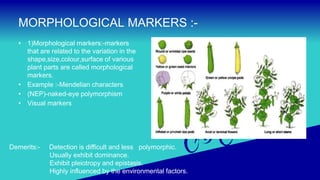
Genetic markers are used to distinguish individuals, populations and varieties based on their DNA sequences and location in the genome. The document discusses different types of genetic markers - morphological, biochemical and molecular markers. It provides details about various molecular marker techniques like RFLP, RAPD, AFLP, CAPS, SNP and SSR. Ideal molecular markers should be highly polymorphic, co-dominant, multiallelic and not influenced by the environment. The techniques help in identifying variations at DNA level which are useful for crop improvement programs.