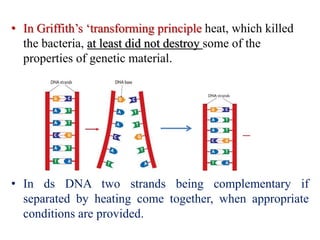
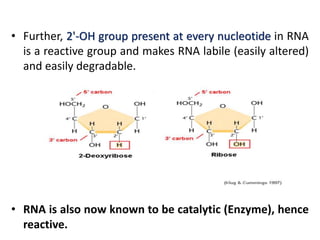
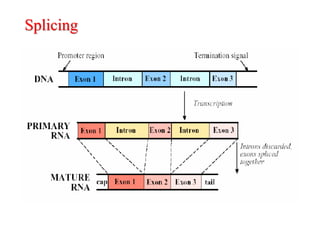
The document discusses the properties of DNA and RNA as genetic material. It notes that while DNA is the predominant genetic material, RNA performs important functions like messenger, adapter, and structural roles. The key criteria for a molecule to act as genetic material are the ability to replicate, be chemically and structurally stable, allow for mutations, and express traits. Both DNA and RNA can replicate, but DNA is more stable due to its double-stranded structure and lack of reactive groups. This stability makes it better suited for long-term storage of genetic information, while RNA's ability to directly code for proteins makes it better for transmitting information. The document suggests RNA may have initially served as the first genetic material.