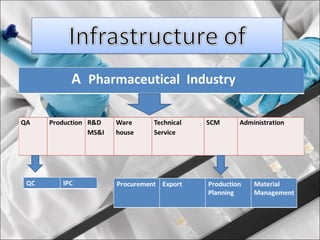
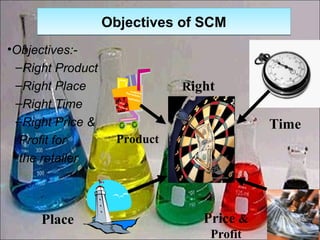
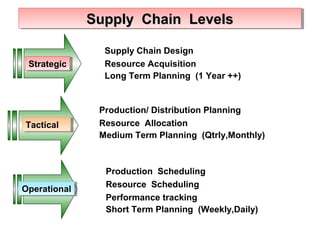
This presentation introduces pharmaceutical quality assurance and quality control. It discusses that quality assurance covers all aspects of production from raw materials to finished products. Quality control ensures drugs are safe, effective and consistent. The presentation covers in-process quality control, production processes like blending and milling, and quality control of the storage facility. It also discusses technology transfer requirements for pharmaceutical production like manufacturing instructions, analytical methods and batch records.