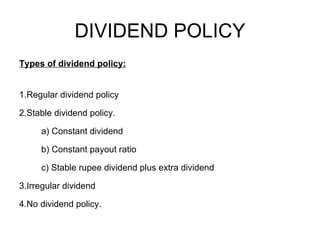
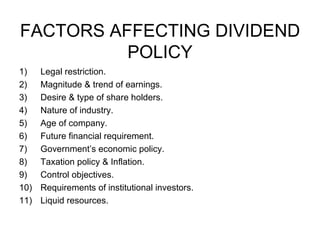
Dividend decisions involve determining what proportion of a firm's equity earnings to pay out to shareholders as dividends, and what proportion to retain for reinvestment. There are two main theories on dividend policy - the relevance theory and the irrelevance theory. The relevance theory posits that dividend decisions impact share prices and firm value, while the irrelevance theory argues that dividend policy does not affect these. The document then discusses various dividend theories and models, types of dividend policies, and factors that influence a firm's dividend policy decisions.