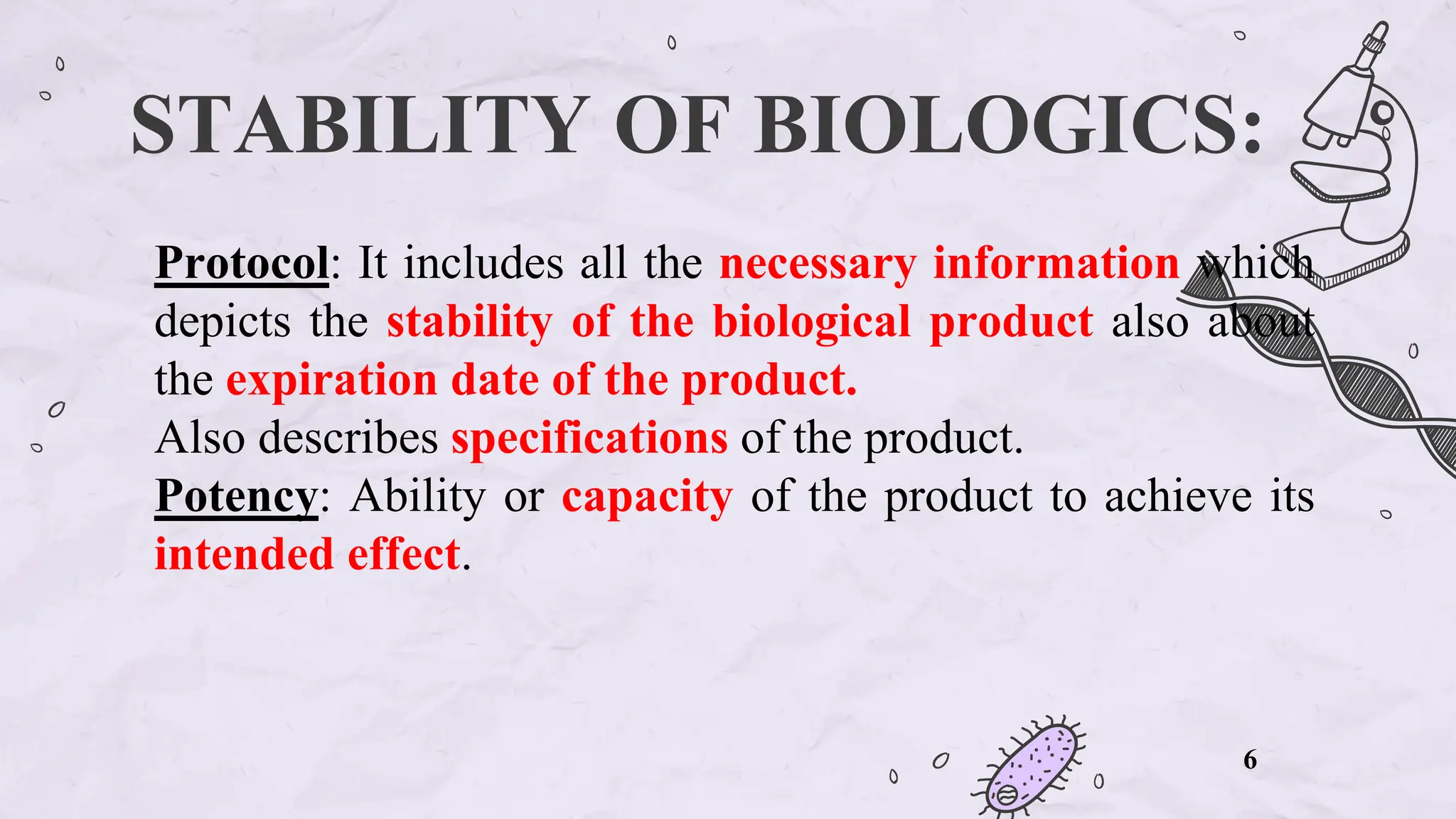
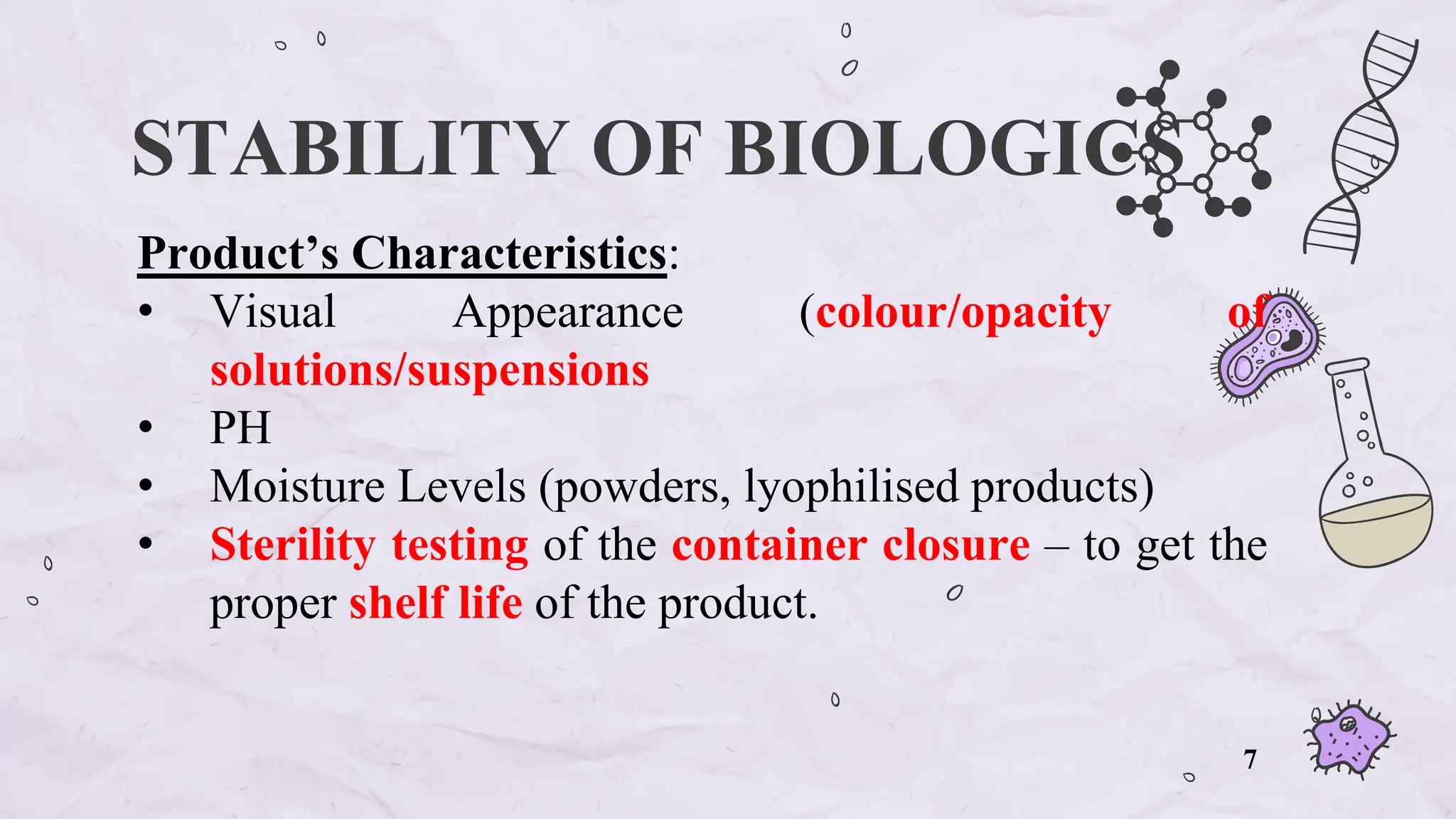
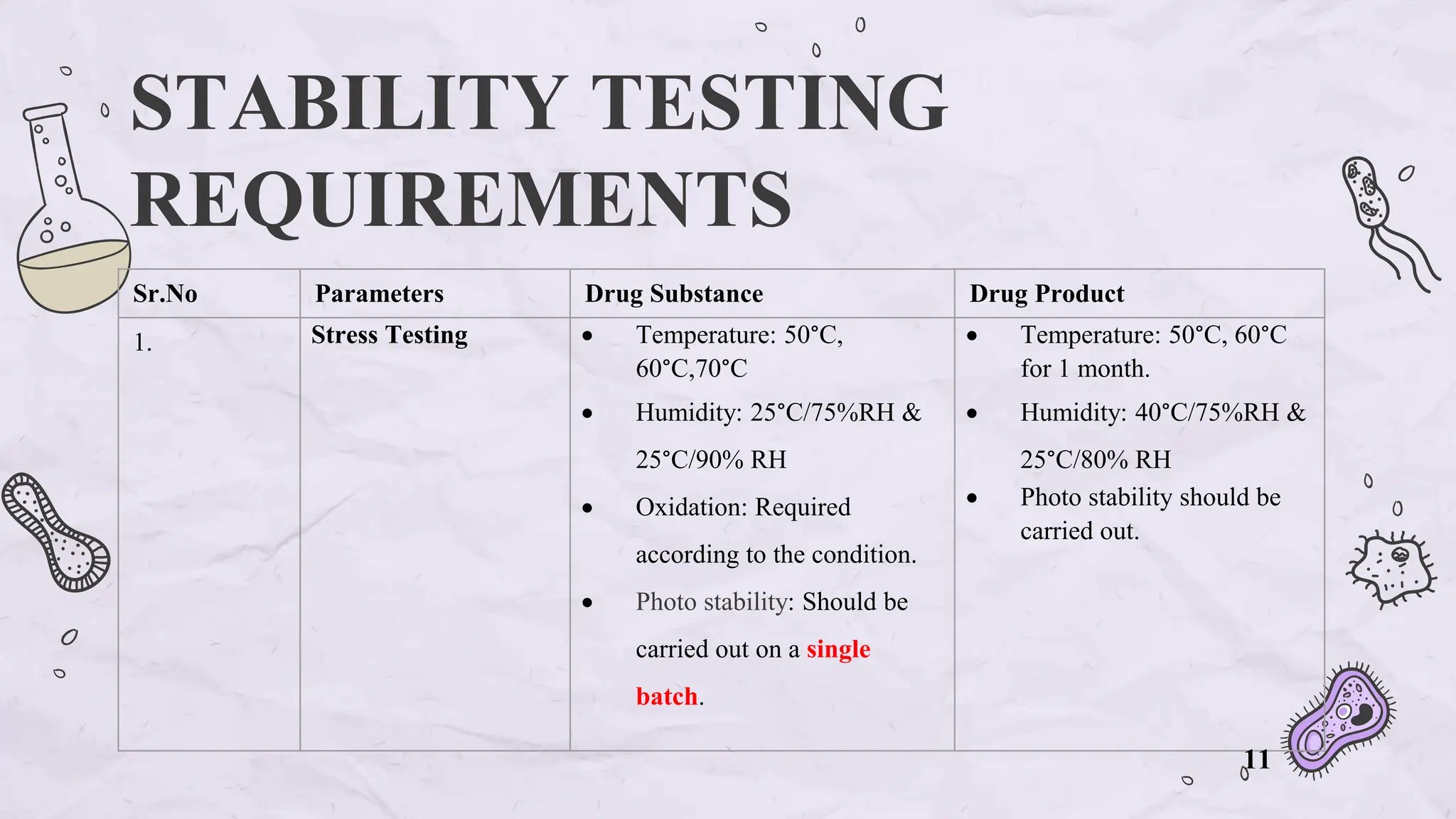
