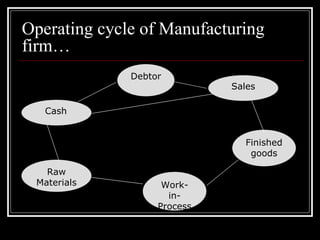
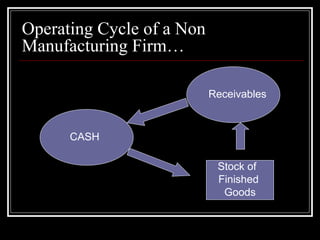
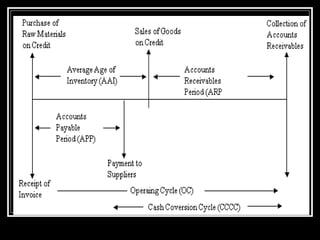
The document discusses methods for estimating a company's working capital requirements. It outlines a four step process: 1) estimating the cash costs of current assets like raw materials, work-in-process, and finished goods inventory, 2) estimating current liabilities like creditors and expenses, 3) calculating net working capital, and 4) adding a contingency percentage. It also describes how to calculate key working capital metrics like operating cycle and cash conversion cycle using formulas involving inventory, accounts receivable, accounts payable, cost of goods sold, and sales figures.