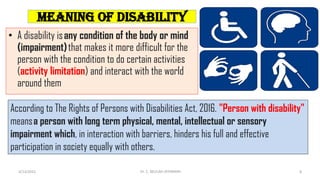
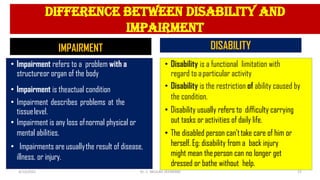
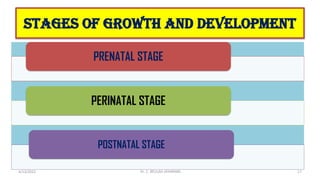
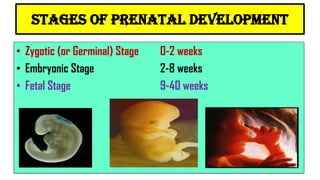
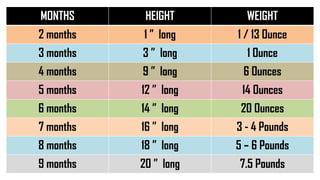
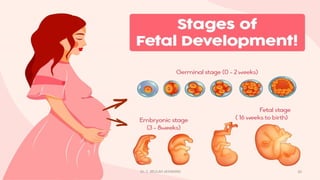
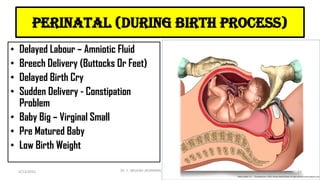
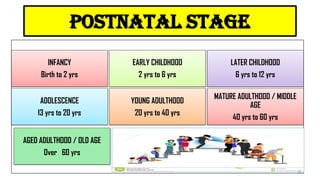
The document discusses the concept of disability, including its definitions, types, characteristics, causes, and the distinction between disability and impairment. It highlights the need for inclusive education and describes various disabilities such as hearing, visual, speech impairments, and others. Additionally, it addresses the developmental stages and factors affecting disabilities, underscoring the impact on an individual's ability to perform daily activities.