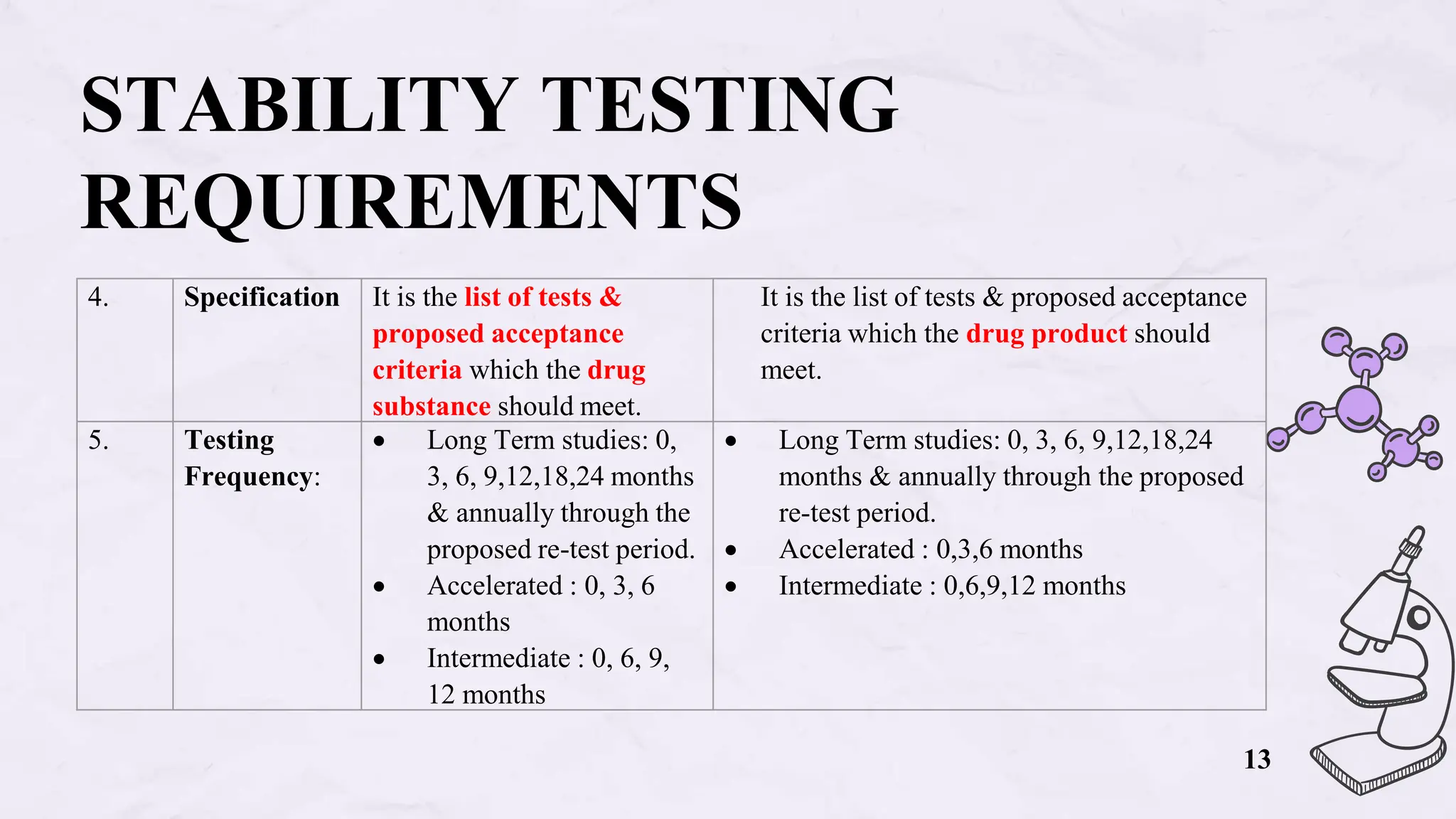
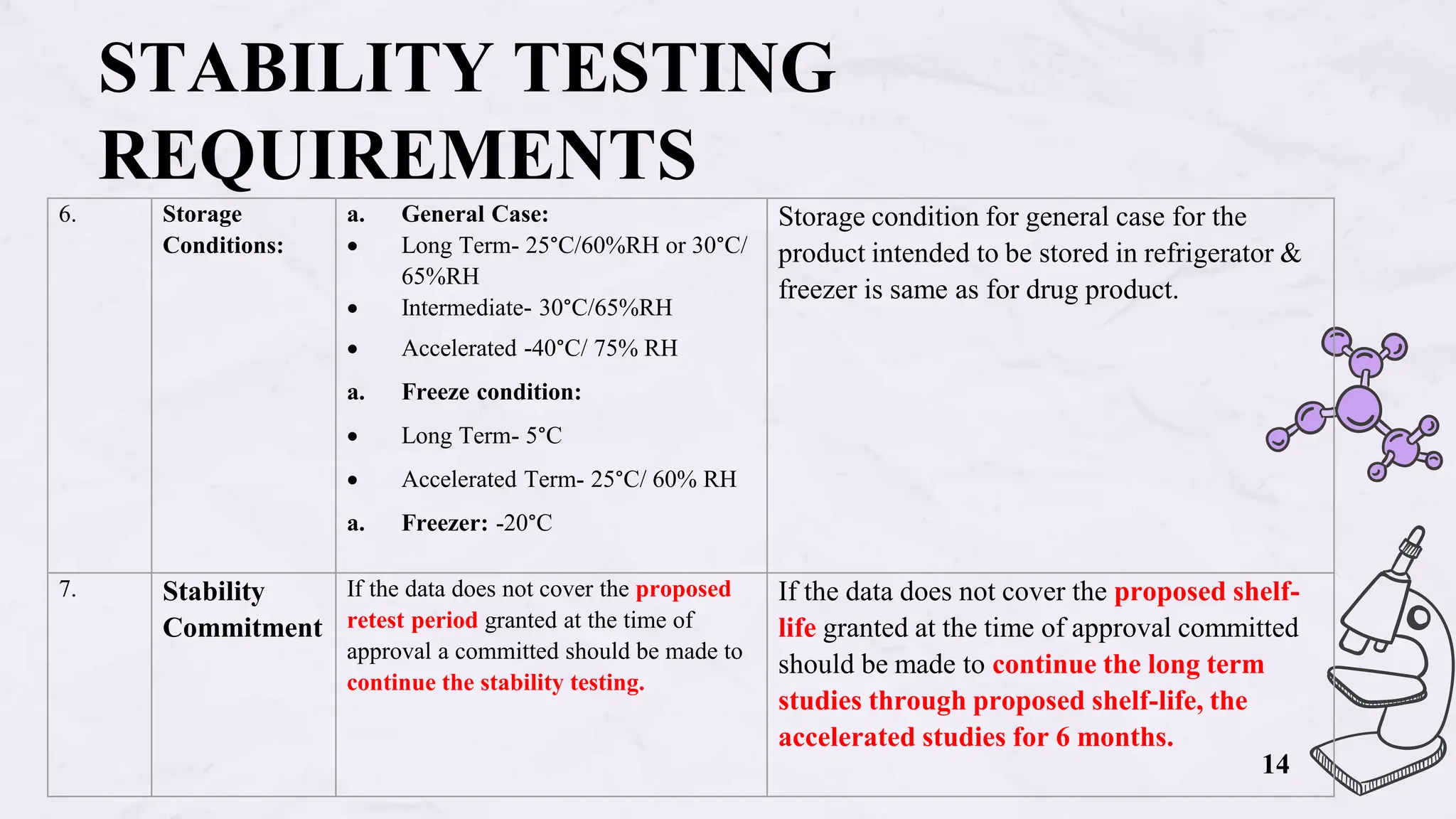
