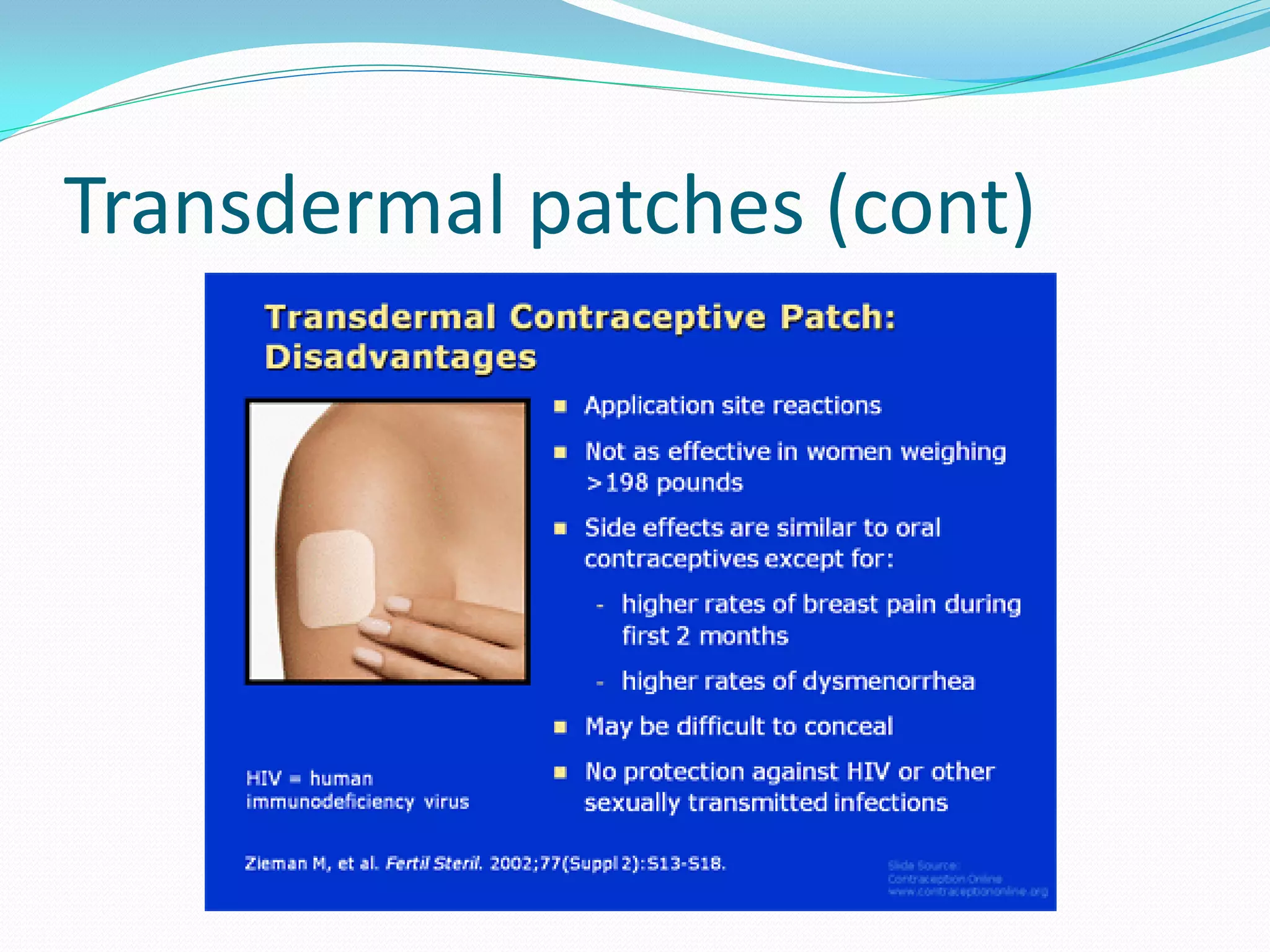
The document discusses various methods of administering hormonal contraceptives and drugs, including subcutaneous injectables, subcutaneous implants, intrauterine devices, and condoms. It provides details on the definition, mechanism of action, advantages, disadvantages, and examples of each method. Deep intramuscular injections and various types of intrauterine devices are explained in more depth. The manufacturing process of condoms is summarized in 7 steps from collection of raw materials to packaging.