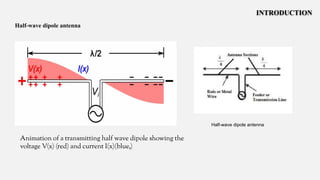
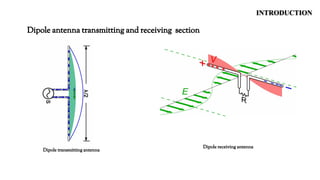
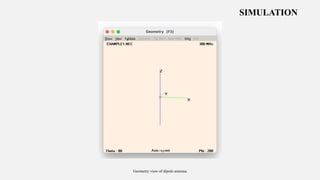
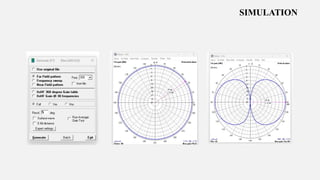
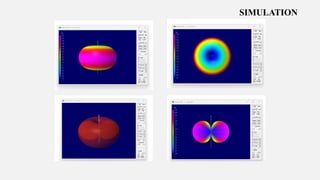
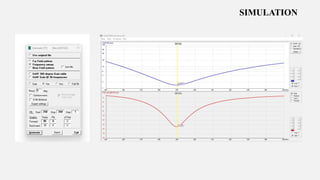
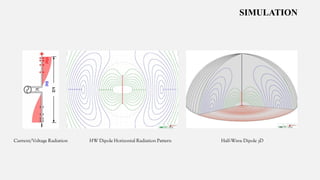
This document summarizes a student project to design and simulate a dipole antenna radiation pattern to improve cellular network coverage in Mirpur, Bangladesh. It outlines the objectives to simulate the radiation pattern, analyze coverage, optimize for enhancement, and validate recommendations. It describes the motivation being insufficient existing coverage causing poor call quality. It then details the methodology used, simulation of the half-wave dipole antenna at 300MHz showing characteristics like low near-field gain, good impedance matching, and received power attenuation over distance. It concludes the antenna performance is characterized by these factors and ways to potentially enhance received power such as using a directional antenna.