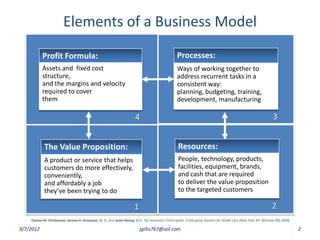
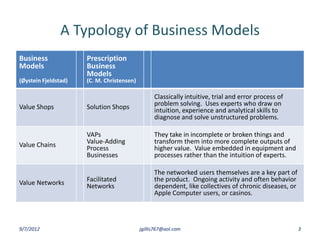
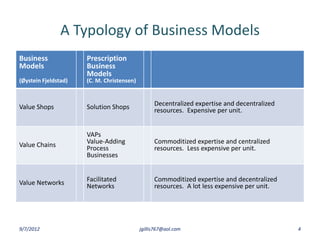
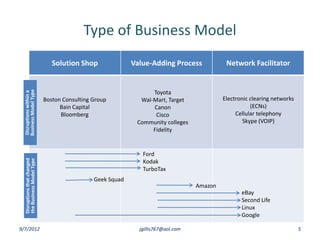
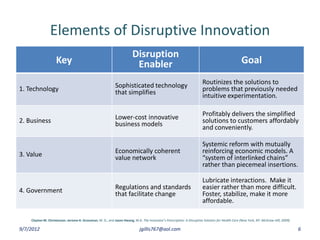
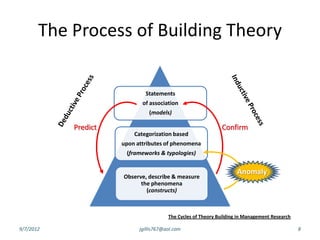
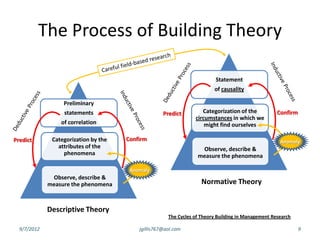
The document discusses disruptive innovation in health care as proposed by Clayton M. Christensen and others, focusing on business models such as value shops and value chains. It outlines key elements of disruptive innovation, including the role of technology, cost-effectiveness, and the importance of economic coherence. Additionally, it touches on cycles of theory building in management research.