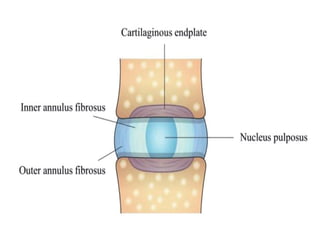
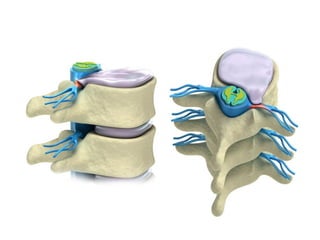
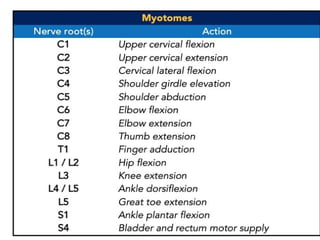
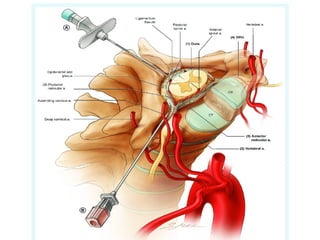
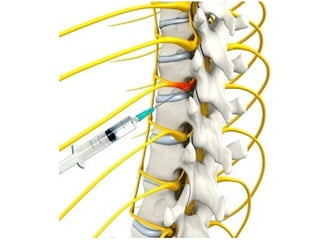
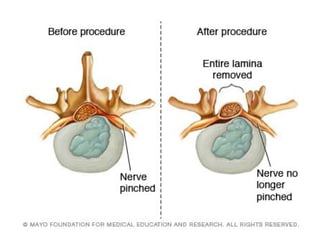
Disc herniation occurs when the nucleus pulposus protrudes through the annulus fibrosus, commonly due to degenerative changes or trauma, primarily affecting the lumbar and cervical spine. Symptoms include localized back pain, numbness, weakness, and radiating pain in the distribution of the affected nerve root. Conservative treatments like NSAIDs and physical therapy are first-line interventions, while surgical options may be necessary for severe cases.