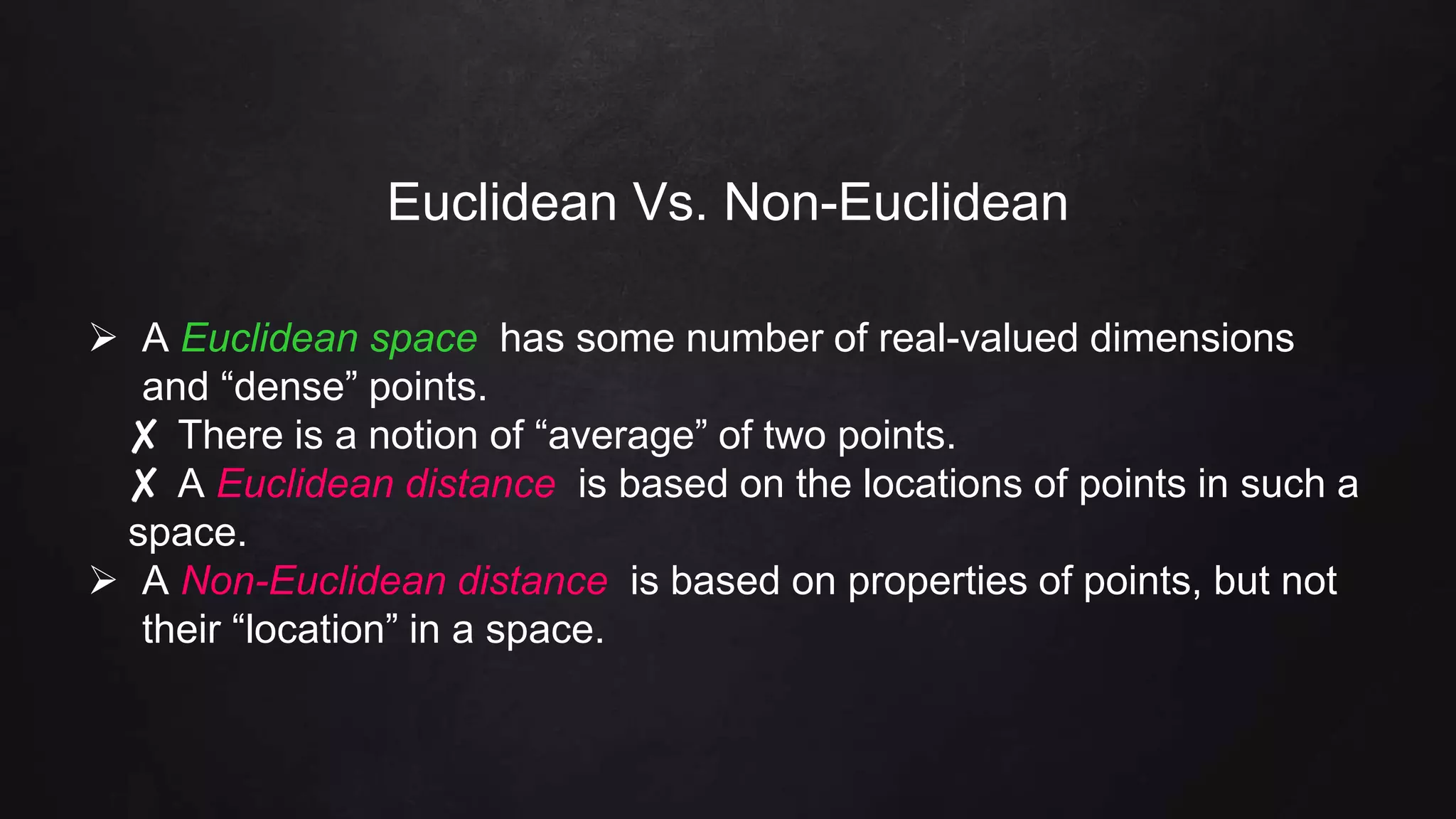
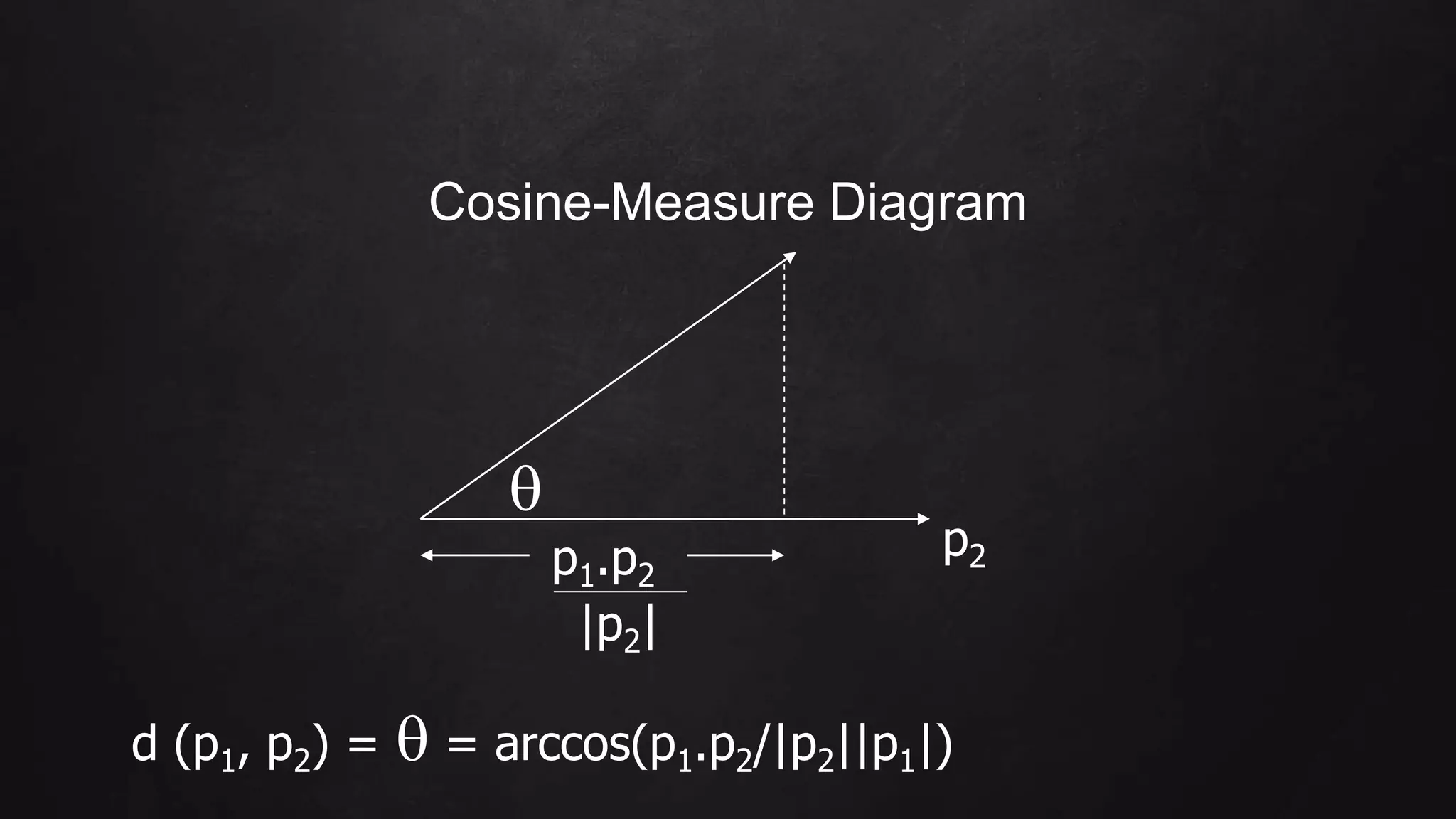
This document discusses different types of distance measures. It defines four axioms that a distance function must satisfy: being positive, only equal to 0 if points are identical, symmetric, and satisfying the triangle inequality. There are two major classes of distance measures - Euclidean and non-Euclidean. Euclidean distances are based on the location of points in a space, while non-Euclidean distances are based on other point properties. Examples of different distance measures are provided, including L1, L2, Jaccard, cosine, edit, and Hamming distances.