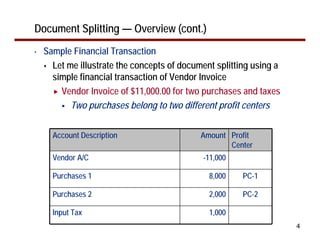
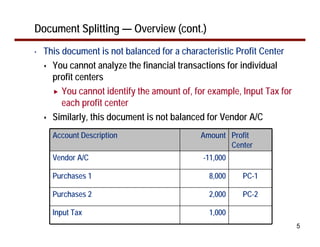
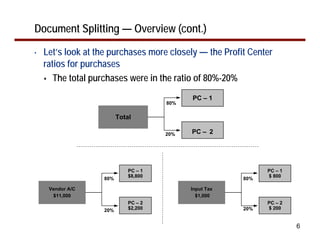
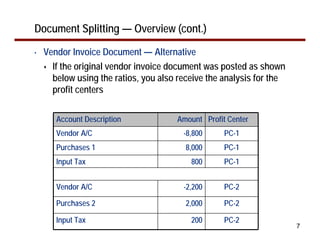
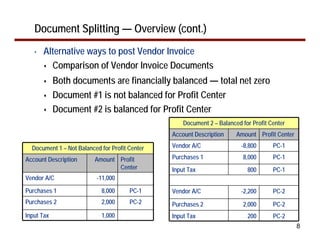
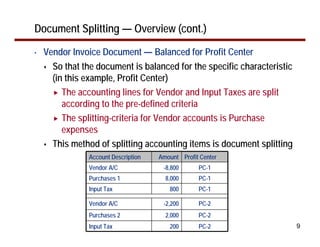
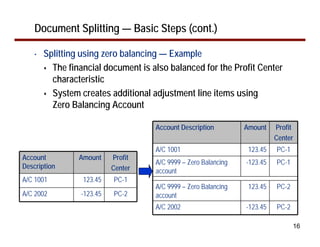
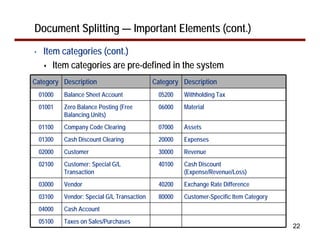
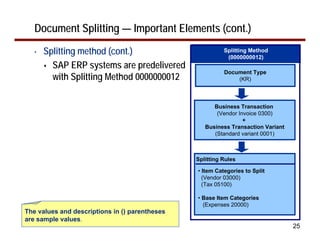
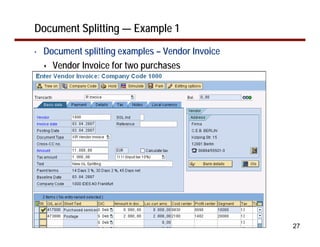
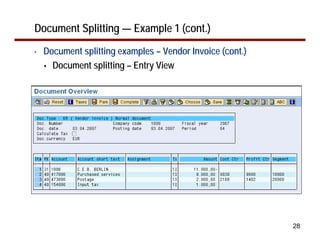
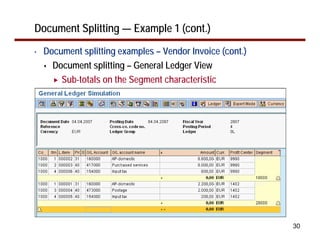
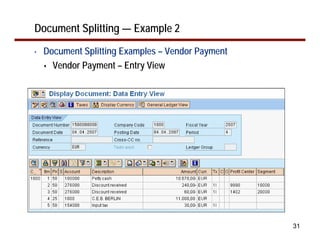
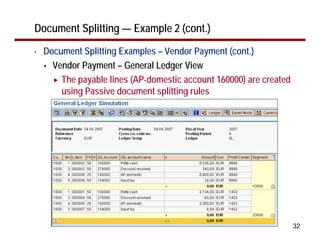
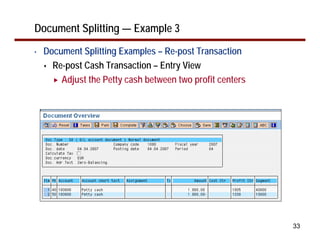
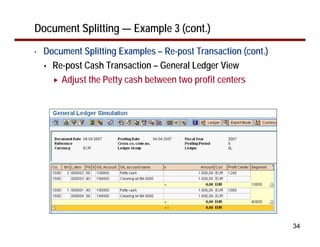
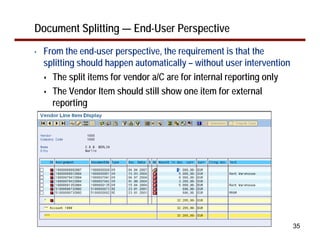
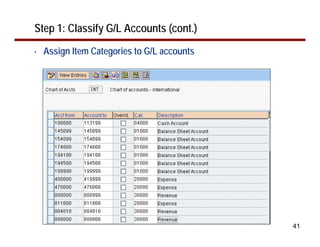
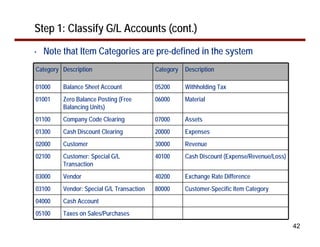
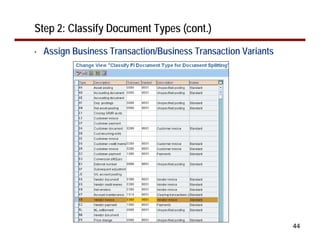
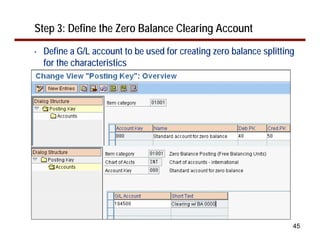
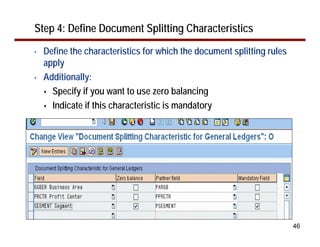
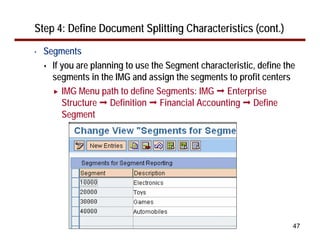
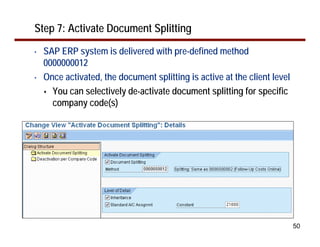
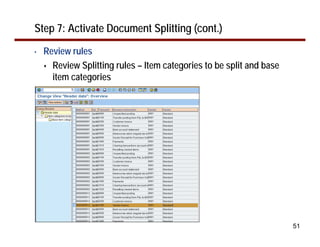
This document provides an overview of document splitting in SAP's new General Ledger. Document splitting allows accounting line items to be split according to specific characteristics like profit center or segment. This enables creation of financial statements for different entities to meet reporting requirements. The document outlines the basic steps of document splitting including passive, active, and zero balancing splits. It also discusses important elements like splitting rules, item categories, and transactions. Setup steps are provided along with examples to illustrate how document splitting works.