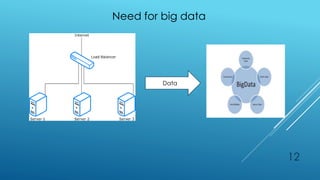
This document discusses distributed load balancing across multiple data centers. It aims to achieve load balancing using a distributed system to increase performance and resource utilization, and to analyze large amounts of data using Hadoop. The key objectives are to distribute dynamic local workloads across nodes in cloud computing to avoid single points of failure, and to efficiently analyze huge amounts of data from data centers.