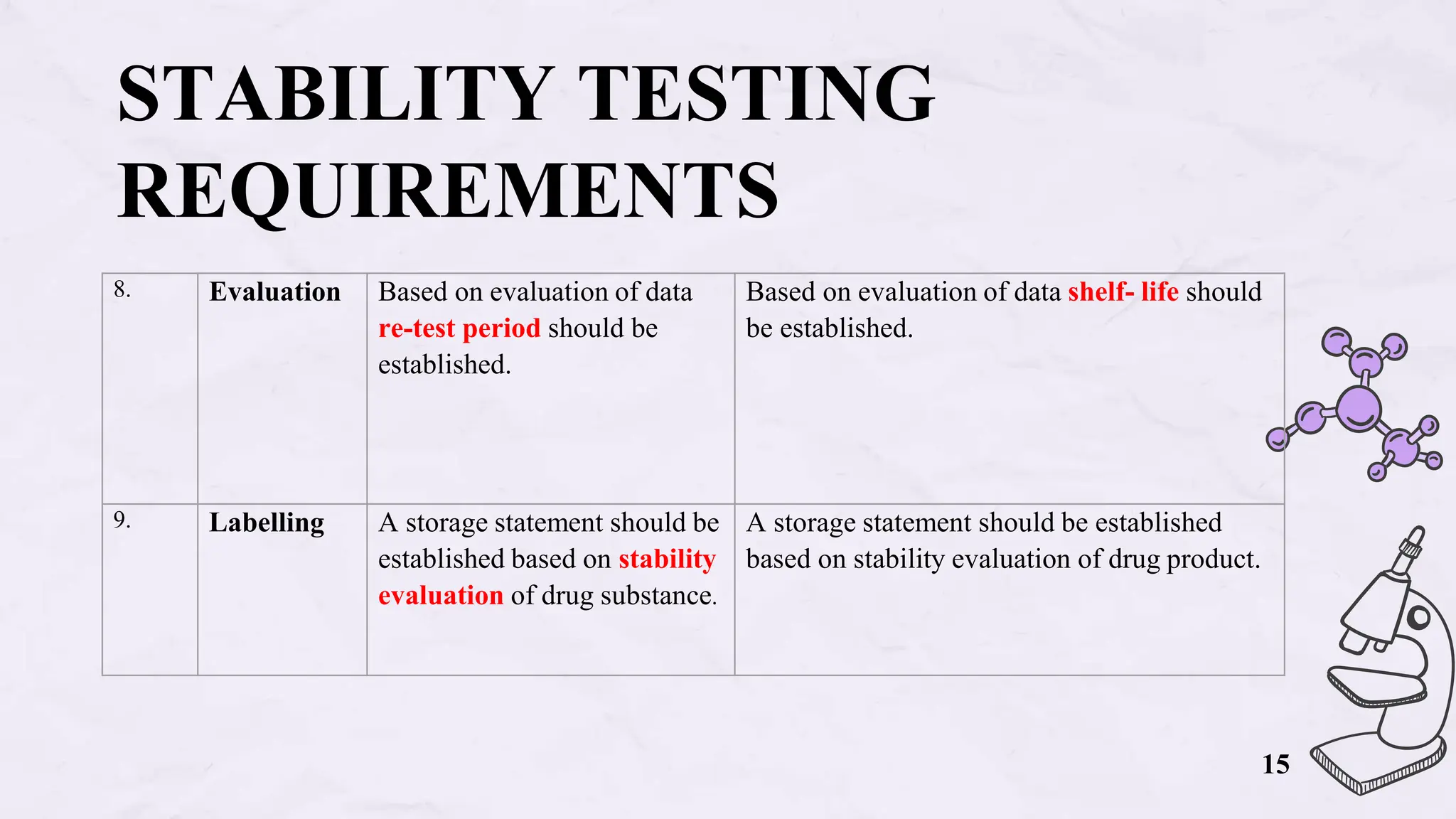
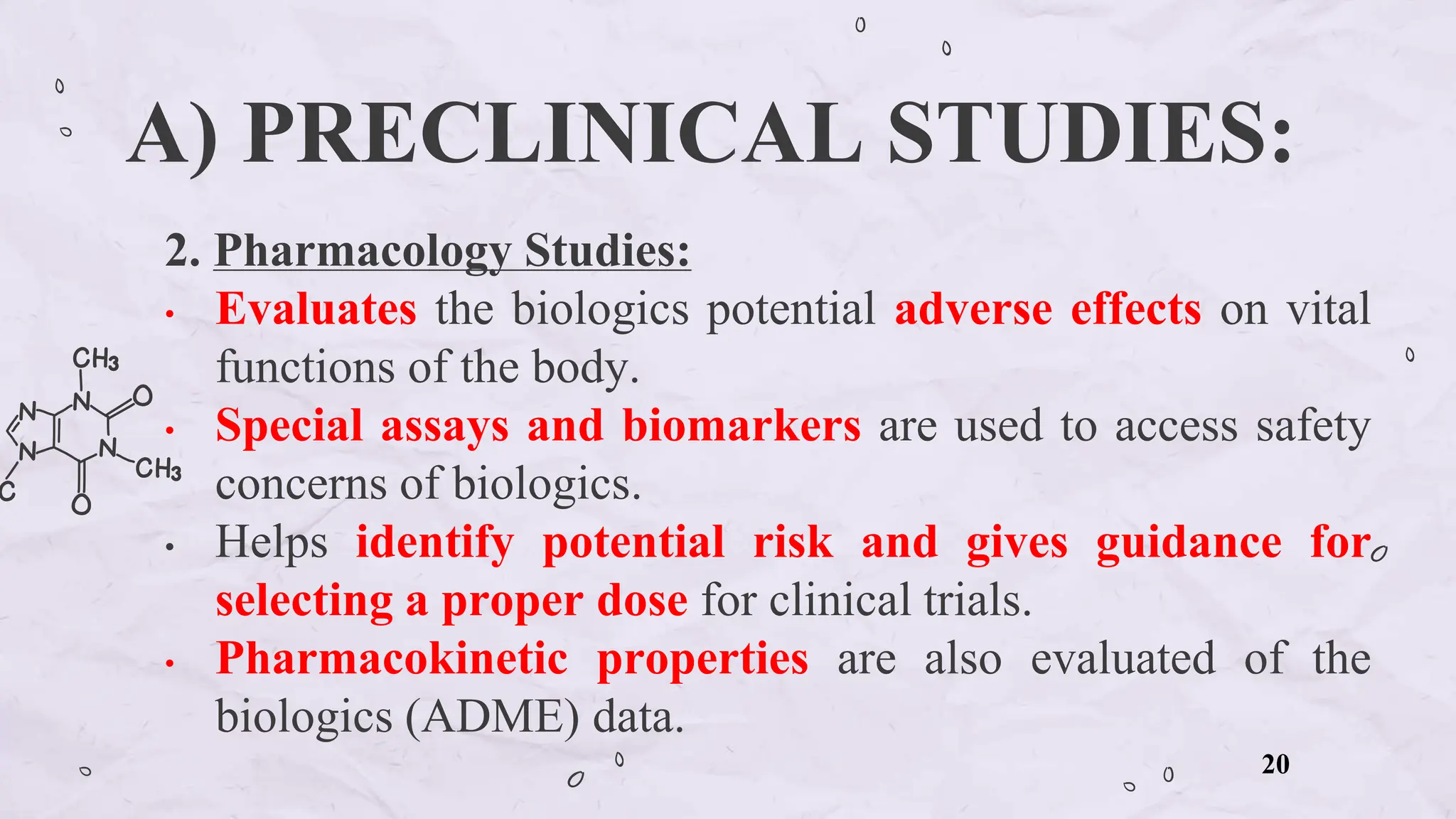
The document presents an overview of biologics in the EU, covering their stability, safety, labelling, packaging, and advertising regulations. It emphasizes the importance of stability testing, preclinical and clinical trials for ensuring safety, and distinct regulatory requirements between the EU and the USA. Key differences in advertising strategies and labelling practices are also highlighted, along with essential reference materials.