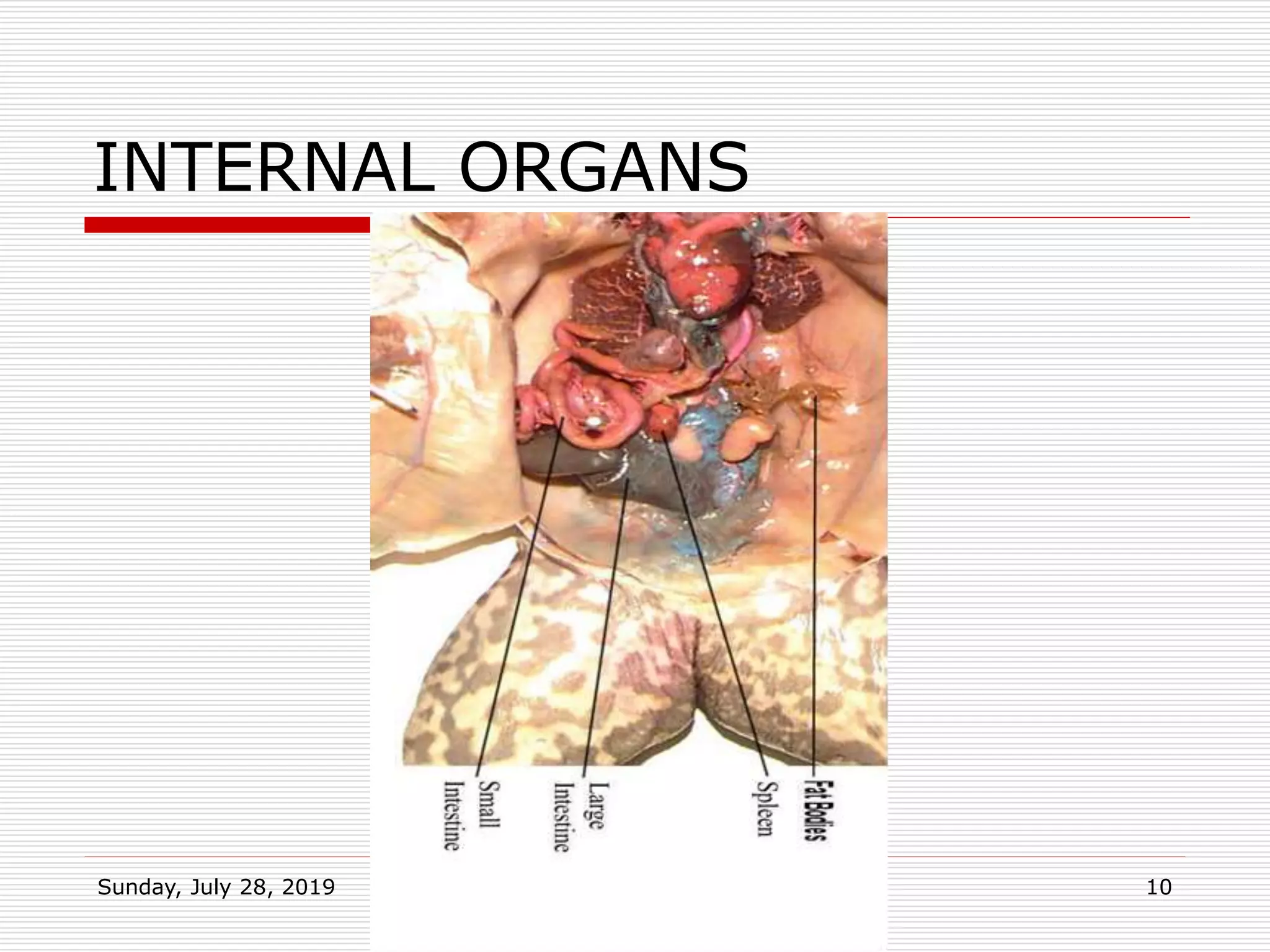
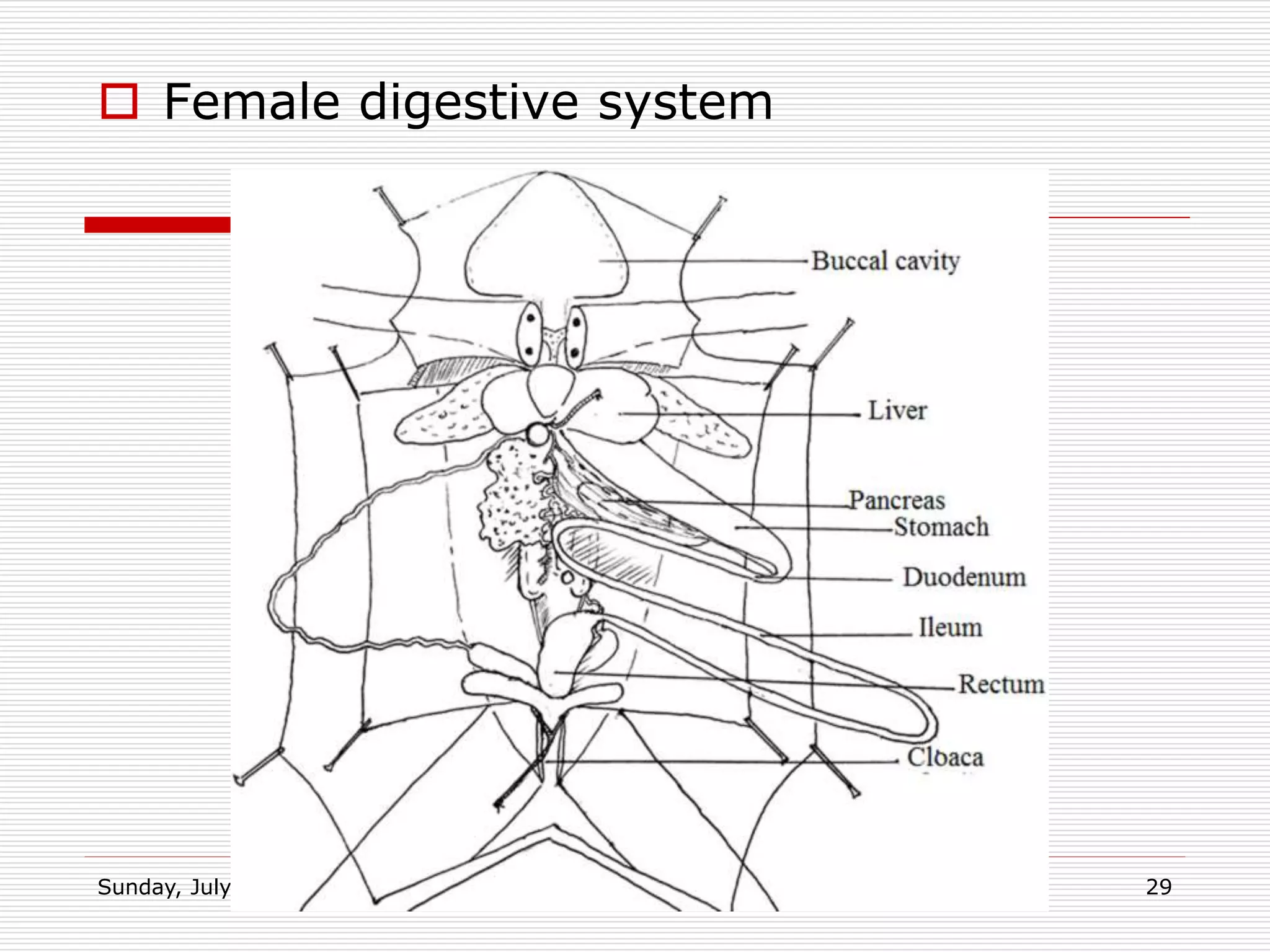
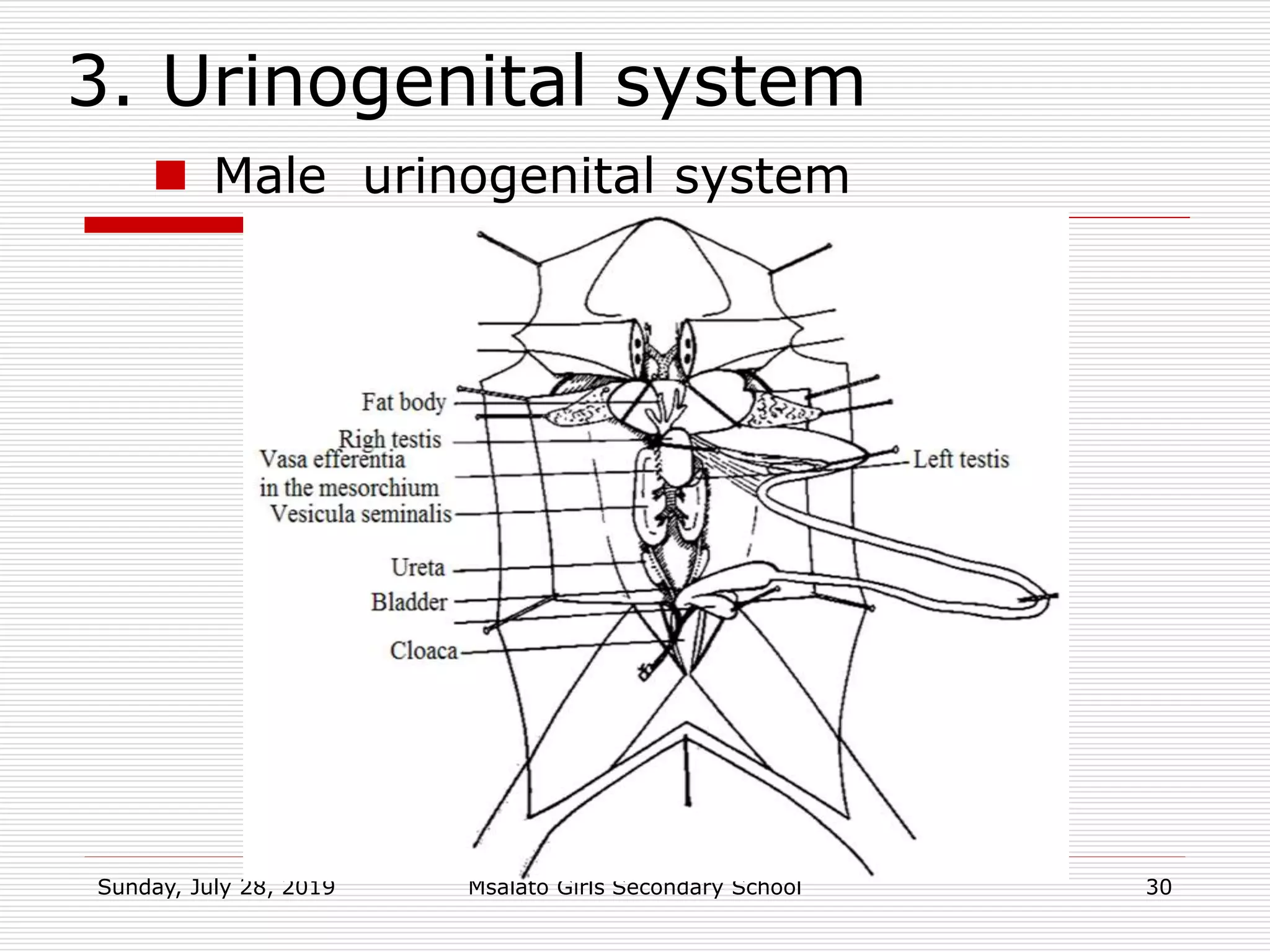
The document provides information about distinguishing male and female frogs both externally and internally. Externally, males are smaller and brighter in color, have thicker forelegs and nuptial pads, while females have a more visible cloaca. Internally, males have testes and sperm ducts and females have ovaries, oviducts, and a visible cloaca. The document also outlines the digestive, urinary, and reproductive systems of frogs and their key adaptations for living both on land and in water.