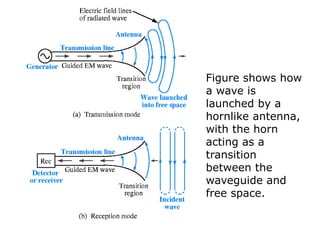
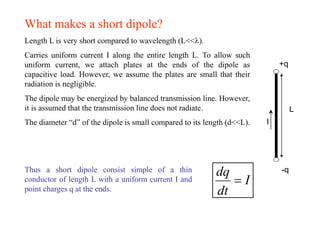
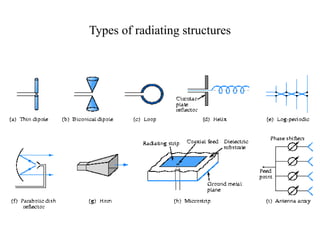
Introduction to Antennas:
Antennas are devices that convert electrical signals into electromagnetic waves and vice versa, enabling wireless communication. They operate in three distinct regions: the near field, where energy is reactive and non-radiative; the intermediate zone, showing a mix of both behaviors; and the far field, where radiated waves propagate freely. Examples of antenna performance include variations in gain, directivity, and radiation pattern, which determine how efficiently an antenna transmits or receives signals across different frequencies.