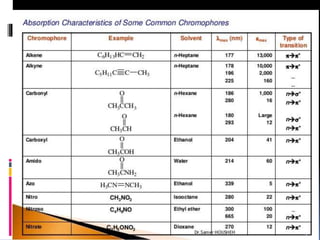
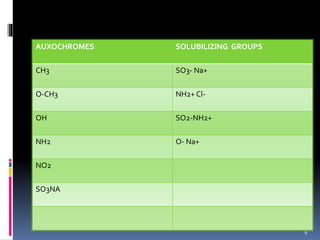
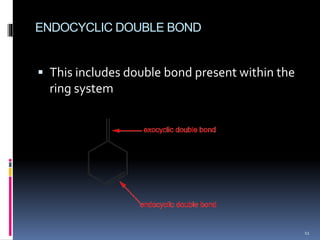
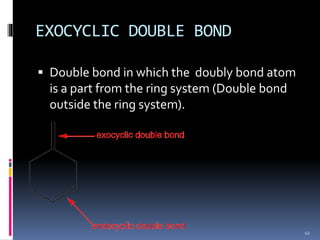
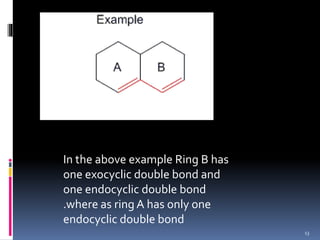
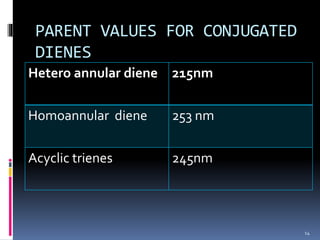
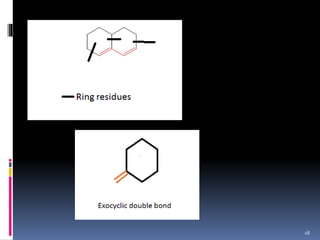
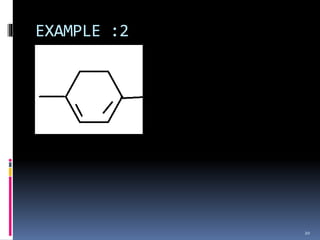
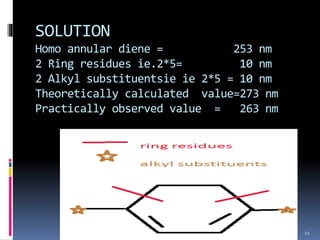
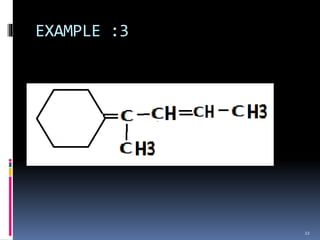
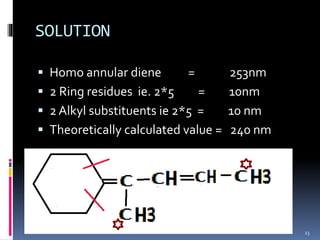
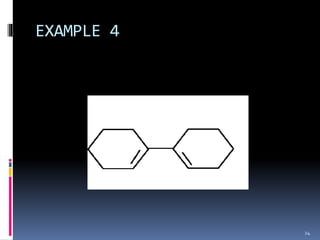
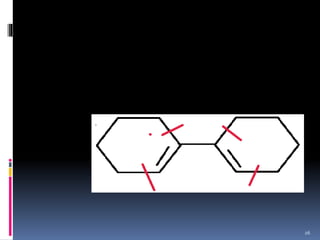
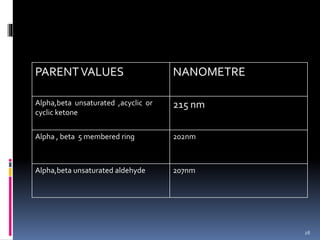
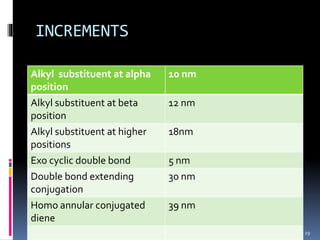
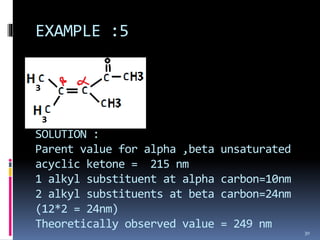
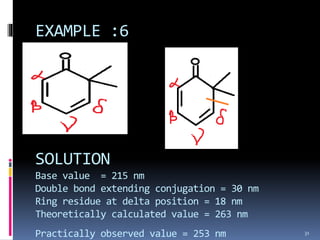
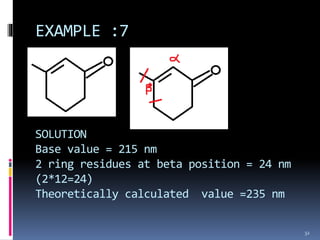
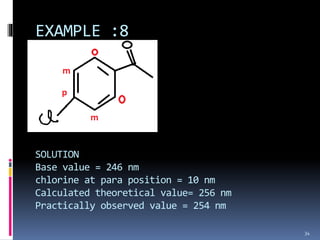
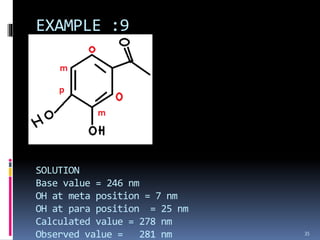
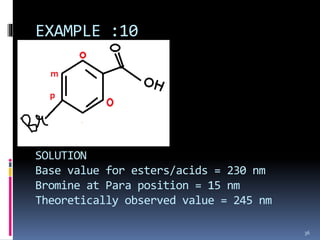
The document discusses the Woodward-Fieser rules, which can be used to theoretically calculate the lambda max (wavelength of maximum absorption) of conjugated systems and chromophores based on their structure. It provides examples of applying the rules to calculate lambda max for various compounds including conjugated dienes, alpha,beta-unsaturated carbonyls, and aromatic compounds. The rules take into account substituent effects and conjugation. The document notes that the theoretically calculated lambda max values usually match well with experimental observations, and that the rules are useful for structural elucidation of unknown compounds.