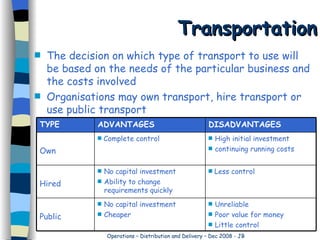
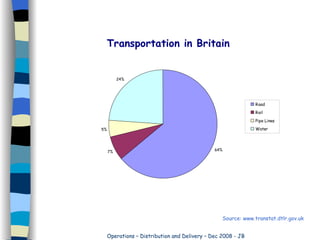
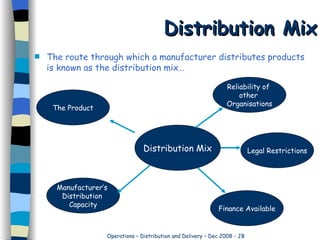
Organizations require warehousing facilities to bulk store goods. Warehouses allow for quick fulfillment of demand and efficient storage depending on stock levels, finances, and customer locations. Transportation methods are chosen based on costs, control, and ability to change requirements. Road transport is most common in Britain but faces issues like high costs, traffic, and restrictions that limit its effectiveness. Rail transport has decreased as roads face constant pressure.