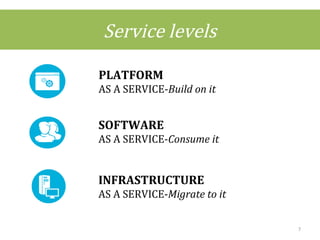
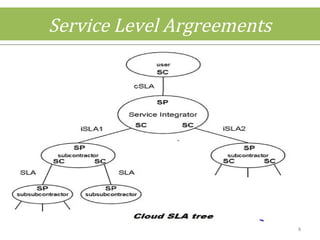
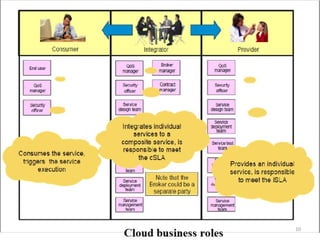
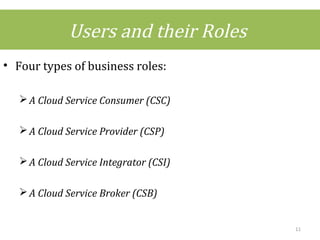
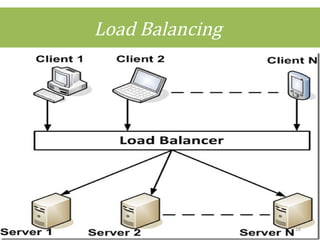
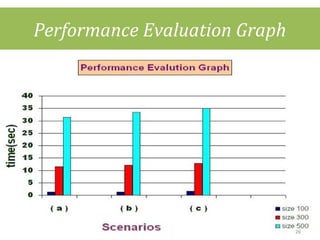
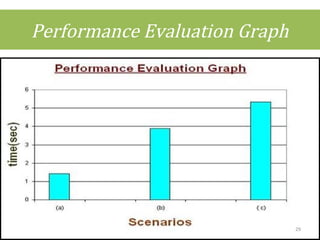
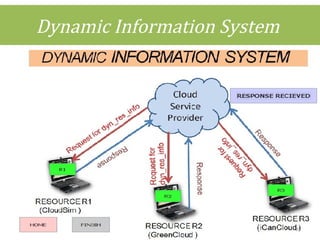
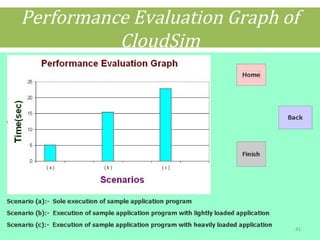
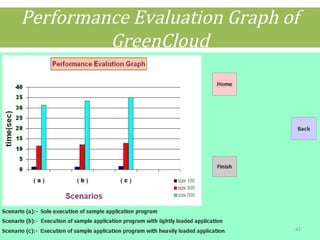
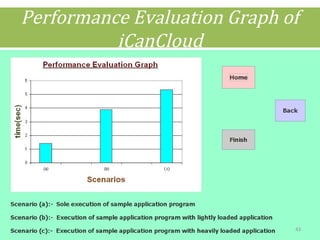
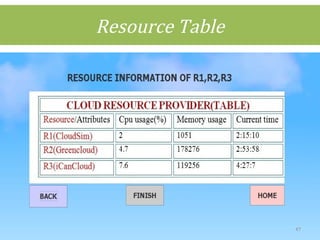
This document discusses cloud computing concepts including definitions, architecture, service models, and simulation tools. It summarizes a student project presentation on cloud computing that examines key aspects like scalability, pay-per-use model, and virtualization. It also evaluates cloud simulators CloudSim, GreenCloud and iCanCloud, comparing their features, scenarios and performance graphs. The document proposes a novel load balancing approach and its implementation through a dynamic information system interface.