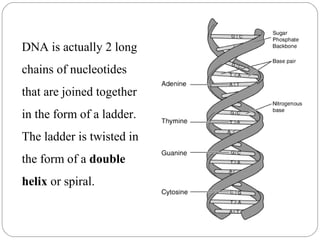
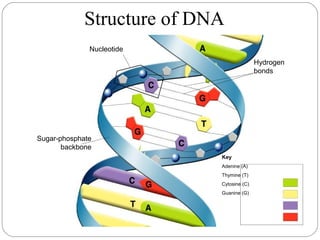
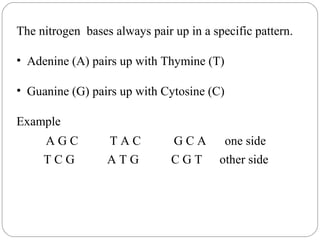
DNA is made up of nucleotides that form a double helix structure. Each nucleotide contains a phosphate group, deoxyribose sugar, and one of four nitrogen bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, or thymine. The bases always pair up in a specific pattern between the two strands - adenine pairs with thymine and guanine pairs with cytosine. This sequence of base pairs contains the genetic code that provides instructions for building and sustaining life. DNA replicates through a process where the strands separate and each base seeks out its complement to form two new, identical DNA molecules.